Cross Price Elasticity
Sean, Industry Editor
Oct 15, 2025
Cross price elasticity shows how demand for one product changes when another product’s price goes up or down. You use this idea to see how products are connected and to make smarter choices.
-
It helps you find out which products are substitutes or complements in your market.
-
You get helpful ideas for setting prices, planning ads, and making product bundles.
Cross price elasticity is important for finding products that change demand when their prices change.
For example, if a premium item costs more, people may pick a cheaper option instead.
Cross Price Elasticity Explained

Definition of Cross Price Elasticity
Cross price elasticity shows how demand for one product changes when another product’s price changes. This idea helps you see how different goods are linked in the market. When you measure cross price elasticity, you check how much the amount people want of one product changes if another product’s price goes up or down.
- Cross-price elasticity of demand can be negative, positive, or zero.
- Cross-price elasticity tells you how much people buy of one product when another product’s price changes.
- This idea helps you see if products are substitutes or complements.
- Cross price elasticity of demand shows how much people change what they buy when another product’s price changes.
To find cross price elasticity, you look at the percent change in how much people buy of one product when another product’s price changes by one percent. This is important because it shows if products are linked as substitutes or complements. Companies use cross price elasticity to help set prices and plan how to sell their products.
New studies in economics use cross price elasticity to see how people switch between things like tobacco and electronic cigarettes. Behavioral economics also uses this idea to see how people change what they buy when prices change. Cross price elasticity is not just an idea in books. It is a real tool that helps us understand how markets work.
Substitutes vs. Complements
When you learn about cross price elasticity, you will hear about substitutes and complements. These two types of products help you see how price changes affect what people buy.
| Type | Cross-Price Elasticity Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Substitutes | Positive | If one product’s price goes up, people buy more of the other. |
| Complements | Negative | If one product’s price goes up, people buy less of the other. |
Substitute products have a positive cross price elasticity. If one product’s price goes up, people may buy more of the other product. For example, if beef costs more, people might buy more chicken. This means beef and chicken are substitutes.
Complements have a negative cross price elasticity. If one product’s price goes up, people usually buy less of the other product. Printers and ink cartridges are an example. If printers cost more, people may buy fewer ink cartridges because they buy fewer printers.
Studies show that prices in one group can change how much people buy in another group. For example, if beer costs more, people may buy less red wine if they see them as substitutes. Cake mix and frosting are complements. If cake mix costs more, people may also buy less frosting.
You can use cross price elasticity to find out who your competitors are. This helps you know which products fight for the same buyers and which products go together. Knowing these links helps you set better prices and make good marketing plans.
Tip: If you understand cross price elasticity, you can spot trends, plan sales, and react fast to changes in the market.
Calculating Cross Price Elasticity

Formula
You can use a formula to see how demand changes. It shows what happens to one product when another product’s price changes. This helps you find out if two products are substitutes or complements. Here are the main parts of the cross price elasticity formula:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| price₁A | Starting price of product A |
| price₂A | Ending price of product A |
| ΔpriceA | How much product A’s price changed |
| quantity₁B | Starting demand for product B |
| quantity₂B | Ending demand for product B |
| ΔquantityB | How much demand for product B changed |
To figure out cross price elasticity, follow these steps: First, find the percent change in how much people buy of one product. Next, find the percent change in the other product’s price. Then, divide the first number by the second number.
The formula is: Percent Change in Quantity Demanded of Product B divided by Percent Change in Price of Product A.
Tip: For better results, use the midpoint method. This method uses the average of the starting and ending numbers. It helps your answer stay the same even if prices change a lot. Economists like this method because it gives more accurate answers.
Example Calculation
Let’s look at an example to make it clear. Suppose you want to see how a price change in coffee affects tea. When coffee’s price goes from 5, people buy more tea. Tea sales go up from 100 to 120 units.
Here are the steps:
- Find the percent change in tea sales:
- (120 - 100) / [(120 + 100) / 2] = 20 / 110 ≈ 0.182 or 18.2%
- Find the percent change in coffee price:
- (4) / [(4) / 2] = 4.5 ≈ 0.222 or 22.2%
- Use the formula:
- 18.2% / 22.2% ≈ 0.82
A positive number means tea and coffee are substitutes. You can use this math to see how one product’s price affects another. Businesses use cross price elasticity to set prices, guess how much people will buy, and make bundles. If you know the cross elasticity, you can change your plans when other companies change prices or when you want to reach new buyers.
Note: Knowing how to do this calculation helps you make smart choices about prices and ads. You can see patterns and act fast when things change in your market.
Interpreting Cross Price Elasticity of Demand
Positive, Negative, and Zero Values
When you check cross price elasticity, you find three main types. Each type tells you how products are connected.
- If cross price elasticity is positive, the products are substitutes. When one price goes up, people buy more of the other. For example, if coffee costs more, people might buy more tea.
- If cross price elasticity is negative, the products are complements. When one price rises, people buy less of the other. Printers and ink cartridges work this way. If printers cost more, people buy fewer ink cartridges.
- If cross price elasticity is zero, the products are not related. Changing one price does not change demand for the other. For example, shoe prices do not affect how many tires people buy.
In big markets, many products have zero cross price elasticity. This means most products do not change each other's demand.
Tip: Knowing the types of cross elasticity helps you see which products compete and which go together.
What Relationships Mean
Cross elasticity of demand helps you learn about product links. The size of cross price elasticity shows how strong the connection is. Economists use these numbers to group products and guess market changes.
| Cross Price Elasticity Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | Substitute goods; if one price goes up, demand for the other goes up. | Coffee and tea |
| Negative | Complementary goods; if one price goes up, demand for the other goes down. | Printers and ink |
| Zero or Near-Zero | Unrelated goods; price changes do not affect demand. | Shoes and tires |
It is important to know about cross-price elasticity for your business. It helps you set prices, plan sales, and manage stock. If you sell complements, you can bundle them or make joint sales. If you sell substitutes, you can change prices to beat rivals.
- Positive cross price elasticity helps you set prices to compete.
- Negative cross price elasticity helps you bundle products that go together.
- Cross price elasticity gives you ideas to control supply and plan stock.
Sometimes, it is hard to understand cross price elasticity data. Old numbers may not fit new trends. Things like seasons or what rivals do can change results. Not enough data makes it tough, especially for stores with lots of products. Elasticity can change over time. Online stores may see ads change the numbers.
Note: Knowing how big cross price elasticity is, and how it compares to other types, helps you make better choices for your business and products.
Cross Price Elasticity of Demand in Practice
Pricing Strategies
You can use cross price elasticity of demand to help with pricing. If you know how demand changes when another product’s price changes, you can set better prices. Companies use cross price elasticity of demand for many reasons.
- They find out if products are substitutes, complements, or not related.
- They see if one product might take sales from another in their own group.
- They bundle complementary products to keep customers and add value.
- They change prices to react to what other companies do.
For example, printers and ink are complementary. If you raise printer prices, you may sell less ink. You can bundle them or give discounts to keep people buying both. If you sell two soft drinks, you should not discount both at once. This could make customers switch between your drinks instead of bringing in new buyers.
Cross price elasticity of demand helps you see which products fight for the same buyers. You can use sales data to check how price changes affect demand. This helps you keep customers and make more money. Knowing about cross elasticity helps you plan good promotions and avoid mistakes that hurt sales.
Tip: Always check how strong cross price elasticity of demand is before making big price changes. This shows you how close products are linked.
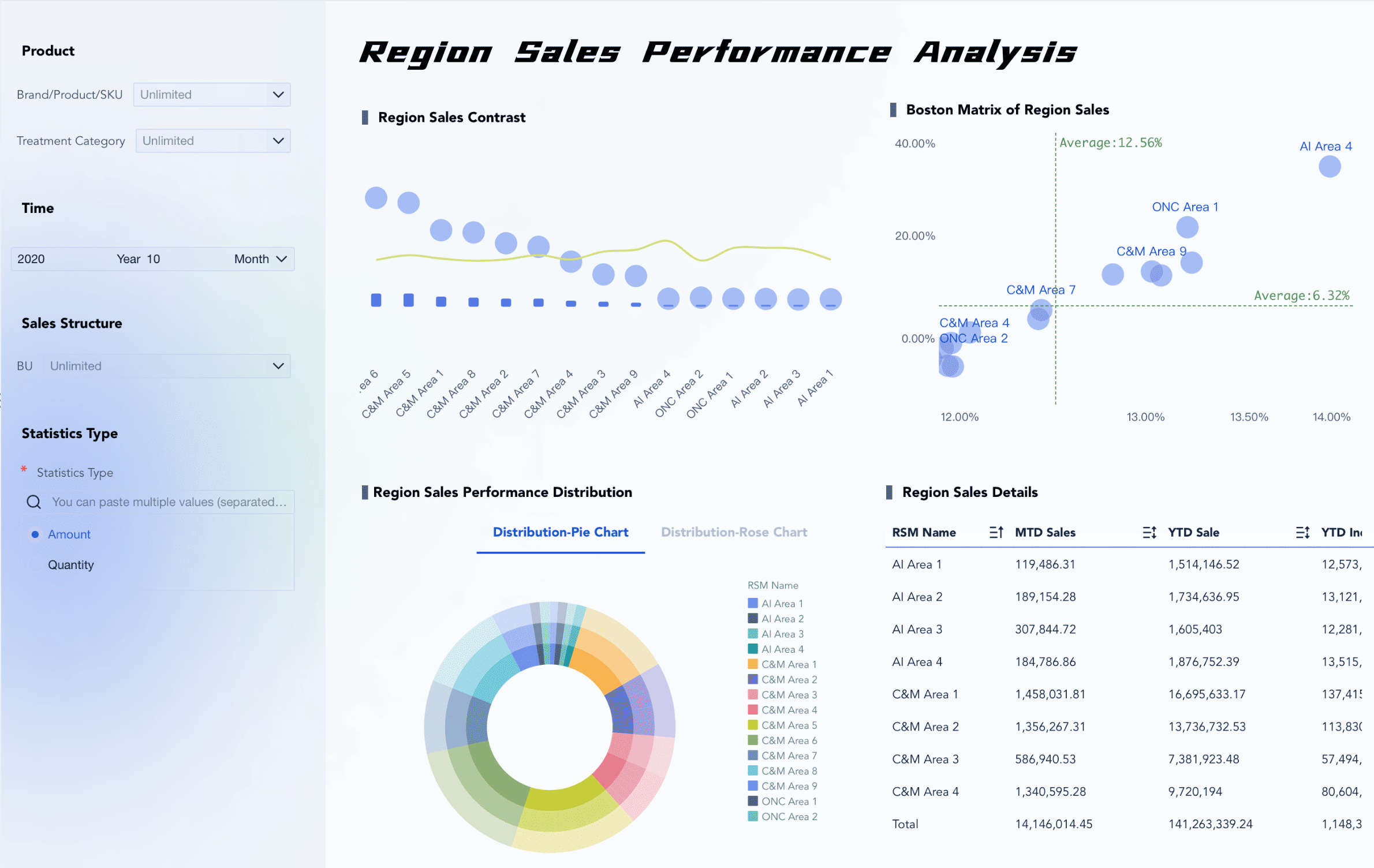
Market Analysis with FineBI
FineBI helps you study cross price elasticity of demand with real-time data. You can connect to many data sources and see how price changes affect demand for your products. FineBI lets you look at data by yourself without needing to code.

| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| User-Friendly Data Visualization | Make charts and graphs easily with drag-and-drop tools. |
| Self-Service Data Analysis | Study data on your own to make quick choices. |
| Folder-Based Data Management | Sort data by business topics for easy access. |
| Data Modeling | Build links between products to study cross price elasticity of demand. |
| Visual Data Analysis | Spot trends and problems fast with clear visuals. |
| Automatic Dimension Recognition | Find key things for cross price elasticity of demand analysis. |
| Dashboard Functionality | Put all your data in one report to track important numbers. |
You can use FineBI to see how your products do in the market (click to engage).
When you use cross price elasticity of demand in FineBI, you can:
- Track how your sales change when a competitor changes prices.
- Find which products are complements and bundle them for better results.
- Set prices that help you get more customers and grow your market share.
Cross price elasticity of demand compared to other types of elasticity gives you a full view of your market. You see how your prices matter and how other products affect your sales. Knowing how strong cross price elasticity is helps you make better choices for pricing and product placement. Cross-price elasticity is more important as markets get more competitive and products become more connected.
Note: FineBI from FanRuan lets you use cross price elasticity of demand to guide your pricing, spot new trends, and stay ahead in your industry.
If you know about cross price elasticity, you can make better choices. This helps you with prices and knowing what people want. You can use this to set prices, group buyers, and guess sales. FineBI gives you ways to look at data and see patterns. You can change your plans fast if you need to. Many companies use data to set prices and make more money. They want to stay ahead of others. Real-time data and market checks help you act fast. This keeps your business safe and strong.
Data tools like FineBI help you watch rivals, learn about buyers, and make better pricing plans.
- You can:
- Make pricing plans that can change.
- Watch for changes in the market.
- Grow your sales and make more money.
FanRuan
https://www.fanruan.com/en/blogFanRuan provides powerful BI solutions across industries with FineReport for flexible reporting, FineBI for self-service analysis, and FineDataLink for data integration. Our all-in-one platform empowers organizations to transform raw data into actionable insights that drive business growth.
FAQ
Cross price elasticity tells you how demand changes. It shows what happens to one product when another product’s price changes. You can use it to find out if products are substitutes or complements.
You can use cross price elasticity to set better prices. It helps you make product bundles and keep an eye on your competitors. This lets you make smart choices and grow your sales.
FineBI lets you connect to lots of data sources. You can see changes as they happen and build dashboards. You can spot trends and make fast choices. You do not need to know how to code.
FineBI works with data from databases, Excel files, APIs, and cloud platforms. You can put all your sales and pricing data together for a full view.