A financial data warehouse acts as a central repository that collects and stores information from various sources in finance. You use it to bring together data from independent systems, which allows you to access accurate financial information for analysis and reporting. Unlike traditional systems, a financial data warehouse gives you a single place for consistent, reliable data. Efficient integration and management help you make better decisions. If you want to build or manage a modern financial data warehouse, FineDataLink provides real-time synchronization and easy data integration across your organization.

A financial data warehouse serves as a specialized type of data warehouse designed for the finance sector. You use it to collect, organize, and store data from various financial systems. This central repository helps you analyze both current and historical data, making it easier to spot trends and make informed decisions. The financial data warehouse stands out because it focuses on financial domains, integrates information from multiple sources, and keeps a record of data over time.
You can better understand the fundamental characteristics of a financial data warehouse by considering these points:
You build a financial data warehouse by bringing together data from many sources. These sources often include operational systems like ERP, CRM, and SCM, as well as external feeds such as social media or weather data. Legacy systems also play a role, especially if your organization relies on older technology.
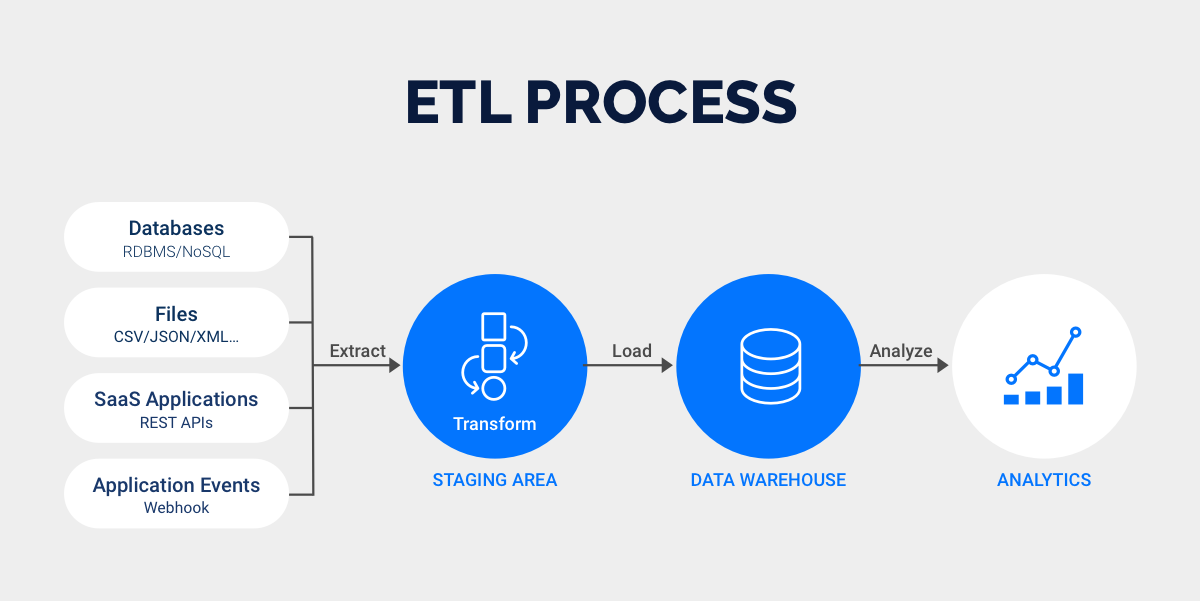
The process of loading and transforming data involves several key stages. The following table outlines the standard steps you follow:
| Process Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Extraction | You extract data from various sources, whether they are similar or different. |
| Data Transformation | You clean, aggregate, and convert data into formats ready for analysis. |
| Data Loading | You insert the processed data into the enterprise data warehouse. |
| Data Quality Management | You validate and monitor data to ensure high quality and document any issues. |
| Loading Methods | You use full loads for initial data and incremental loads for updates. |
You ensure the accuracy and timeliness of your data warehouse by focusing on several important metrics. These include data completeness, accuracy, consistency, timeliness, validity, and relevance. By reducing data redundancy and consolidating information from different sources, you maintain consistency and accuracy. Real-time insights become possible, allowing you to make quick decisions based on up-to-date information.
Cloud data warehouse solutions and cloud-based data warehouse platforms have made these processes even more efficient. You can now synchronize data in real time and scale your storage as your needs grow.
A financial data warehouse includes several essential components that help you manage and analyze your data effectively:
Metadata management and ETL tools play a crucial role in your financial data warehouse. Metadata defines and enforces data quality rules, tracks data ownership, and ensures compliance with access policies. It also guides ETL processes, helping you map data correctly and resolve quality issues.
When you use an enterprise data warehouse or a cloud-based data warehouse, you gain the flexibility to handle large volumes of data from many sources. These platforms support both current and historical data, giving you a complete view of your financial operations.
When you use a financial data warehouse, you improve the quality and consistency of your data. You bring together information from many sources, which helps you avoid errors caused by manual data consolidation. This single source of truth reduces inconsistencies and supports better business intelligence. You can trust your data for accurate financial reporting and data analysis. Automation of data processes ensures your information stays current and reliable.
A financial data warehouse gives you powerful tools for reporting and analytics. You can generate customizable reports that meet your specific needs. Finance teams use these reports to make informed decisions and respond quickly to business changes. The platform transforms complex financial data into actionable insights, helping you streamline processes and improve decision-making. You also gain real-time insights through web-based portals, which keep your organization up to date. The table below shows how data warehouse solutions support advanced reporting and analytics:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Integration of multiple sources | Provides a single source of truth, reducing errors from manual work. |
| Automation of data processes | Ensures data is accurate and current for timely reporting. |
| Customizable reports | Lets you tailor reports to your needs, improving decision-making. |
You need to protect sensitive financial information and follow strict regulations. A financial data warehouse helps you meet requirements like SOX and GDPR by ensuring data integrity, security, and auditability. You can organize data by sensitivity, assign user roles, and use encryption to keep information safe. Role-based access control and virtual private databases limit who can see certain data. These features help you avoid penalties and maintain strong compliance.
FineDataLink stands out among data warehouse solutions for finance. You get real-time integration, a low-code platform, and support for over 100 data sources. FineDataLink breaks down data silos by connecting different systems and automates ETL processes, which saves you time and reduces errors. You can scale your data warehouse as your business grows, and you do not need to write complex code. FineDataLink makes data analytics and business intelligence more accessible, helping you manage financial data efficiently and securely.
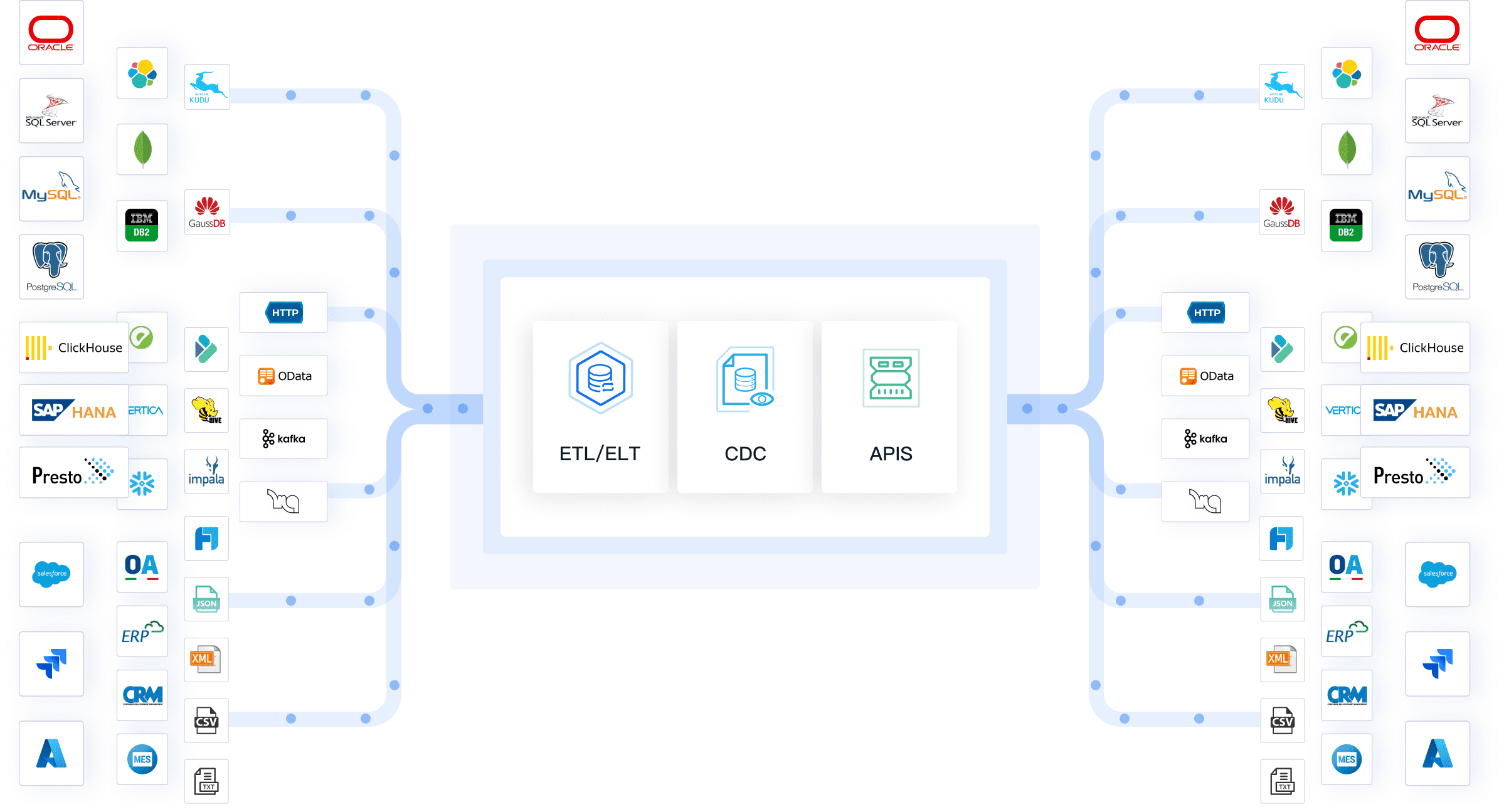
You can use a financial data warehouse to strengthen your risk and fraud detection strategies. By centralizing data from multiple sources, you gain a complete view of transactions and user activities. This approach helps you spot unusual patterns quickly. For example, you can monitor for unauthorized access, abnormal spending, or suspicious login attempts. The table below shows common use cases for risk and fraud detection in finance:
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Fraud Detection and Prevention | Detects anomalies in transaction data to prevent losses. |
| Credit Card Fraud Detection | Flags unusual activities in real time. |
| Account Takeover Prevention | Monitors login behaviors for unauthorized access. |
| Insider Fraud Monitoring | Analyzes internal transactions for suspicious activities. |
| Loan Fraud Detection | Scrutinizes loan applications for inconsistencies. |
| Cyber Fraud and Phishing Detection | Identifies phishing threats through content analysis. |
| AML Compliance | Detects money laundering activities through transaction analysis. |
| Transaction Fraud Detection | Analyzes digital transactions for anomalies. |
A cloud data warehouse makes it easier to process large volumes of data and run advanced analytics. You can respond to threats faster and reduce financial risks.
A financial data warehouse improves the accuracy and speed of your financial reporting. You can consolidate data from different departments and systems, which reduces errors and inconsistencies. This centralization supports real-time access to financial reports, so you can make decisions quickly. The following benefits highlight how a cloud data warehouse supports financial reporting:
For example, DAS Corporation used FineDataLink to automate data integration and reporting across its global branches. By building an enterprise data warehouse, DAS gained real-time access to financial data and improved decision-making. You can achieve similar results by adopting automated reporting tools.
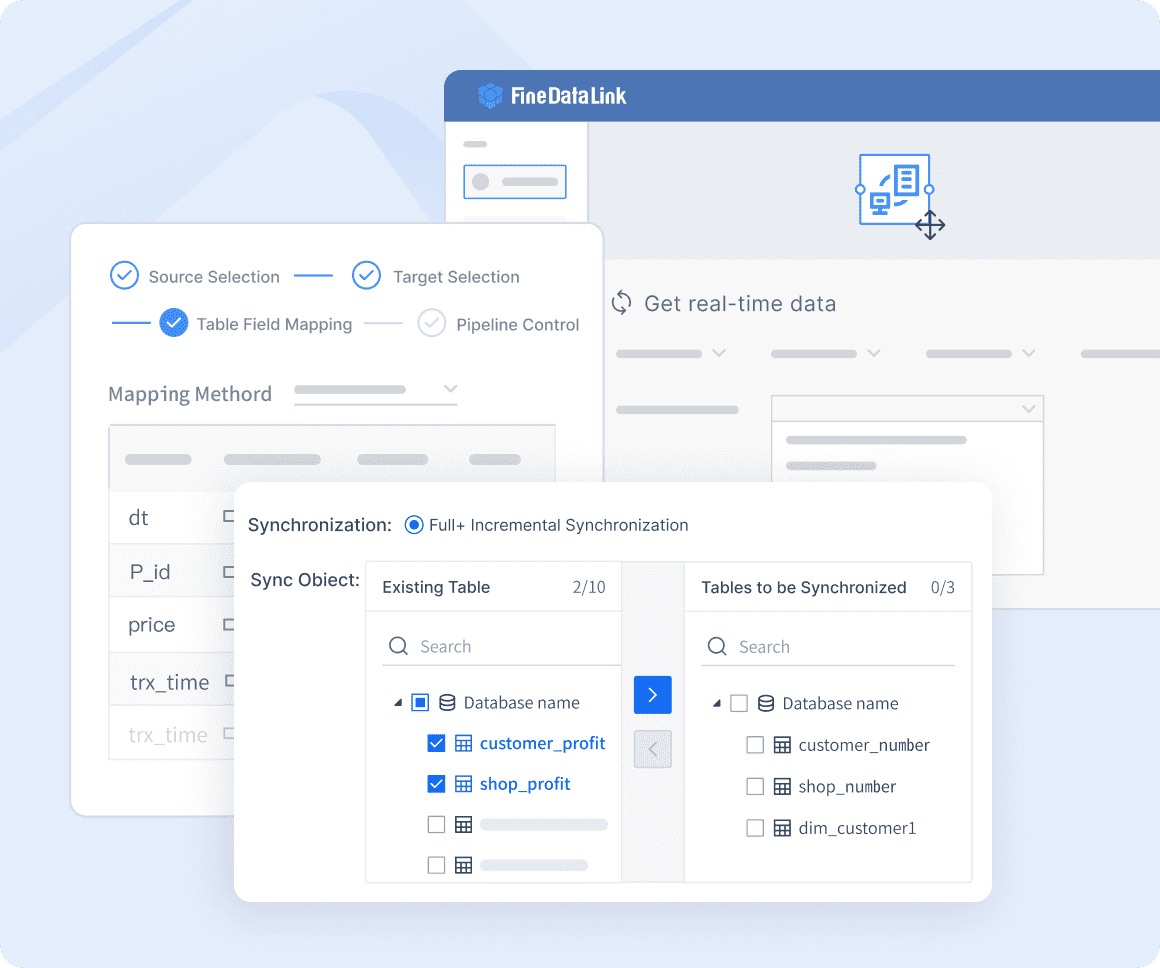
FineDataLink helps you unlock real-time insights by integrating data from over 100 sources. You can automate ETL processes and synchronize data across systems with minimal effort. The platform’s low-code interface lets you build and manage your financial data warehouse without complex coding. You can create APIs in minutes and share data between applications easily.
With FineDataLink, you gain:
You can use FineDataLink to support financial management, risk detection, and reporting. This approach ensures your organization stays agile and informed.
You may wonder how a data warehouse compares to a data lake, especially in financial management. Both solutions help you store and analyze information, but they serve different purposes. A data warehouse stores processed and structured information, making it ideal for financial reporting and forecasting. In contrast, a data lake holds raw, unprocessed information, which gives you flexibility for big data applications.
Here is a table to help you see the differences:
| Feature | Data Warehouse | Data Lake |
|---|---|---|
| Data Storage | Stores processed, structured data optimized for analysis | Stores raw, unprocessed data for various purposes |
| Data Structure | Uses schema-on-write approach for consistency | Uses schema-on-read approach for flexibility |
| Data Types | Primarily structured data (tables, rows, columns) | Supports structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data |
| Use Cases | Ideal for financial reporting, budgeting, and forecasting | Suitable for big data applications, including finance-related data analysis |
A data warehouse gives you consistency and reliability for financial analysis. A data lake offers flexibility when you need to work with many types of information.
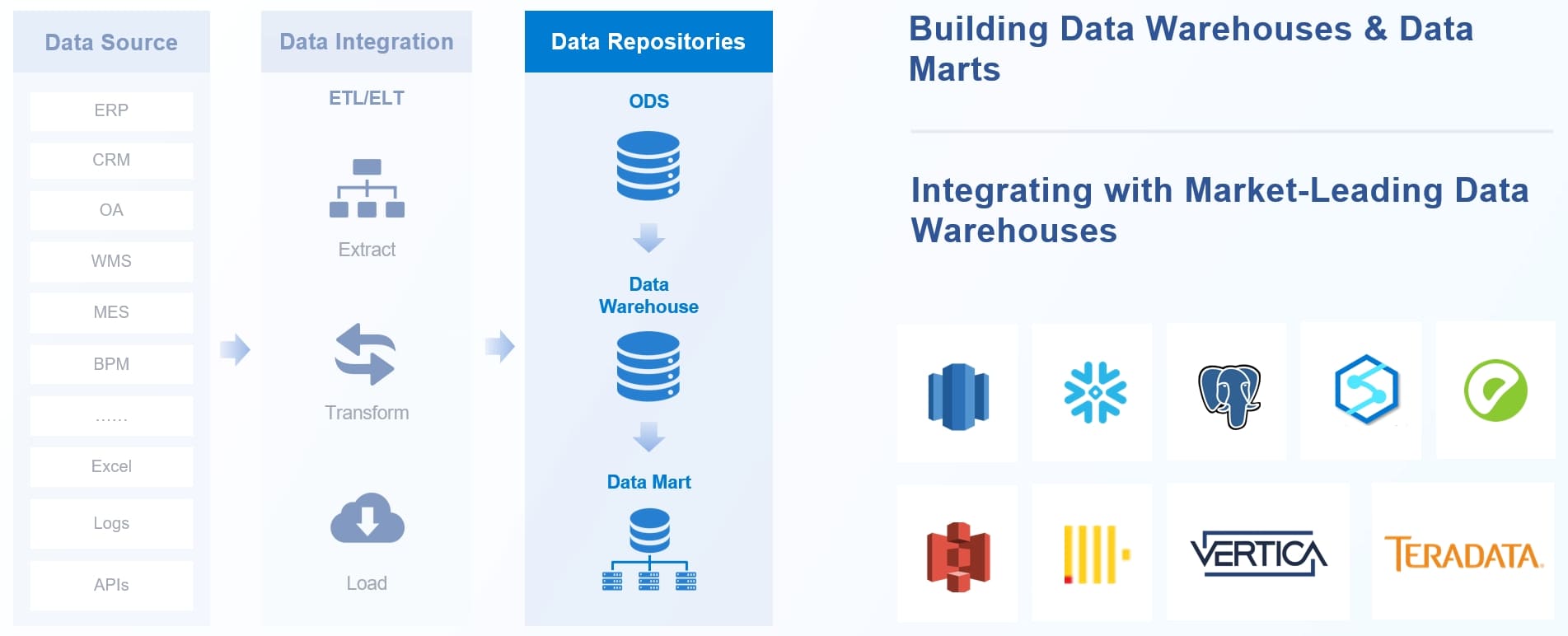
You might also compare a data warehouse to a traditional database. Each serves a unique role in financial data management. A data warehouse is designed for analytical workloads, such as complex queries and historical analysis. A traditional database focuses on daily transactions and operational tasks.
Consider these key differences:
| Aspect | Financial Data Warehouse | Traditional Database |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose and Workloads | Optimized for OLAP workloads, focusing on analytical queries | Designed for OLTP workloads, focusing on transactional processing |
| Data Storage and Organization | Uses denormalized schemas for optimized query performance | Uses normalized schemas to minimize redundancy |
| Performance and Scalability | High-throughput processing for large-scale queries | Low-latency responses for individual transactions |
| Data Integration and Transformation | Manages ETL processes for data from multiple sources | Handles real-time data ingestion with minimal transformation |
| Query Capabilities | Specializes in complex analytical queries | Excels at simple queries and transactional consistency |
Selecting the right solution depends on your needs. If you handle complex analytical workloads and need strong governance, a data warehouse fits best. If you want flexibility for diverse information types, a data lake may suit you. For daily operations and transactions, a traditional database works well.
Here is a table to guide your choice:
| Criteria | Data Warehouse | Data Lake | Database |
|---|---|---|---|
| Workload Types | Best for complex analytical workloads | Flexible for diverse data types | Suitable for operational transactions |
| Data Diversity | Structured data primarily | Supports structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data | Primarily structured data |
| Governance | Requires strong governance and data consistency | Risk of becoming a 'data swamp' without governance | Governance is essential for data integrity |
| Performance Optimization | Needs effective partitioning and indexing | Performance can vary based on organization | Performance tuning is crucial for efficiency |
| Cost Management | Can incur high costs with query-heavy workloads | Cost-effective for storage, but processing can be unpredictable | Generally predictable costs based on usage |
Tip: Review your business goals and data requirements before choosing a solution. The right tool helps you manage information efficiently and supports your financial strategy.
When you design a financial data warehouse, you choose from several common architectural models. The star schema organizes your data into fact tables and dimension tables, making queries fast and easy to understand. The snowflake schema adds more layers to dimension tables, which helps you manage complex relationships. You might also use a data vault model for flexibility and scalability. Many organizations now prefer a cloud data warehouse architecture because it offers cost efficiency and easy scaling. You can store large volumes of financial data and access insights quickly.
You face several challenges when you implement a financial data warehouse. Data gaps, unreliable sources, compliance risks, and productivity loss often slow progress. You overcome these issues by making organizational changes, training your team, and upgrading technology. You also adopt modern data warehousing practices. Managing costs is important, so you explore affordable cloud data warehouse solutions to balance performance and budget.
Here are best practices for successful implementation:
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Assess Data Maturity | Evaluate your current processes and infrastructure to find gaps and plan effectively. |
| Align Stakeholders | Involve business users early to match your project with business goals. |
| Design for Scalability | Build a flexible architecture that grows with your data needs. |
| Implement Robust Security | Use strong encryption and access controls to protect sensitive information. |
| Monitor Progress | Check performance regularly and optimize to maintain quality and effectiveness. |
You must comply with regulatory standards. Timely and accurate reporting is essential. A poorly tuned financial data warehouse can hinder compliance and lead to fines or legal issues.
You see several trends shaping the future of financial data warehouse technology. Cloud-native data warehouse solutions are becoming popular for scalability and cost savings. Automation streamlines complex tasks and improves data accuracy. The data lakehouse model combines the flexibility of data lakes with the reliability of warehouses, giving you better analytics. Data democratization and self-service analytics let non-technical users access insights easily. Edge computing analyzes data closer to its source, reducing costs and delays.
Artificial intelligence is transforming financial data warehouse solutions. You use AI for predictive analytics, forecasting trends from historical data. Machine learning automates governance tasks and improves data quality. AI simplifies data aggregation and supports compliance by tagging sensitive information. Financial institutions use AI to enhance fraud detection and risk management, leading to better insights and decision-making.
A financial data warehouse gives you a single, reliable place to manage and analyze your financial data. You gain enhanced reporting, better analytics, and improved productivity. FineDataLink supports you with real-time data synchronization and a user-friendly interface.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Real-time Data Synchronization | Keeps your information current and actionable. |
| Efficient Construction | Simplifies building and scaling your warehouse. |
To learn more, involve stakeholders early, define user roles, and explore best practices for implementation.
Enterprise Data Integration: A Comprehensive Guide
What is enterprise data and why does it matter for organizations
Understanding Enterprise Data Centers in 2025
Enterprise Data Analytics Explained for Modern Businesses

The Author
Howard
Engineer Data Management & Ahli Data Research Di FanRuan
Related Articles
What is a data management platform in 2025
A data management platform in 2025 centralizes, organizes, and activates business data, enabling smarter decisions and real-time insights across industries.
Howard
Dec 22, 2025

Top 10 Database Management Tools for 2025
See the top 10 database management tools for 2025, comparing features, security, and scalability to help you choose the right solution for your business.
Howard
Dec 17, 2025

Best Data Lake Vendors For Enterprise Needs
Compare top data lake vendors for enterprise needs. See which platforms offer the best scalability, integration, and security for your business.
Howard
Dec 07, 2025