You need to understand the difference between data governance and data compliance to manage your organization's data privacy and security. Data governance creates the foundation for reliable data, while compliance ensures you meet legal and regulatory standards. Companies that focus on both report higher operational efficiency and fewer risks from data breaches. Many organizations struggle with finding reliable analytics because they lack a strong governance framework. You can streamline your data governance and compliance efforts with modern solutions like FineDataLink, which helps you integrate and manage data from multiple sources.

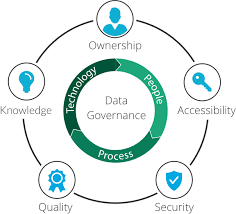
You need to understand data governance if you want to manage your organization's data effectively. Data governance gives you a framework for making decisions about data. It sets the rules, standards, and responsibilities for how you collect, store, use, and protect information. Leading authorities like DAMA International, the Data Governance Institute, and Gartner all agree that data governance is about exercising authority and control over your data assets. You can see how these organizations define it in the table below:
| Authority | Definition |
|---|---|
| DAMA International | Data Governance is “the exercise of authority and control (planning, monitoring, and enforcement) over the management of data assets.” |
| Data Governance Institute | “A system of decision rights and accountabilities for information-related processes, executed according to agreed-upon models which describe who can take what actions with what information, and when, under what circumstances, using what methods.” |
| Gartner | “The specification of decision rights and accountability framework to ensure the appropriate behavior in the valuation, creation, consumption, and control of data and analytics.” |
A strong data governance framework includes rules, standards, and procedures that help you keep your data accurate, reliable, secure, and accessible. You assign roles and responsibilities so everyone knows who manages which data. You also set up processes to make sure your data stays consistent and trustworthy across all your systems. When you follow best practices, you empower your team to use data confidently and make better decisions.
Some key components and objectives of data governance include:
| Core Components | Objectives |
|---|---|
| Data Policies | Define rules and guidelines for data usage and protection. |
| Data Standards | Establish how data should be structured, formatted, and stored. |
| Data Procedures | Outline processes for collecting, storing, and handling data. |
| Data Stewardship | Identify individuals responsible for managing data within the organization. |
| Data Quality | Ensure data is accurate, complete, and up to date. |
| Data Security | Protect data from unauthorized access and breaches. |
| Data Integrity | Maintain accuracy, consistency, and trustworthiness of data across systems. |
| Safeguarding Data and Privacy | Ensure sensitive information is handled according to policies and regulations. |
| Granting Business Value | Enable teams to find, understand, and use data effectively without compromising compliance. |
| Compliance with Regulatory Requirements | Document data collection, storage, protection, and access to navigate regulations. |
You will notice that data governance covers a wide range of activities. It helps you democratize data, standardize processes, and improve business performance. When you have strong data governance, you can break down silos and make sure everyone in your organization works with the same, reliable information.
Data compliance means you follow the laws and regulations that apply to your data. You need to protect personal and sensitive information according to rules set by governments and industry bodies. Regulations like GDPR and HIPAA require you to set up clear policies, procedures, and guidelines for handling data securely. You must also define roles and responsibilities for data processing to ensure accountability and transparency.
Some important points about data compliance include:
The table below shows some of the main drivers for data compliance in organizations:
| Category | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Regulatory environment | Stringency of regulations and evolving regulations impact compliance strategies. |
| Industry requirements | Sector-specific regulations and compliance audits ensure legal and ethical data handling. |
| Data sensitivity and types | Sensitivity of data and varied data types dictate the level of protection and compliance needed. |
| Global operations | Cross-border data transfers and harmonization efforts influence compliance on a global scale. |
| Data lifecycle management | Data collection practices and retention policies are crucial for compliance. |
| Technology infrastructure | Security measures and data handling systems must align with regulatory requirements. |
You need to remember that data compliance is not just about avoiding fines. It also builds trust with your customers and partners. When you show that you handle data responsibly, you strengthen your reputation and reduce the risk of legal problems.

When you compare data governance vs data compliance, you see that they serve different but related purposes. Data governance focuses on how you manage data inside your organization. Data compliance focuses on meeting external legal and regulatory requirements. The table below highlights the main differences:
| Aspect | Data Governance | Data Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Broader scope encompassing overall data management strategy | Focused on external legal and regulatory requirements |
| Objective | Ensure data is managed efficiently to support business goals | Protect organization from legal penalties and ensure compliance with laws |
| Activities | Establishing data management frameworks and policies | Ensuring adherence to specific laws and regulations |
You can also look at the difference in terms of internal vs external focus:
| Aspect | Internal Compliance (Data Governance) | External Compliance (Data Compliance) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Day-to-day operations, policies, and procedures. | Demonstrating adherence to standards through audits and certifications. |
| Responsibility | Managed by the organization’s internal teams. | Verified by external auditors or certification bodies. |
| Outcome | Improved internal processes and risk mitigation. | Assurance to stakeholders and regulatory authorities of compliance. |
You need both data governance and data compliance to succeed in today’s data-driven world. Data governance gives you the structure and control to manage your data well. Data compliance ensures you meet all legal and regulatory obligations. When you align your internal policies with external requirements, you reduce risks and improve efficiency. Many organizations face challenges in keeping these areas aligned, especially as regulations change and data environments become more complex. Training your staff and using modern tools can help you overcome these challenges.
Data governance vs data compliance is not just a theoretical debate. You see the impact in your daily operations, your ability to innovate, and your success in passing audits. By understanding the differences and connections between data governance and data compliance, you put your organization in a stronger position to manage risks and unlock the full value of your data.
You play a key role in making data governance and compliance work in your organization. Each team member has specific responsibilities that support the data governance framework and help meet regulatory requirements. The table below shows how different roles contribute:
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Chief Data Officer (CDO) | Develops and oversees the data strategy, ensuring alignment with business goals. |
| Data Governance Manager | Manages day-to-day operations of the data governance program, including policy enforcement. |
| Data Steward | Ensures data quality and integrity, managing data assets and resolving issues. |
| Audit and Compliance Manager | Ensures compliance with regulations, conducts audits, and implements compliance measures. |
| Compliance Officer | Monitors regulatory compliance and conducts audits to ensure adherence to policies. |
You see that data governance focuses on managing data quality, integrity, and access, while data compliance ensures you meet external regulatory requirements. Both areas require clear roles and shared accountability.
Data governance and compliance teams must collaborate to protect your organization’s data and reputation. You need to align your data governance framework with regulatory requirements to ensure success. Here is how organizations structure their teams for effective collaboration:
You can see that these roles work together to enforce data access, manage data relationships, and reduce compliance risks. For example, automated workflows help you enforce data policies, respond to data issues, and document metadata for compliance reporting. In industries like healthcare and insurance, strong data governance enables accurate analytics and supports compliance with strict regulations. When you update your data governance framework, you adapt to new regulatory requirements and keep your organization compliant.
You often face challenges with data silos and manual processes when trying to align data governance and compliance. FineDataLink helps you bridge these gaps by integrating data from multiple sources and automating workflows. With FineDataLink, you can synchronize data in real time, build a high-quality data layer, and ensure your data governance framework supports both business intelligence and regulatory requirements. The platform’s low-code interface and support for over 100 data sources make it easier for you to manage data governance and compliance together. You gain better data quality, improved efficiency, and stronger compliance—all in one solution.

When you implement strong data governance and data compliance, your organization gains measurable advantages. You improve data quality, reduce risks, and boost operational efficiency. You empower teams to make confident decisions with reliable data. The following table shows the main benefits organizations report:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Data Quality | You establish data ethics and meet regulations, which builds trust and strengthens risk management. |
| Data-Driven Decision-Making | You make decisions based on comprehensive insights, increasing accuracy and confidence. |
| Increased Operational Efficiency | You optimize data assets, respond faster to market changes, and collaborate more effectively. |
You see these benefits in real organizations. Delta Dental Michigan extended its governance structure to AI requests, preventing problematic use cases. USTRANSCOM advanced logistical decision-making by supporting a data strategy. Becks Hybrids educated staff about data governance, which led to quicker query turnaround times.
If you neglect data governance and data compliance, you expose your organization to serious risks. You may face decreased data quality, compliance failures, and security breaches. Operational inefficiencies and misuse of resources can also occur. Here are the most common risks:
Neglecting data governance can result in inconsistent and inaccurate data, which hampers decision-making. Compliance failures may lead to legal penalties and damage your reputation. Security breaches can cause financial losses and erode trust. Poor data management wastes resources and creates confusion. Without clear governance, you risk unnecessary costs and outdated processes. For example, a manufacturer suffered a data breach that exposed over 90,000 Social Security numbers due to weak data security. Organizations have reported a 40% increase in breach incidents when data management is fragmented.
SAMOA, a leading distributor for OPPO in Taiwan, faced major challenges with data governance and data compliance. Rapid expansion created data silos, inconsistent reporting, and manual processes. Departments struggled to align on governance responsibilities, and evolving regulations made compliance difficult. SAMOA lacked clarity in roles and had limited resources for building a robust framework. Data quality issues led to errors in reporting and decision-making.
SAMOA addressed these problems by implementing FanRuan’s business intelligence solutions. The company standardized sales recognition, unified report formats, and automated performance calculations. SAMOA integrated data sources and built visual dashboards for real-time insights. These changes improved data governance and data compliance, eliminated silos, and enhanced decision-making. SAMOA now enjoys transparent operations, reliable data, and scalable governance for future growth.
You need to remember the main differences between data governance and data compliance when building your data strategy. The table below highlights what sets them apart:
| Aspect | Data Governance | Data Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Strategy vs. Operations | Defines high-level policies and rules for data use | Executes the strategy through daily operations |
| Making the Rules vs. Following Them | Establishes official policies for data usage and compliance | Implements tools and workflows to adhere to policies |
| Ensuring Compliance vs. Managing Daily Tasks | Focuses on meeting regulations like GDPR and HIPAA | Handles technical tasks like data cleansing and backup |
You achieve better results when you integrate data governance and data compliance. This approach improves regulatory alignment, operational efficiency, and data quality. FineDataLink helps you automate workflows, standardize processes, and streamline data integration for both governance and compliance.
Enterprise Data Integration: A Comprehensive Guide
What is enterprise data and why does it matter for organizations
Understanding Enterprise Data Centers in 2025
Enterprise Data Analytics Explained for Modern Businesses

The Author
Howard
Engineer Data Management & Ahli Data Research Di FanRuan
Related Articles
What is a data management platform in 2025
A data management platform in 2025 centralizes, organizes, and activates business data, enabling smarter decisions and real-time insights across industries.
Howard
Dec 22, 2025

Top 10 Database Management Tools for 2025
See the top 10 database management tools for 2025, comparing features, security, and scalability to help you choose the right solution for your business.
Howard
Dec 17, 2025

Best Data Lake Vendors For Enterprise Needs
Compare top data lake vendors for enterprise needs. See which platforms offer the best scalability, integration, and security for your business.
Howard
Dec 07, 2025