Location data management plays a crucial role in various industries. Businesses leverage location data to enhance customer interactions and make informed decisions. According to Forbes, 75% of retailers consider location intelligence vital for revenue growth strategies. Over the past five years, location data has evolved significantly. Companies like D&B and Yellow Pages have long listed businesses. Today, numerous websites, directories, maps, and social media networks utilize this information. This blog aims to explore key techniques and tools in location data management.

Location data management involves handling various types of location-based information. This section explores the primary categories.
Geospatial data refers to information that describes objects, events, or other features with a location on or near the Earth's surface. Researchers often use geospatial data for mapping and analysis. Key sources include satellite imagery, aerial photography, and geographic surveys. The Esri Community Blog highlights the increasing volume of research tied to geospatial data. Scholars utilize platforms like Google Scholar and library databases to access peer-reviewed studies.
Geographical Information Systems (GIS) represent a crucial tool in location data management. GIS integrates hardware, software, and data for capturing, managing, analyzing, and displaying all forms of geographically referenced information. Popular GIS platforms include ArcGIS and QGIS. These systems enable users to visualize spatial data through maps and 3D scenes, facilitating better decision-making.
Various sources contribute to the collection of location data. This section outlines the primary sources.
Global Positioning System (GPS) and satellite data provide precise location information. Satellites orbiting the Earth transmit signals to GPS receivers, which calculate exact positions. Industries such as transportation, agriculture, and emergency services rely heavily on GPS data for operations and planning.
Mobile devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) generate vast amounts of location data. Smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices continuously collect and transmit location information. IoT devices, including smart home systems and industrial sensors, also contribute valuable data. Businesses use this data to enhance customer experiences and optimize operations.
Public and private databases serve as significant sources of location data. Government agencies, research institutions, and private companies maintain extensive datasets. Examples include census data, environmental monitoring records, and commercial location databases. Access to these resources allows businesses to enrich their location data management strategies.

Surveys and field data collection represent foundational techniques in location data management. Researchers use surveys to gather specific information from targeted populations. Field data collection involves on-site visits to record geographic coordinates and other relevant details. For example, transportation agencies often conduct field surveys to monitor traffic patterns and infrastructure conditions. These methods ensure accurate and up-to-date location data.
Remote sensing involves acquiring information about the Earth's surface without direct contact. Satellites and drones capture high-resolution images and data. This technique proves invaluable for environmental monitoring, urban planning, and disaster management. Companies like Unacast leverage remote sensing to revolutionize retail site selection and commercial real estate investment decisions. Remote sensing provides comprehensive and scalable data collection solutions.
Spatial databases store and manage geospatial data efficiently. These databases support complex queries and spatial indexing. Popular spatial databases include PostgreSQL with PostGIS extension and Oracle Spatial. Businesses use spatial databases to handle large volumes of location data. Efficient data storage ensures quick access and retrieval, enhancing location data management capabilities.
Data warehousing involves consolidating data from multiple sources into a central repository. This technique supports large-scale data analysis and reporting. Enterprises use data warehouses to integrate location data with other business data. Cloud-based solutions like Amazon Redshift and Google BigQuery offer scalable and flexible data warehousing options. Effective data organization facilitates comprehensive insights and informed decision-making.
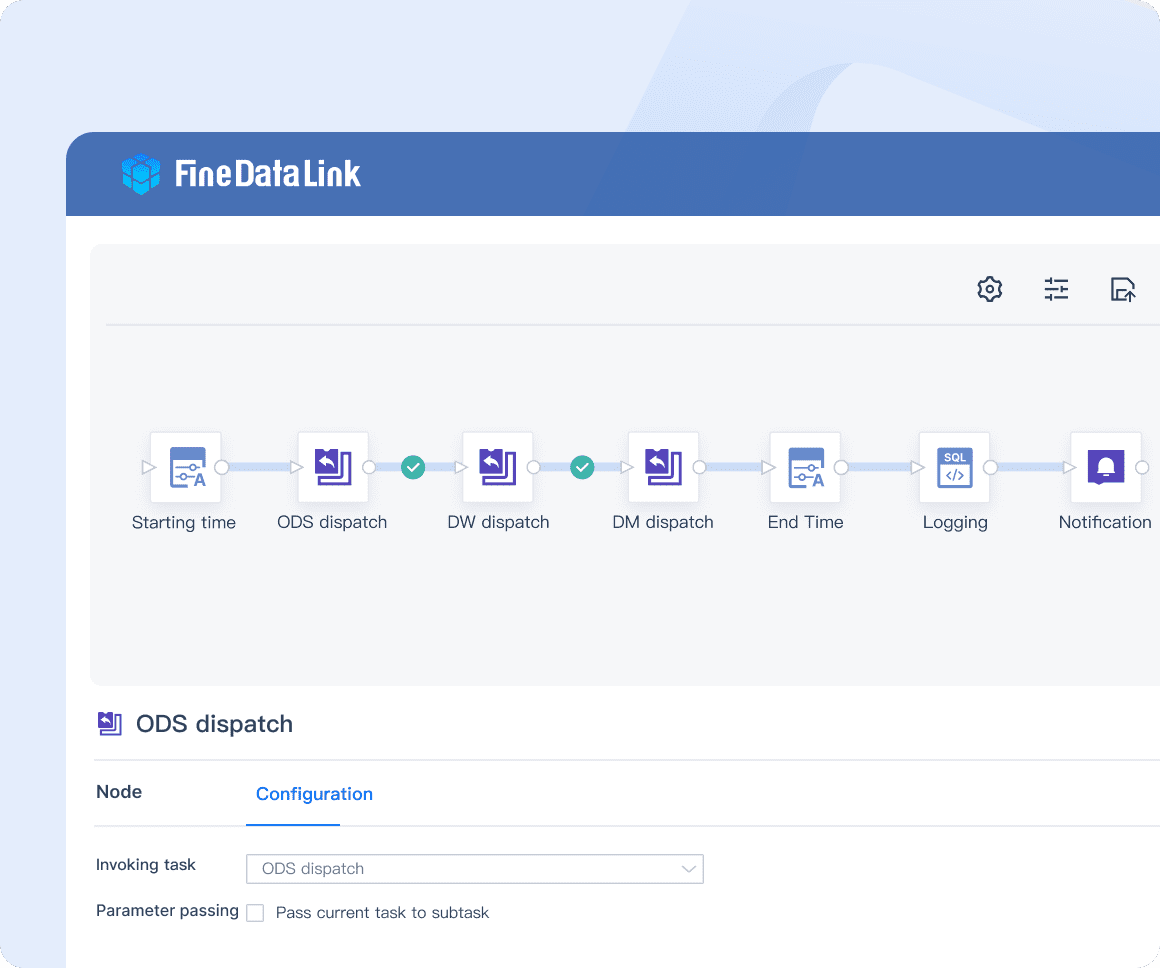
FineDataLink: build Data Warehouse efficiently through timing data calculation and synchronization.
Geospatial analysis techniques process and interpret location data to uncover patterns and trends. Analysts use spatial statistics, clustering, and interpolation methods. These techniques help identify relationships between geographic features and phenomena. For instance, transportation agencies analyze geotagged data to optimize routes and improve traffic flow. Geospatial analysis enhances the value of location data management.
Mapping and visualization tools transform raw location data into comprehensible visual formats. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software like ArcGIS and QGIS provide robust mapping capabilities. Visualization platforms such as Tableau and Power BI offer interactive dashboards and visualizations. These tools enable stakeholders to understand complex spatial data intuitively. Effective visualization supports strategic planning and decision-making in location data management.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software plays a pivotal role in location data management. These platforms provide robust tools for capturing, managing, analyzing, and displaying geographically referenced information.
Several popular GIS platforms dominate the market:
Key features and capabilities of GIS software include:
Effective location data management requires robust data management and storage solutions. These solutions ensure data integrity, accessibility, and scalability.
Cloud-based solutions offer several advantages for location data management:

FineDataLink: Efficient Data Warehouse Construction with timing data calculation and synchronization
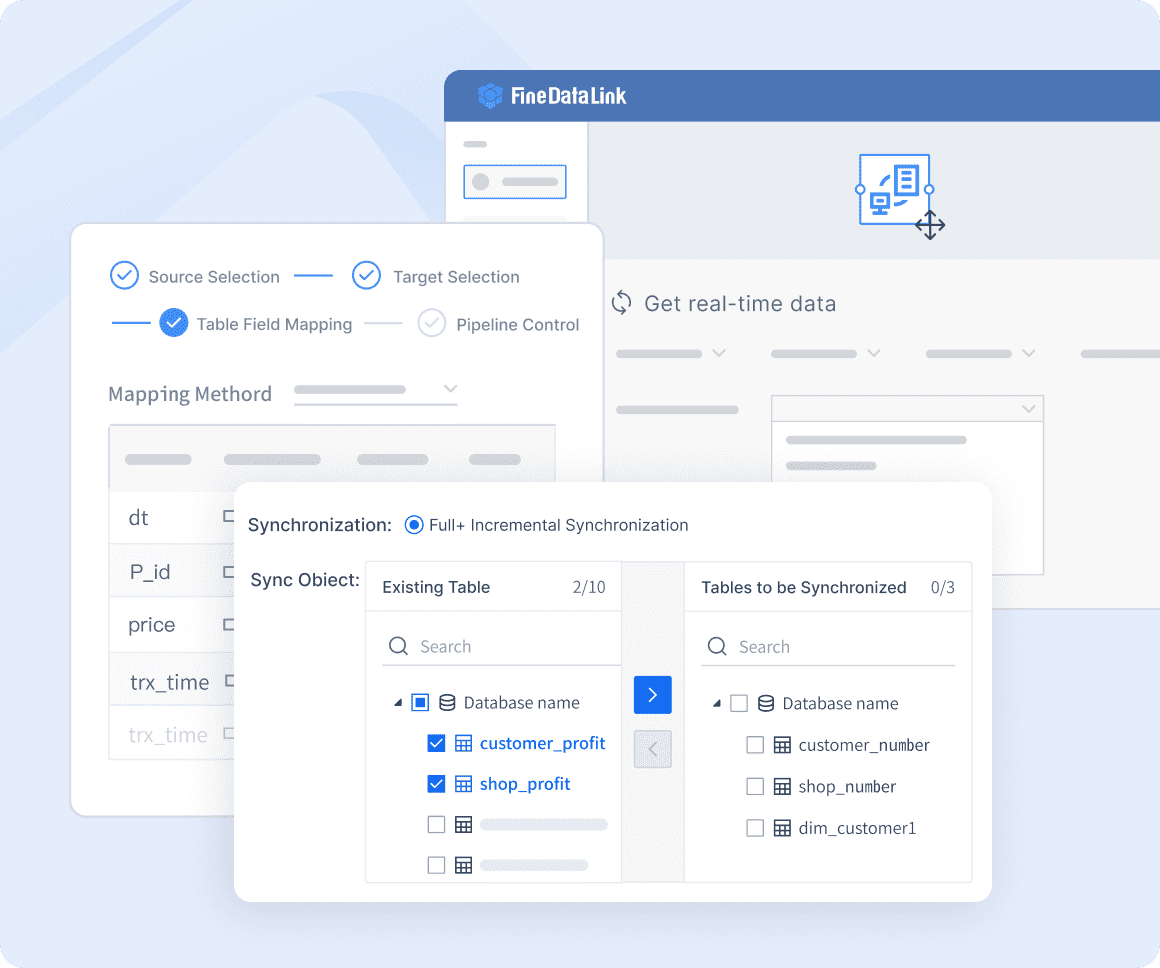
FineDataLink: Real-time Data Integration-it can synchronize data across multiple tables in real-time with minimal latency, and can be used for database migration and backup.
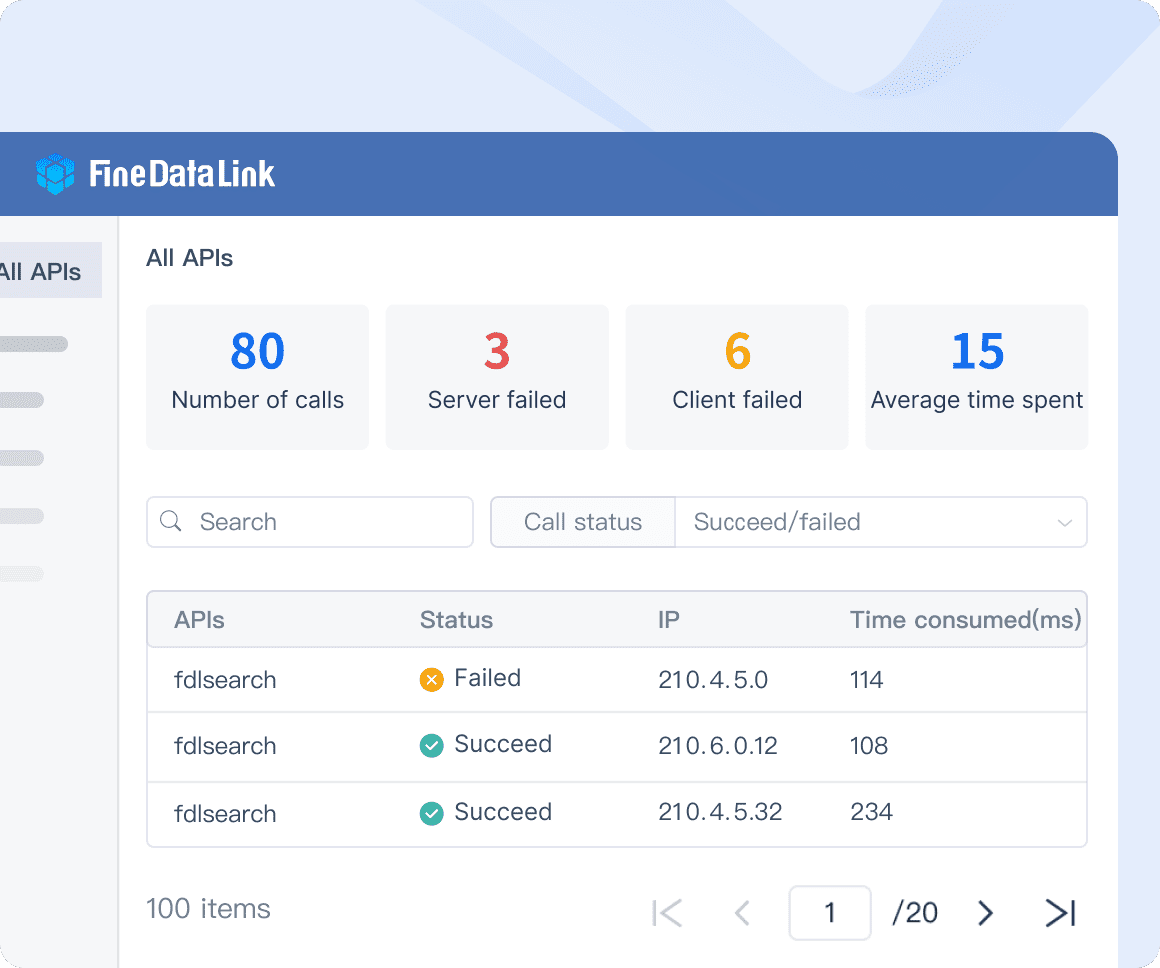
FineDataLink: Application and API Integration- as an API interface can be developed and launched in 5 minutes without writing code, it can be widely used to share data between various systems, especially SaaS application.
You can click the following banner to explore FineDataLink for free!
Benefits of cloud-based solutions include:
On-premises solutions remain essential for organizations requiring complete control over their data:
Benefits of on-premises solutions include:
Analytical and visualization tools transform raw location data into actionable insights. These tools enhance the value of location data management by providing clear and comprehensible visual representations.
Data analytics platforms process and analyze large datasets to uncover valuable insights:
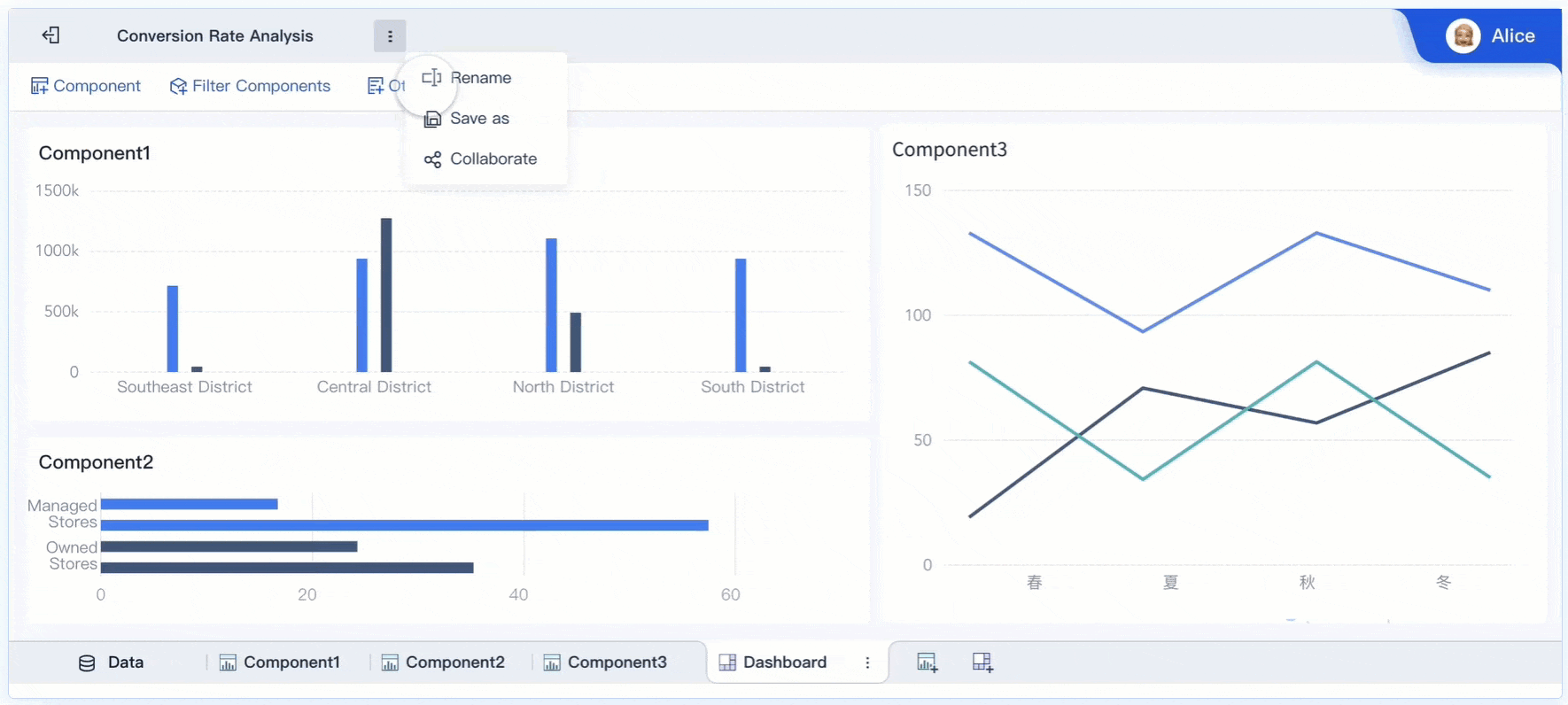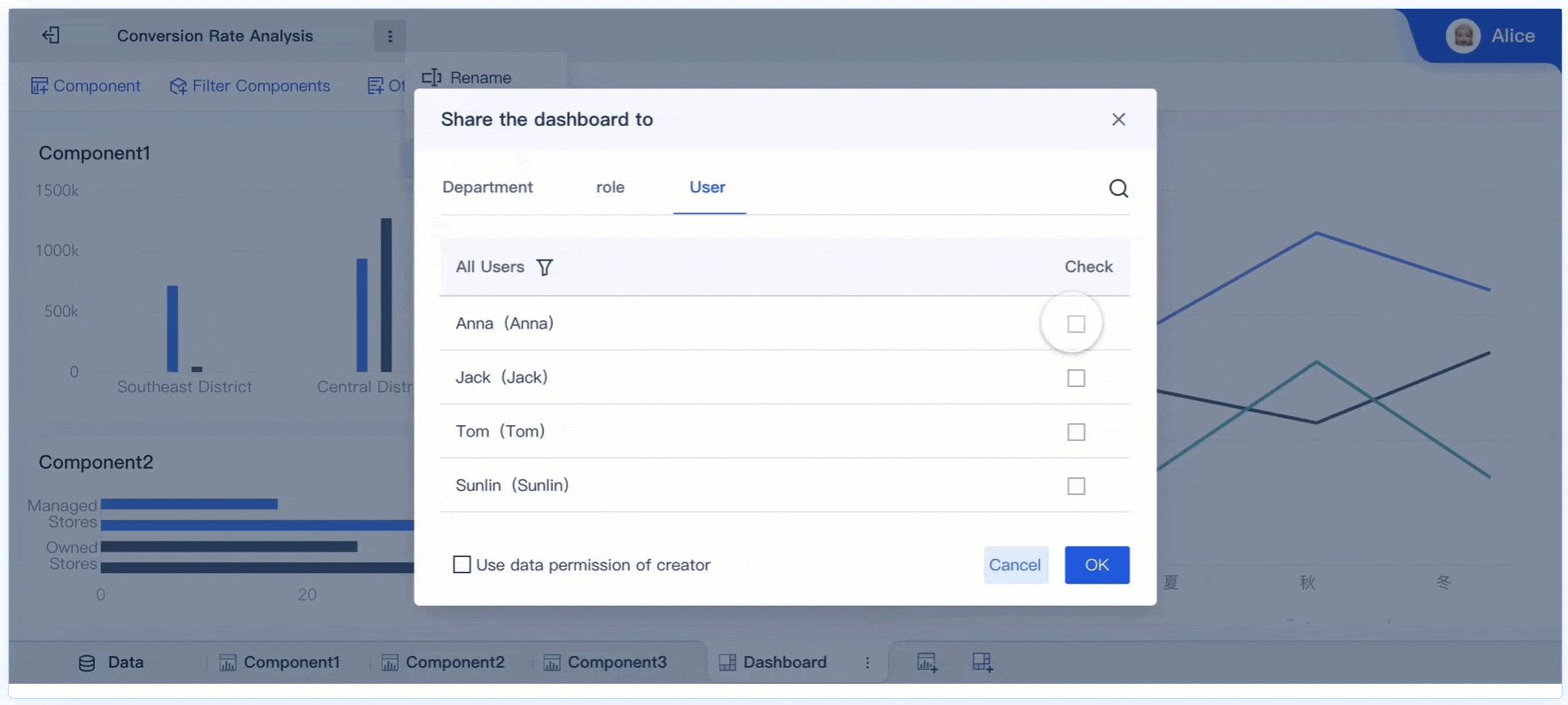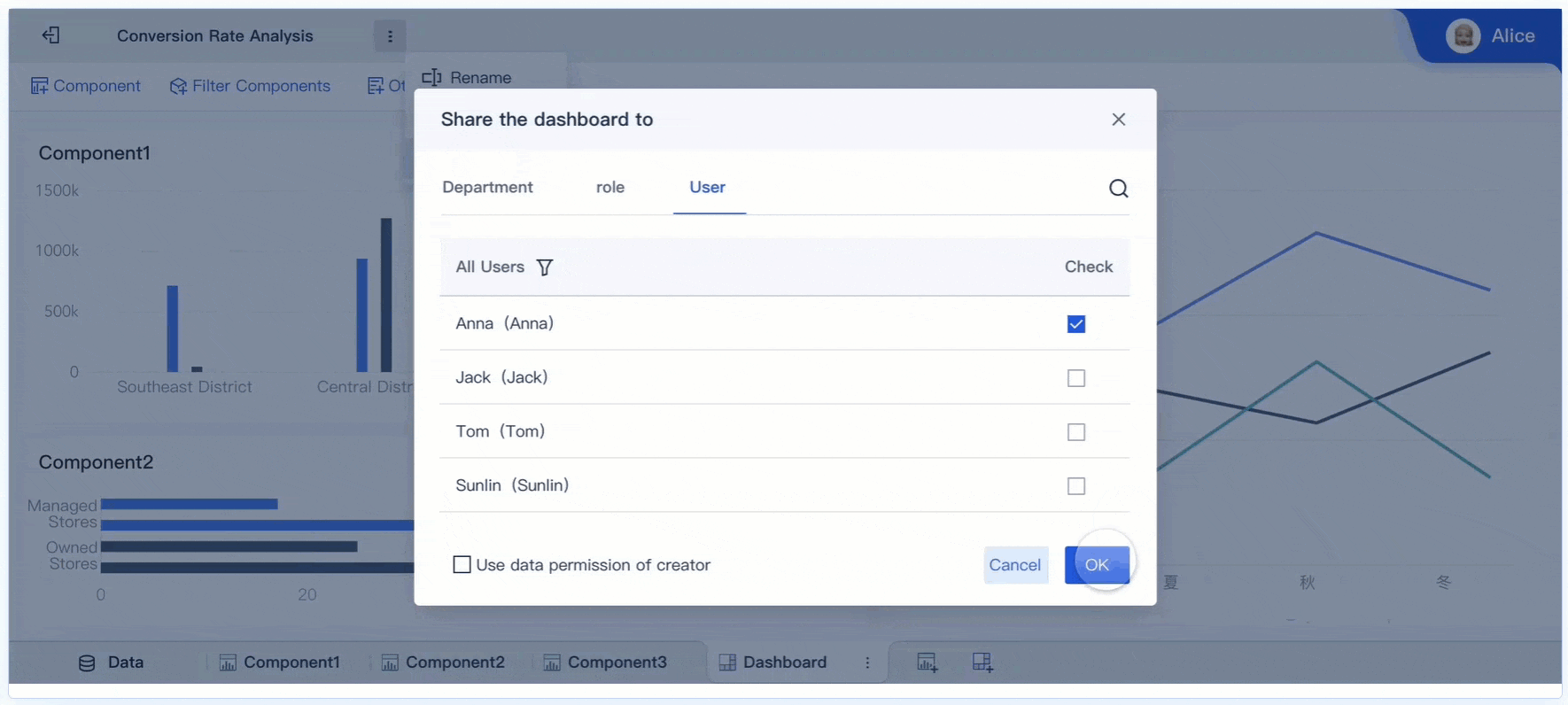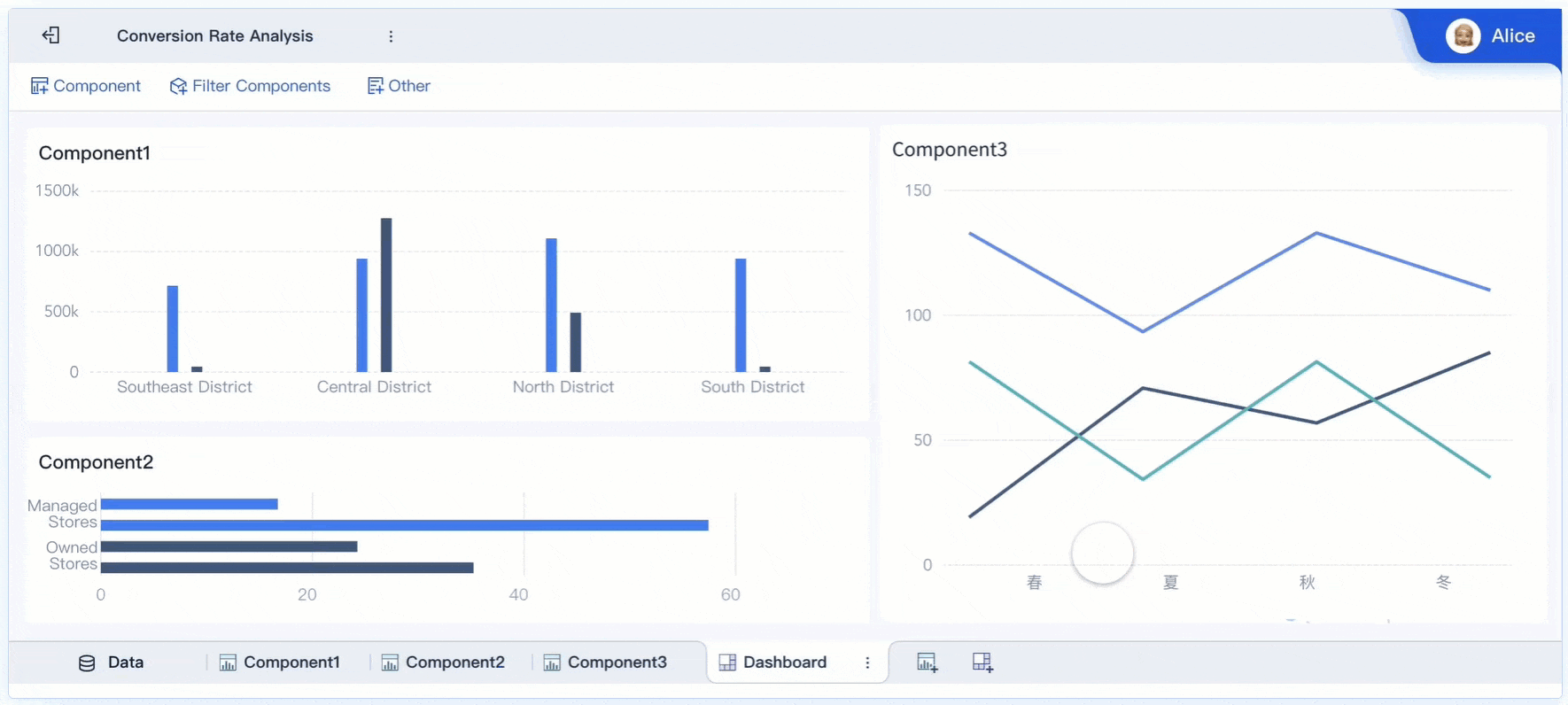
FineBI: Efficient Data Collaboration and Communication.
Key features of data analytics platforms include:
Visualization software converts complex data into easily understandable visual formats:
FineReport: Flexible Dashboard Designer, a powerful data visualization software.
Benefits of visualization software include:
Urban planning benefits significantly from location data management. Planners use geospatial data to design efficient city layouts, optimize land use, and manage resources. For example, RJM Design Group utilizes precise location insights to allocate resources effectively for urban park optimization. This approach ensures that cities and municipalities can make informed decisions about infrastructure development and public amenities.
Environmental monitoring relies on robust location data management to track changes in natural landscapes. Remote sensing and GIS tools help monitor deforestation, water quality, and air pollution. Agencies use satellite imagery and geotagged data to assess environmental impacts and plan conservation efforts. Accurate location data enables timely interventions and supports sustainable development initiatives.
Transportation and logistics industries leverage location data management to enhance operational efficiency. GPS and IoT devices provide real-time location information, enabling companies to optimize routes and reduce fuel consumption. Unacast's geotagged data has revolutionized transportation by offering valuable insights for route planning and traffic management. These advancements lead to cost savings and improved service delivery.
Effective location data management enhances business visibility and customer experience. The key techniques include data collection, analysis, and visualization, and the essential tools encompass GIS software, data management solutions, and visualization tools. Future trends in location data management will drive improved analytics and decision-making. Businesses should explore and implement these techniques to gain a competitive edge. FineDataLink is definitely a great choice for you!
Mastering Data Management: Your Complete Guide
Essential Guide to Master Data Management

The Author
Howard
Data Management Engineer & Data Research Expert at FanRuan
Related Articles
What is a data management platform in 2025
A data management platform in 2025 centralizes, organizes, and activates business data, enabling smarter decisions and real-time insights across industries.
Howard
Dec 22, 2025

Top 10 Database Management Tools for 2025
See the top 10 database management tools for 2025, comparing features, security, and scalability to help you choose the right solution for your business.
Howard
Dec 17, 2025

Best Data Lake Vendors For Enterprise Needs
Compare top data lake vendors for enterprise needs. See which platforms offer the best scalability, integration, and security for your business.
Howard
Dec 07, 2025