Understanding what is accounting gives you the power to manage money wisely. Accounting tracks your business’s cash flow, keeps records accurate, and helps you avoid costly mistakes. Four in ten businesses lose money because of poor accounting. 82 percent of failures happen from negative cash flow management. The worst outcome is business failure. Accounting also helps you meet legal standards and build trust.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Legal Compliance | Companies must follow accounting rules to avoid penalties. |
| Building Stakeholder Confidence | Good accounting shows investors and customers you run a responsible business. |
| Benefits of Compliance | Accurate reports help you make smart choices and plan for growth. |

When you ask what is accounting, you explore a field that forms the backbone of every business. Accounting is the process of recording, categorizing, summarizing, analyzing, and reporting financial transactions. You use accounting to track every dollar that enters or leaves your business. This system helps you organize financial data so you can understand your company’s financial position at any moment.
Accounting covers several essential functions. You record transactions as they happen. You classify these transactions into categories such as assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses. You summarize the data to create financial statements. You analyze the information to spot trends and make sense of your business’s financial health. You report the results to stakeholders, including managers, investors, and regulators. Accounting also involves budgeting and forecasting, which help you plan for the future. You ensure compliance with laws and standards, protecting your business from penalties.
Accounting gives you a clear view of your business’s finances. You rely on it to make sense of complex data and to communicate results to others.
Here is a table that shows the primary functions of accounting and why each matters:
| Function | Purpose | Importance | Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recording Transactions | Systematically capturing all financial transactions in journals and ledgers. | Ensures accuracy and completeness of financial records. | Involves documenting every financial transaction as it occurs. |
| Classifying Transactions | Grouping transactions into appropriate categories. | Facilitates easy tracking and reporting of financial data. | Transactions are categorized into assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses. |
| Summarizing Data | Compiling detailed transaction data into summarized financial statements. | Provides an overview of the business's financial health. | Preparation of income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. |
| Analyzing Financial Information | Examining financial data to understand the business's financial condition. | Identifies trends and assesses financial health for strategic decisions. | Utilizes tools like ratio analysis and trend analysis. |
| Reporting Financial Information | Presenting financial information to stakeholders in a standardized format. | Ensures transparency and accountability for informed decision-making. | Financial statements are prepared according to accounting standards like GAAP or IFRS. |
| Budgeting and Forecasting | Planning future financial activities and predicting outcomes. | Helps allocate resources effectively and set financial goals. | Involves estimating revenues and expenses for future periods. |
| Ensuring Compliance | Adhering to financial reporting laws and regulations. | Avoids legal penalties and maintains the integrity of financial information. | Regular audits and reviews ensure compliance with applicable laws and standards. |
You use accounting to achieve many objectives in your business. When you understand what is accounting, you see how it supports every part of your operations. Accounting helps you keep systematic and accurate records. You plan your budget and allocate resources wisely. You make informed decisions based on reliable financial data. You evaluate your business’s performance using financial indicators. You manage cash flow to meet obligations and avoid shortages. You secure financing by providing clear financial information to lenders and investors. You implement internal controls to protect your resources. You promote accountability by evaluating performance. You address the information needs of stakeholders, including employees, managers, investors, and regulators.
Here are the main objectives of accounting in business operations:
Accounting supports decision-making for business owners and managers. Financial statements give you a current view of your company’s well-being. You use these statements to assess financial health and make smart choices. Well-formed financial statements enhance management efficiency. You streamline operations and improve strategic planning. Incremental decision-making relies on financial information from different perspectives. You evaluate options based on financial data, leading to better decisions. Financial information helps you understand costs and how they change over time. You use this knowledge for budgeting and forecasting. Historical pricing and customer trends guide your future decisions. You analyze past data to predict market behavior and set strategic goals.
| Evidence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Financial statements provide company management with a current view of the company’s well-being. | This allows managers to assess the financial health of the business, which is crucial for informed decision-making. |
| Well-formed financial statements enhance management efficiency. | They enable managers to streamline operations and make better strategic choices. |
| Incremental decision-making focuses on financial information from different perspectives. | This approach helps in evaluating various options based on financial data, leading to more informed decisions. |
| Financial information allows companies to understand costs incurred and how they change over time. | This understanding is vital for budgeting and forecasting future expenses. |
| Historical pricing and customer trends inform future decisions. | Analyzing past data helps in predicting future market behavior and making strategic plans accordingly. |
Accounting is not just about numbers. You use it to build trust, meet legal requirements, and drive your business forward. When you master what is accounting, you gain the tools to manage your company’s finances, make better decisions, and achieve long-term success.
Understanding key accounting concepts gives you the foundation to manage your business’s finances with confidence. These concepts help you interpret financial statements, assess your company’s health, and make informed decisions. Let’s break down the essentials: assets and liabilities, revenue and expenses, financial statements, and the accounting cycle.
You encounter assets and liabilities in every aspect of accounting. Assets represent resources your business owns that will bring future economic benefits. Liabilities are obligations you owe to others, such as loans or unpaid bills. Recognizing the difference between these two is crucial for understanding your company’s financial position.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Asset | A resource owned by a business expected to provide future economic benefits. Can be current or non-current. |
| Liability | An obligation owed to another party, such as bank loans or credit card debts. Can be current or long-term. |
Assets and liabilities play a central role in accounting because they reveal your business’s financial health and stability. You use them to measure liquidity, solvency, and profitability. The balance sheet equation—Assets = Liabilities + Equity—shows how your resources and obligations relate. This equation helps you track growth and performance over time.
When you understand these accounting concepts, you can better manage your resources and plan for the future.
Revenue and expenses form the core of your business’s financial activity. Revenue is the money you earn from selling goods or providing services. Expenses are the costs you incur to generate that revenue. This distinction matters because it shapes how you report your business’s financial performance.
In accounting, revenue refers to the income generated from providing goods or services, while expenses are the costs incurred to generate that revenue. This distinction is crucial for accurate financial reporting, as it helps in understanding the financial health of an organization.
Managing revenue and expenses directly affects your profitability. You need to set prices, control costs, and optimize your product mix to maximize profit. Remember, profit is what remains after you subtract all expenses from revenue. Covering fixed costs is necessary before any revenue contributes to profit.
For example, imagine a food truck that brings in $650 a day but spends $420 on supplies, wages, and rent. The profit is $230. This example shows that high revenue does not always mean high profit. Expenses can reduce what you actually earn.
“Without profit, high revenue is just a lot of work for nothing.” -Unknown
You need to monitor both revenue and expenses to keep your business healthy and sustainable.

Financial statements are the primary tools you use to communicate your business’s financial information. These documents summarize your accounting data and provide a clear picture of your company’s performance and position. You rely on four main types of financial statements:
These four financial statements are essential for small business owners, especially when seeking investors or applying for credit, as they provide crucial insights into the financial health of the business.
Each financial statement serves a unique purpose:
You use financial statements to analyze trends, compare results across periods, and make strategic decisions. Accurate financial statements help you build trust with investors, lenders, and other stakeholders.

The accounting cycle is the step-by-step process you follow to record, process, and report your business’s financial transactions. This cycle ensures your accounting records remain accurate and consistent.
Here are the key steps in the accounting cycle:
You repeat these steps each period to keep your accounting system up to date. The accounting cycle involves ongoing steps such as analyzing, journalizing, and posting transactions, which contribute to continuous monitoring of financial performance. End-of-cycle activities, like preparing and adjusting trial balances, provide crucial data for informed decision-making regarding future spending and financial strategies. The standardized process of the accounting cycle facilitates better financial analysis and enables meaningful comparisons of financial data across different periods.
Using the same accounting methods from one period to the next allows stakeholders to compare results accurately, making it easier to identify trends, measure progress, and pinpoint areas for improvement.
By mastering the accounting cycle, you ensure your financial statements are reliable and your business decisions are based on solid data.
Understanding the types of accounting helps you manage your business more effectively. Each type serves a unique purpose and addresses different needs. You will encounter financial accounting, managerial accounting, and tax accounting in most organizations.
Financial accounting focuses on tracking and reporting your business’s financial transactions. You use it to prepare statements that show your company’s financial health. These statements follow strict rules, such as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), to ensure accuracy and consistency. Financial accounting provides information to people outside your business, like investors, creditors, and regulators.
Here is a table that highlights the differences between financial accounting and managerial accounting:
| Aspect | Financial Accounting | Managerial Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | External reporting and compliance with GAAP | Internal decision-making |
| Standards | Follows GAAP | Does not adhere to strict standards |
| Audience | External parties | Internal management and decision-makers |
| Data Used | Financial data only | Financial and operational data |
| Objective | Disclose business performance and health | Aid in strategic planning and resource use |
You rely on financial accounting to communicate with external users. These include:
Financial accounting gives you a clear picture of your business’s position and helps you build trust with stakeholders.
Managerial accounting supports your internal decision-making. You use it to plan, control, and evaluate your business operations. Unlike financial accounting, managerial accounting does not follow strict rules. You can tailor reports to fit your needs.
Managerial accounting helps you with:
| Aspect | Contribution to Decision-Making |
|---|---|
| Budgeting | Create detailed budgets that match your goals. |
| Cost Analysis | Find inefficiencies and potential savings. |
| Performance Measurement | Track progress using key performance indicators and variance analysis. |
| Risk Management | Understand financial risks and plan how to handle them. |
| Cash Flow Management | Forecast cash needs to avoid running out of money. |
You also use several tools and techniques in managerial accounting:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Margin Analysis | Optimize production and calculate breakeven points. |
| Constraint Analysis | Identify bottlenecks that limit revenue. |
| Capital Budgeting | Analyze investments using methods like NPV and IRR. |
| Inventory Valuation | Assess product costs and allocate overhead. |
| Trend Analysis and Forecasting | Spot patterns and compare actual results to forecasts. |
Managerial accounting gives you the insights you need to make smart choices and improve your business.
Tax accounting deals with your business’s tax obligations. You use it to calculate, report, and comply with tax laws. Tax accountants examine and interpret records, prepare statements, and offer advice. They also audit statements and may help set up systems for tracking costs.
Key responsibilities of tax accounting include:
Tax accounting ensures you meet legal requirements and avoid penalties. It also helps you plan for taxes and manage cash flow. By working with management, tax accountants develop strategies that align with your business goals. They identify opportunities to save on taxes and improve your financial position. Integrating tax accounting into your planning helps you make informed decisions and maintain compliance.
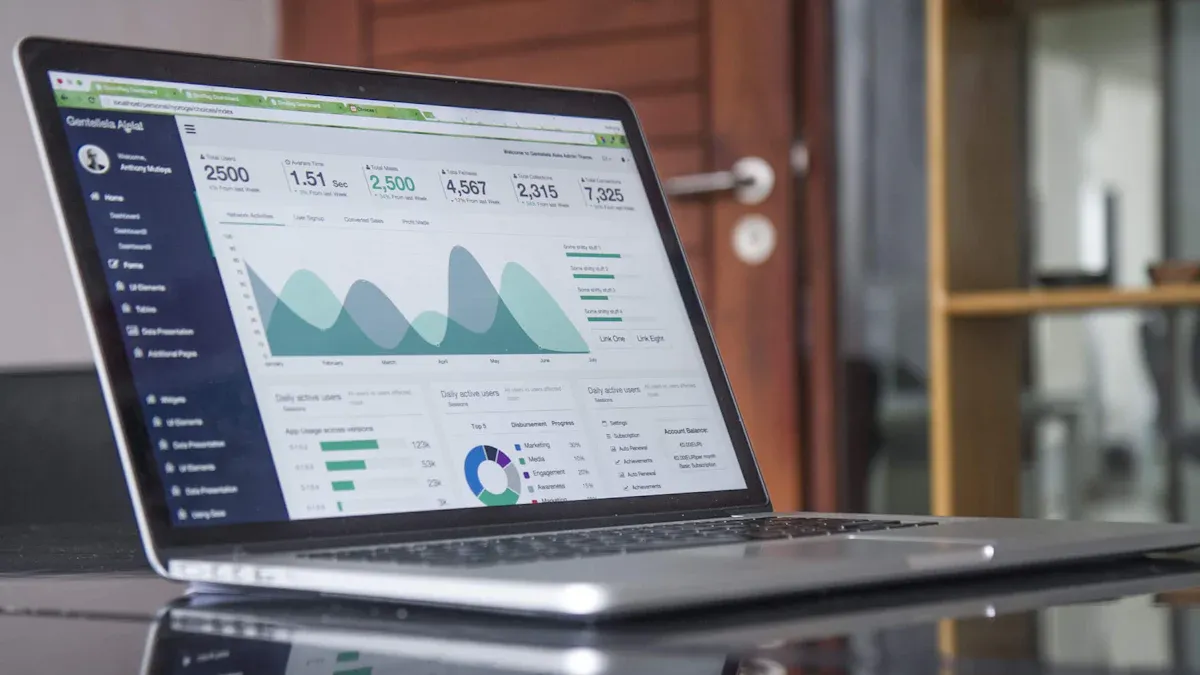
You need reliable tools to manage accounting and reporting tasks efficiently. Modern accounting solutions help you automate processes and improve accuracy. You can choose from several widely used reporting tools in the market:
Modern reporting tools transform accounting by automating data collection and reducing manual entry. You save time and avoid errors. These tools gather data from multiple sources, creating a unified repository for analysis. Automated processes scale with your business growth, handling larger datasets and complex reporting tasks. You focus more on strategic financial analysis and less on routine data entry. This shift boosts productivity and accuracy in financial reporting.
Modern accounting reporting tools allow you to concentrate on decision-making rather than manual tasks.
FineReport stands out as a modern solution for accounting and reporting. You use FineReport to automate report generation and streamline data entry. The software connects seamlessly to various databases and integrates with existing business systems. You benefit from single sign-on, which links user accounts and simplifies access after deploying a report project as a web application. FineReport supports real-time data entry, automatic data aggregation, and intuitive dashboards. You can access reports on PCs, tablets, and mobile devices, making accounting information available anywhere.
| Feature | Benefit for Accounting and Reporting |
|---|---|
| Automated Reporting | Saves time and reduces errors |
| Data Integration | Connects multiple sources for unified analysis |
| Dashboards | Visualizes key accounting metrics |
| Mobile Access | Enables reporting on the go |
You customize reports to fit your accounting needs. FineReport’s drag-and-drop interface makes reporting easy for users at any skill level. You can schedule automated reporting tasks and distribute financial reporting to stakeholders without manual intervention.
You gain several advantages when you use modern accounting reporting solutions like FineReport. Automated reporting improves efficiency and accuracy. Data integration provides a complete view of your accounting information. Dashboards help you monitor key financial reporting metrics in real time. Mobile access ensures you stay informed wherever you are.
FineReport addresses common accounting challenges by reducing manual data entry, minimizing errors, and supporting informed decision-making. You streamline financial reporting processes and enhance collaboration across departments. You make better decisions with timely and accurate accounting data. FineReport's integration capabilities allow you to connect with existing business systems, ensuring seamless workflow and secure data management.
You empower your business to grow and adapt by choosing the right accounting reporting tools.

You rely on accounting to make informed decisions that shape your business’s future. Accounting services give you critical insights through financial reporting and cost analysis. You use budgeting and forecasting to allocate resources efficiently and reach your goals. Cost accounting helps you find areas where you can reduce costs while keeping quality high. Financial statements let you assess profitability, liquidity, and overall financial health. You use this information to guide your strategic choices and evaluate potential investments. Accounting data helps you weigh the risks and rewards of capital investments, ensuring you make choices that support your business objectives.
FineReport’s finance solutions make these processes easier. You can automate report generation, visualize key metrics, and access real-time data. For example, companies like Founder Securities use FineReport to empower employees with self-service analytics, leading to faster and more accurate decisions.
Accounting helps you meet legal and regulatory requirements. You must follow rules for tax payments, financial reporting, and data protection. Accurate accounting ensures you avoid penalties and maintain your business’s reputation. The table below shows key compliance areas:
| Compliance Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Tax compliance | Paying the correct taxes on time, following tax laws. |
| Financial reporting compliance | Preparing statements according to standards like GAAP. |
| Internal Controls | Preventing fraud and ensuring accurate reporting. |
| Data Protection | Protecting electronic financial information. |
| Recordkeeping compliance | Keeping organized records for required periods. |
| Payroll compliance | Meeting labor laws for wages, taxes, and benefits. |
FineReport supports compliance by automating data collection and reporting. You can set up internal controls, schedule regular audits, and ensure your records meet all standards.
Effective accounting drives long-term business growth. You transform raw financial data into actionable insights. Accounting supports budgeting and forecasting, so you can align resources with your goals. Detailed cost analysis helps you spot inefficiencies and boost profitability. Accounting also plays a key role in risk management, helping you avoid costly mistakes. You use financial modeling to evaluate investments and make smart capital allocation decisions.
FineReport's finance solutions help you scale by integrating data from multiple sources and providing clear dashboards. Companies that use FineReport report improved efficiency, better collaboration, and stronger financial performance.
Understanding accounting gives you the foundation for business success. When you master accounting concepts and use modern tools like FineReport, you gain better control over your finances. You can automate accounting tasks, improve compliance, and make smarter decisions. Consider these recommended next steps:
| Recommended Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Leverage Technology | Automate compliance checks and use AI for data analysis. |
| Enhance Client Engagement | Use advanced platforms to keep clients informed and involved. |
| Offer Value-Added Services | Provide advisory services like predictive analytics and modeling. |
| Embrace Virtual Collaboration | Use secure portals and video conferencing for remote engagement. |
Apply accounting principles and tools to drive better outcomes for your business.
What Is a Quarterly Report and Why Investors Should Care
How to Use Inventory Report for Better Business Decisions
How to Build a Service Report Template for Your Business
What Is a Research Report and Why Does It Matter

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles

Top 10 Best Automation Reporting Tool Picks for Businesses
Compare the top 10 best automation reporting tool options to streamline business data, automate reports, and boost decision-making efficiency.
Lewis
Jan 03, 2026
Top 10 Reporting Systems and Tools for Businesses
See the top 10 reporting systems that help businesses automate data, build dashboards, and improve decision-making with real-time analytics.
Lewis
Jan 03, 2026
What is integrated reporting and why is it important
Integrated reporting combines financial and non-financial data, offering a full view of value creation, transparency, and stakeholder trust.
Lewis
Dec 12, 2025