A table in data management organizes information into rows and columns, making it easier for you to view and work with your data. When you understand the different types of tables, you can choose the right structure for your needs. For example, some tables handle static data, while others, like PivotTables, support advanced analysis and help you extract insights from large datasets. This knowledge lets you manage data more efficiently, adapt to changing requirements, and improve your workflow. Tools such as FineReport further enhance your ability to organize and analyze data across various scenarios.

When you work with tables in data management, you use a powerful tool for organizing information. In data management software, especially relational databases, a table is a structure that arranges data into rows and columns. Each row holds a record, such as a customer or product, while each column represents a field like an address or account number. This structure helps you store and retrieve data efficiently.
Here are the key components that define a table in database systems:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Columns | Fields or attributes that hold specific types of information in a vertical arrangement. |
| Rows | Also known as tuples or records, representing data for a specific entity in a horizontal format. |
| Column Names | Unique identifiers for each column, indicating the type of data stored. |
| Data Items | Specific values stored in the intersection of rows and columns. |
| Data Types | Defines the kind of data each column can store, ensuring data integrity. |
| Primary Key | A unique identifier for each row, ensuring no duplicates exist. |
| Foreign Key | A reference to a primary key in another table, establishing relationships between tables. |
You can see that the structure of tables in data management provides clarity and consistency. This makes it easier for you to manage large amounts of data and maintain accuracy.
Tables in data management serve several important functions. You use tables to store, organize, and analyze data. When you enter new information, the table structure ensures that each piece of data goes into the correct place. You can sort, filter, and search for specific records quickly.
Tables also help you link related data. For example, you might connect customer records to orders using keys. This relationship allows you to track business activities and generate reports. You can use tables to summarize data, calculate totals, and identify trends.
Tip: When you design tables in data management, focus on clear structure and logical organization. This approach helps you avoid errors and makes your data easier to use.
Tables in data management support many tasks, from simple record keeping to complex analysis. You rely on tables to keep your data organized and accessible, which is essential for making informed decisions.
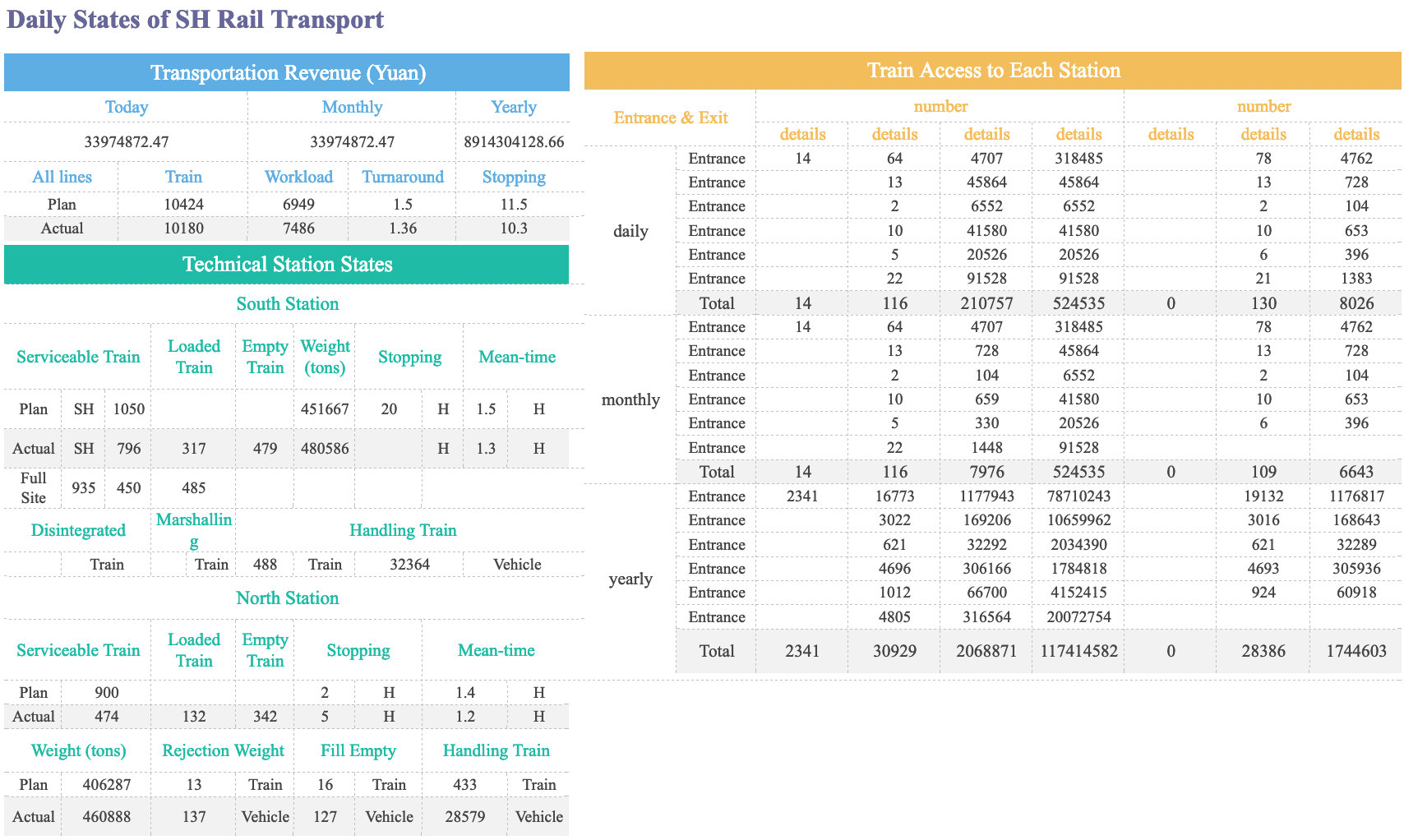

Understanding the types of tables in data management helps you organize, store, and analyze data more effectively. Each table type serves a unique purpose in databases and reporting systems. You will see how these tables work in real-world scenarios and how tools like FineReport support their creation and management.
Data tables form the foundation of most databases. You use a data table to store information in rows and columns. Each row represents a record, and each column holds a specific attribute. For example, a customer data table might include columns for customer ID, name, and email address. You can quickly add, update, or delete records in a data table.
| Type of Data Table | Description |
|---|---|
| Basic Data Table | A fundamental structure consisting of rows and columns, used to record information. |
| Cross-Tab Report | Groups and organizes data in a summarized way for better intelligibility in business intelligence. |
| E-commerce Sales Report | Displays product name, category, monthly sales figures, and revenue for performance tracking. |
| Customer Feedback Survey | Compiles survey results to analyze customer satisfaction and identify areas for improvement. |
You often use data tables to track sales, inventory, or employee records. In data management, these tables help you maintain accurate and accessible information. FineReport supports data tables by allowing you to connect to multiple databases, import Excel files, and design reports with multiple sheets. You can also use parameter queries to filter and analyze data efficiently.
Relational tables are a key part of relational databases. You organize data into tables that represent entities, such as customers or orders. Each table contains rows and columns, and you use primary and foreign keys to define relationships between tables. This structure supports normalization, which reduces data redundancy and improves integrity.
For example, an airline database might have a "travelers" table with traveler IDs and names, and a "passports" table with passport IDs and traveler IDs. You can join these tables to find which traveler holds a specific passport.
| Table Name | Attributes |
|---|---|
| travelers | traveler_id, name |
| passports | passport_id, traveler_id, ... |
Relational databases rely on relational tables to ensure data consistency. FineReport connects to various relational databases, including MySQL, Oracle, and SQL Server. You can design reports that pull data from multiple relational tables, visualize relationships between tables, and perform advanced SQL queries for data analysis.

Decision tables help you manage complex business rules in a clear and structured way. You use a decision table to list all possible conditions and actions, making it easier to evaluate scenarios and make consistent decisions. Each row represents a rule, while columns define conditions and outcomes.
| Feature/Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Structure | Decision tables simplify complex business logic into a digestible format. |
| Evaluation | They help evaluate and execute complex decisions consistently. |
| Clarity | Decision rules are defined precisely, allowing for efficient analysis of various scenarios. |
| Completeness | By listing all possible combinations of conditions, they ensure no scenarios are missed. |
| Flexibility | As business needs change, decision tables can be easily modified by adding rows or columns. |
| Communication | They provide a shared framework that reduces miscommunication between IT and business teams. |
| Efficiency | Decision tables break down complex decisions into smaller sub-decisions for structured decision-making. |
You might use a decision table to automate loan approvals or insurance claims. FineReport enhances decision tables by supporting interactive effects, parameter passing, and component linkage. You can click on data points to update related charts or tables, making your decision processes more dynamic and transparent.
HTML tables display tabular data on web pages. You use HTML tags to define the structure:
| Element | Purpose |
|---|---|
<table> | Starts the table |
<tr> | Defines a row |
<th> | Used for headers |
<td> | Used for data cells |
You often use HTML tables to present data in a browser, such as product lists or schedules. In data management, HTML tables help you share information online in a structured format. FineReport generates reports in HTML format, allowing you to embed tables in web applications or dashboards. You can customize the appearance and make your data accessible on any device.
Pivot tables give you a powerful way to analyze data. You can summarize large datasets, reorganize information, and spot trends or outliers. A pivot table lets you transform rows and columns to view your data from different perspectives. For example, you can create a sales report that shows totals by region and product.
Pivot tables are essential for data analysis in business intelligence. You use them to generate insightful reports and make informed decisions. FineReport supports pivot tables through cross-tab reports and dynamic templates. You can drag and drop fields, group data, and apply hierarchical formulas to analyze data quickly and accurately.
Note: Choosing the right types of tables in data management ensures you can store, organize, and analyze data efficiently. FineReport provides robust support for all these table types, helping you build flexible and insightful reports.
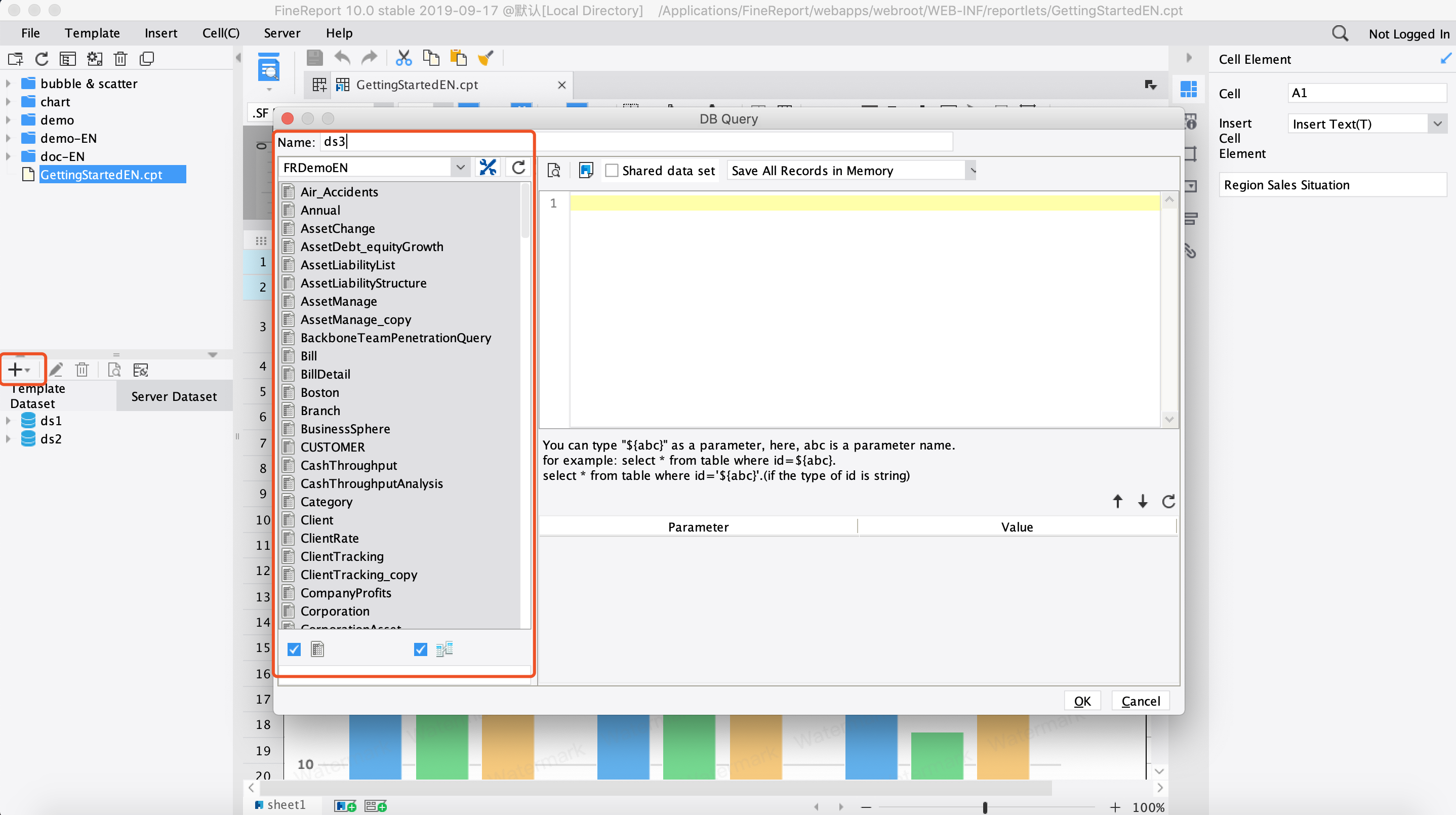
When you start creating and managing tables in data management, you lay the foundation for organized data storage and efficient data processing. In most database management systems, you follow a clear process to set up a new table. First, you create a new data table and give it a name that reflects its contents, such as "Customers" or "Orders." Next, you add fields to define the type of data each column will hold. You can also import tables from CSV files, which helps you move existing data into your database quickly.
Here is a typical process for creating a table in data management software:
You may face challenges during table creation, such as ensuring mobile users can view data without scrolling or managing tables without advanced technical skills. Fixed column sizes and accessibility can also affect how you display and use your data.
FineReport streamlines creating and managing tables in data management by offering user-friendly tools and intelligent features. You can use the Template Detection Assistant, which guides you through template creation and helps you avoid performance issues. FineReport also detects potential problems and suggests optimizations, making your experience smoother.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Template Detection Assistant | Guides you during template creation for better performance. |
| Performance Issue Detection | Identifies issues and helps you improve your templates. |
| Optimization Suggestions | Recommends ways to enhance your table creation process. |
For ongoing management, FineReport supports dynamic data tables. You can query tables in your dataset dynamically, filter data based on changing conditions, and define datasets with parameters for customized queries. This flexibility helps you adapt to evolving data analysis and reporting needs.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Dynamic Data Tables | Query tables dynamically for flexible data management. |
| Dynamic Conditions | Filter data using various conditions for adaptable queries. |
| Implementation Method | Define datasets with parameters for customized data processing. |
Efficient data entry and integration are essential for organized data storage and effective data processing. FineReport provides robust data entry forms that simplify collecting and updating information. You can design forms for tasks like employee onboarding or customer records, ensuring accurate and consistent data input.
FineReport excels in multi-source integration. You can connect to multiple databases and file types, making it easy to combine data from different sources. The platform offers visual SQL building, syntax prompts, and auto-completion for field names. You can also use FineReport formulas within SQL queries and generate parameter filtering statements visually. These features support seamless data integration and enhance your ability to manage complex data environments.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| SQL Simplification | Simplifies SQL entry and integrates queries with editing tools. |
| Visual SQL Building | Supports visual query creation and parameter filtering. |
| Syntax Prompt and Auto-completion | Enhances user experience with field name suggestions. |
| Support for FineReport Formulas | Allows formulas within SQL queries for advanced data analysis. |
| Parameter Filtering | Generates filtering statements visually for multi-source data integration. |
By mastering creating and managing tables in data management, you ensure your database remains organized and ready for advanced data analysis and reporting. FineReport empowers you to handle these tasks efficiently, supporting both traditional database management systems and modern dbms platforms.
You interact with tables in data management to drive business decisions and improve operational efficiency. Business users rely on tables to track sales, monitor inventory, and manage customer records. Decision tables present rules in an intuitive format, making it easy for you to review and update business logic without programming skills. This approach enhances collaboration between departments and reduces misunderstandings. You benefit from comprehensive documentation and simplified updates, which help you adapt quickly to changing business needs.
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Accessible to nontechnical stakeholders | Decision tables present rules in an intuitive format, enabling business users to review and modify rules without programming skills. |
| Enhanced collaboration | They foster better communication between technical teams and business stakeholders by providing a shared understanding of logic. |
| Reduced cognitive load | The layout simplifies complex rules into manageable components, aiding in error identification. |
| Comprehensive documentation | Decision tables serve as self-documenting tools, laying out conditions, rules, and outcomes clearly. |
| Easy updates | They allow for straightforward adjustments to logic as business needs change, without extensive redevelopment. |
| Avoiding misunderstandings | The tabular format minimizes misinterpretation, making decision processes transparent for all stakeholders. |
You use tables in data management to ensure that your data remains organized and accessible for reporting and analysis.
IT professionals and data analysts play a crucial role in managing tables in data management. You plan, maintain, and optimize database systems to support business operations. Your tasks include database administration, data warehousing, and analytics functions. You store business logic and prepare data for consumption in centralized locations. You create interactive dashboards and charts to visualize data and support decision-making.
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
| Database Administration | Involves planning, maintaining, and managing databases, often under traditional IT roles. |
| Data Warehousing | Focuses on storing business logic and preparing data for consumption in a centralized location. |
| Analytics Functions | Utilizes data from warehouses to create interactive charts and dashboards for reporting. |
You ensure that tables in data management remain secure, scalable, and efficient for all users.
You use tables in data management for daily tasks such as organizing schedules, tracking expenses, or comparing information. Everyday users benefit from static data tables for viewing information and interactive tables for sorting and filtering. Flat data tables help you make quick comparisons, while hierarchical tables allow you to explore parent-child relationships in your data.
You rely on tables in data management to keep your information clear and accessible, whether you work in a business environment or manage personal data.
FineReport supports all types of users with flexible reporting and dashboard tools. You can create custom reports, visualize data from multiple sources, and access dashboards on any device. FineReport’s intuitive design helps you manage tables in data management efficiently, whether you are a business user, IT professional, or everyday user.
Understanding different table types and mastering table management empowers you to make smarter, data-driven decisions. When you choose the right tools, you unlock new ways to organize, analyze, and present information. FineReport helps you achieve measurable benefits:
Explore FineReport to create, manage, and visualize tables that fit your business needs.
Bar Chart Race: A Complete Guide
16 Types of Chart for Effective Data Visualization
22 Different Types of Graphs in Data Visualization: A Practical Guide

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles

Top 10 Best Automation Reporting Tool Picks for Businesses
Compare the top 10 best automation reporting tool options to streamline business data, automate reports, and boost decision-making efficiency.
Lewis
Jan 03, 2026
Top 10 Reporting Systems and Tools for Businesses
See the top 10 reporting systems that help businesses automate data, build dashboards, and improve decision-making with real-time analytics.
Lewis
Jan 03, 2026
What is integrated reporting and why is it important
Integrated reporting combines financial and non-financial data, offering a full view of value creation, transparency, and stakeholder trust.
Lewis
Dec 12, 2025