

Sean, Industry Editor
Mar 14, 2025
Server management refers to the processes and tools you use to keep your server systems running smoothly and securely. Effective server management ensures IT reliability by reducing downtime and maintaining stable operations. Poor server management can lead to costly server outages, expose you to security threats, and result in data loss. You face real risks when servers remain unpatched or unmanaged, as shown below:
| Impact of Server Management on Business Continuity | Description |
|---|---|
| Connected endpoints | Unpatched servers expose all connected devices to vulnerabilities. |
| Server downtime | Brief outages can cost organizations thousands or millions of dollars. |
| Ongoing vulnerabilities | 34% of data breaches are due to exploitation of vulnerabilities. |
| Stability issues | Lack of updates can lead to crashes and compatibility problems. |
| Compliance implications | Delayed patching can result in fines and loss of certifications. |
Modern organizations must prioritize server management to protect business operations and meet compliance standards. You need to address hardware, security, and power backup trends to keep your server environment reliable

Server management is the process you use to monitor and maintain your servers so they operate efficiently and securely. You need server management to keep both hardware and software running smoothly. This process protects your organization from downtime and data loss. Server management covers everything from checking server health to applying updates and managing backups. You must focus on minimizing slowdowns, preventing outages, and creating a secure environment for your data and applications.
When you practice effective server management, you supervise and maintain your servers to ensure optimal performance. You handle hardware, software, security, and backup tasks. Your goal is to keep your servers reliable and ready to meet your organization’s changing needs. Server management also helps you adapt to new technologies and business requirements. You can avoid costly disruptions by following best practices and using the right tools.
You need to understand the core components of server management to build a reliable IT environment. Each component plays a key role in keeping your servers healthy and your business running.
Note: Server management also involves planning for storage, integrating with cloud services, and standardizing management across different environments.
The essential functions of server management include monitoring, security, backup, storage planning, and integration with cloud platforms. You need to monitor server resources and performance to catch issues early. Security measures like access control and patch management protect your servers from threats. Backups and disaster recovery plans help you recover from data loss. Storage planning ensures your applications remain responsive. Integration with cloud services allows you to manage both physical and virtual servers efficiently.
| Essential Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Monitoring | Continuous monitoring of server resources, health, and performance to catch issues early. |
| Security | Implementing security measures such as hardening OS, access control, and regular patch management. |
| Backup | Combining on-prem data backups with cloud replication and defining disaster recovery plans. |
| Storage Planning | Right-sizing storage and memory to ensure application responsiveness and prevent contention. |
| Integration with Cloud | Standardizing management strategies across physical, virtual, and cloud environments. |
You will find differences in server management between cloud-based and on-premises environments. Cloud solutions offer built-in disaster recovery and easy scalability. Cloud providers handle most maintenance tasks, which reduces your workload. On-premises servers require you to manage hardware, maintenance, and upgrades directly. You must plan for higher upfront investments and more hands-on management.
| Key Factors | Cloud | On-Premise |
|---|---|---|
| Server Location | Third-party Cloud | Physical, On-premises |
| Maintenance | Off-site | On-site |
| Server Blackouts | Possible but Scalable | Possible |
| On-Demand | Easily Scalable | Consumes Time and Effort |
| Installation | Easy and fast | Time-consuming |
| Availability | On-demand | When bought and deployed |
| Investment | Less | High |
| Business Risks | Low | High |
You should avoid common mistakes in server management. Weak security practices can expose your data to breaches. Failing to automate configuration and scaling can lead to errors and inefficiencies. Inadequate planning during server moves may cause budget overruns and disruptions. Overlooking application dependencies can make essential applications fail. Underestimating downtime can result in unexpected costs.
Server management forms the backbone of your IT operations. By understanding and applying these basics, you can keep your servers reliable, secure, and ready to support your business goals.
Server management involves a series of essential tasks that keep your server infrastructure reliable and efficient. You must focus on both hardware and software to achieve effective server management. Hardware tasks include monitoring server health, performing preventive maintenance, and managing resources like CPU, memory, and storage. Software tasks require you to update operating systems, install patches, and troubleshoot application issues. The choices you make for hardware and software can affect the complexity of server management. Virtualization software, for example, allows you to run multiple virtual machines on a single server, which improves resource use but also requires careful management and troubleshooting.
Security is a core part of server management. You need to secure server access to prevent unauthorized entry and protect sensitive data. Strong password policies and multi-factor authentication help you control access. You should also use real-time monitoring and alerts to detect suspicious activity. Role-based restrictions limit access to only those who need it. Modern advancements like biometric authentication and AI-powered access control further strengthen your security. You must regularly update systems and use encryption to keep your server environment safe.
Tip: Employee security training reduces risks from social engineering and helps maintain effective server management.
Monitoring is vital for effective server management. You must track server performance in real time to identify issues before they impact operations. Tools like Nagios, Monitis, Pandora FMS, and Netdata provide insights into CPU, memory, and disk usage. These tools help you detect bottlenecks, troubleshoot problems, and maintain high performance. Regular monitoring ensures your server infrastructure remains stable and responsive.
Backup and recovery are critical components of server management. You should follow the 3-2-1 rule for data backup and recovery: keep three copies of your data, store them on two different media, and keep one copy off-site. Increase backup frequency to minimize data loss and automate recovery processes to reduce errors. Use a mix of full, incremental, and differential backups for comprehensive protection. You must measure the effectiveness of your backup and recovery plans by tracking metrics like recovery time objective (RTO), recovery point objective (RPO), and backup success rate. Regular testing and monitoring of your backup and recovery strategies ensure you can restore data quickly and maintain business continuity.
Server management gives you the tools and processes to keep your server environment reliable and efficient. When you use server management, you create a foundation for stable operations and protect your business from unexpected disruptions. You can see the benefits in reliability, security, compliance, performance, and scalability. By following best practices, you ensure your server systems support your business goals and adapt to changing needs.
Server management directly improves reliability and uptime. You monitor your server hardware and software, apply updates, and use best practices to prevent failures. Reliable server management reduces the risk of outages and keeps your business running smoothly. Consider these industry findings:
You can achieve high uptime by using best practices such as proactive monitoring, regular maintenance, and timely updates.
Server management helps you meet security and compliance standards. You protect sensitive data and follow legal requirements by using best practices for access control, patching, and monitoring. Effective server management supports:
You build trust with customers and partners when you show strong security and compliance.
Server management lets you optimize performance and scale your systems as your business grows. You track key metrics to measure improvements, including:
You use these metrics to identify bottlenecks and apply best practices for tuning your server environment. When you manage your server resources well, you support higher workloads and deliver fast, reliable service. Best practices in server management help you plan for growth and ensure your systems remain responsive under pressure.
Server management presents several obstacles that you must address to maintain reliable IT operations. You need to understand these challenges to build a strong foundation for your server environment. Server management involves more than just routine maintenance. It requires you to overcome resource limits, defend against security threats, and manage integration complexity.
You often face resource limits when handling server management. Many IT teams struggle with overly complex processes that make it hard to manage servers efficiently. You may find it difficult to maintain visibility and control across different environments. The shift to cloud infrastructure adds new layers of complexity that traditional server management tools cannot always handle.
Security threats remain a constant concern in server management. You must protect your server infrastructure from a range of attacks.
You need to stay alert and update your security measures regularly to defend your servers from these evolving threats.
Integration complexity can create major challenges in server management, especially if you work with legacy systems. Modern workloads, such as AI, require more power and advanced cooling systems. Legacy data centers were not designed for these demands, so you may need to upgrade your infrastructure.
Many organizations, like NTT DATA Taiwan, have faced these challenges. They needed to break down data silos and automate manual processes to create a unified data platform. Without integration, you risk operational inefficiencies and incomplete business insights.
Server management requires you to address these challenges head-on. By understanding resource limits, security threats, and integration complexity, you can build a more resilient and efficient server environment.


Server management forms the backbone of reliable IT operations. You need a strong server management plan to maintain optimal performance, ensure data protection, and support business growth. Effective server management strategies help you address challenges such as security protocols, configuration, and troubleshooting.
You can improve server management by setting up proactive monitoring. Regular system health checks let you identify issues early. Continuous performance monitoring helps you spot bottlenecks and maintain optimal performance. Analyzing historical trends supports capacity planning and prevents resource shortages. You should consistently check hardware performance, such as CPU temperature and RAM usage, to avoid failures. Managing alerts effectively ensures your team responds quickly to problems. Remote monitoring and management tools enhance asset tracking and help you detect missing or aging hardware. A well-designed monitoring setup is essential for server performance monitoring and improved performance.
Automation is a key part of any server management plan. Automated systems handle repetitive tasks, freeing your IT staff to focus on complex troubleshooting. Scheduling regular maintenance and updates reduces manual errors and ensures timely patching. Automation simplifies configuration management and helps you monitor server performance and resource usage. Automated monitoring tools can detect issues quickly, allowing for early intervention. Automated failover and self-healing features increase resilience and minimize downtime. These server management tips help you maintain security protocols and keep your servers running smoothly.
Clear documentation supports every server management strategy. You should maintain infrastructure documentation to provide a complete view of your IT environment. Operational workflows documentation ensures consistency and helps new employees learn procedures. Standard operating procedures (SOPs) reduce errors and improve efficiency. Good documentation speeds up troubleshooting, supports regulatory compliance, and improves collaboration.
| Type of Documentation | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Infrastructure Documentation | Aids troubleshooting and planning upgrades |
| Operational Workflows Documentation | Ensures consistency and helps train new employees |
| Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) | Reduces errors and improves efficiency |
Integration platforms play a vital role in modern server management. FineDataLink helps you streamline data flows, achieve real-time synchronization, and manage ETL/ELT processes across multiple systems. You can connect over 100 data sources and automate data integration, reducing manual work and minimizing errors.
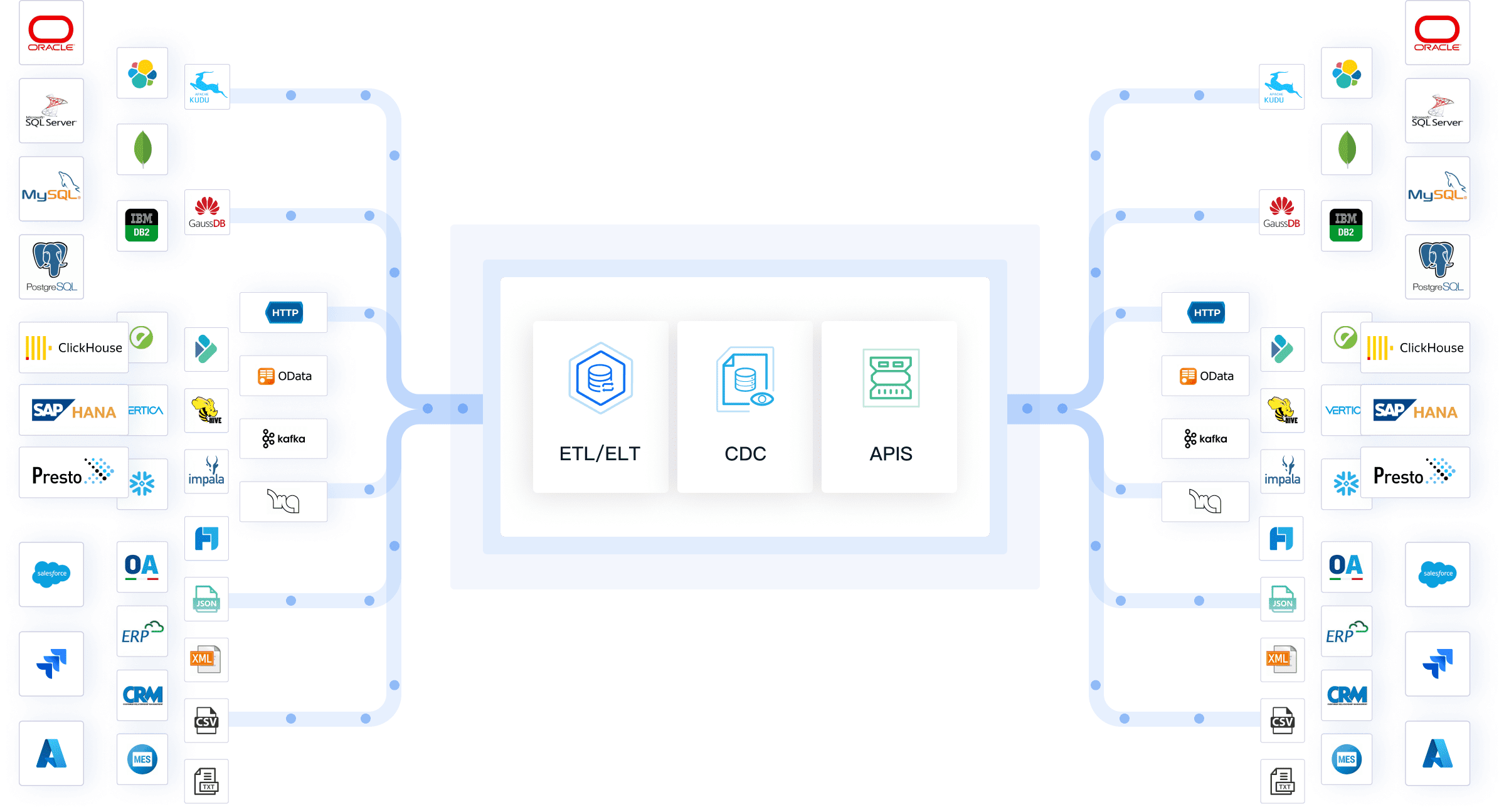
FineDataLink supports remote monitoring and management, making it easier to maintain a unified data platform. The NTT DATA Taiwan customer story shows how integrating backend systems with FineDataLink led to cost reduction, improved workspace utilization, and high employee satisfaction. By adopting integration platforms, you strengthen your server management strategy and support business intelligence and data-driven decision-making.

Server management plays a critical role in reliable IT operations. You depend on it for stability, security, and growth. When you use it, you improve agility and innovation. It enhances scalability and adapts to business needs. It gives you dashboards for key metrics. It lowers operational costs. It increases speed, quality, and agility. It automates business processes. You evaluate it by regular monitoring and performance tracking. You automate tasks for efficiency. You implement robust security measures. You establish a reliable backup strategy. You plan for scalability and growth. You optimize server performance through regular maintenance. You document and standardize processes. You focus on incident response and disaster recovery. It supports your business outcomes. It helps you achieve operational excellence. It ensures your IT environment stays resilient. It empowers you to make informed decisions. It keeps your data safe. It reduces downtime. It streamlines workflows. It supports compliance. It adapts to change. It enables real-time insights. It drives digital transformation. It supports your team. It prepares you for the future. It gives you a competitive edge. It makes IT management easier. It is essential for every organization.
FanRuan
https://www.fanruan.com/en/blogFanRuan provides powerful BI solutions across industries with FineReport for flexible reporting, FineBI for self-service analysis, and FineDataLink for data integration. Our all-in-one platform empowers organizations to transform raw data into actionable insights that drive business growth.
Server management means monitoring, maintaining, and securing your servers. You need server management to keep your systems reliable, prevent downtime, and protect your data from threats. Good server management supports your business operations and helps you meet compliance requirements.
Server management improves security by enforcing updates, monitoring for threats, and controlling access. You can use strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and regular patching. These steps help you reduce risks and keep your data safe from cyberattacks.
You handle hardware monitoring, software updates, security checks, performance tracking, and backups. Server management also includes planning for storage and integrating with cloud services. These tasks help you maintain a stable and efficient IT environment.
Automation lets you schedule updates, monitor performance, and manage backups without manual effort. You save time and reduce errors. Automated server management tools help you respond quickly to issues and keep your systems running smoothly.
Integration platforms like FineDataLink help you connect different data sources, automate ETL processes, and enable real-time data synchronization. You can break down data silos and improve decision-making. FineDataLink makes server management more efficient and supports business intelligence.

