

You use EBITDA margin to measure how efficiently a company turns revenue into earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. EBITDA highlights core operational results and helps you compare companies across industries. Many analysts value EBITDA because it shows performance without the impact of financing or accounting choices. The table below shows how EBITDA stands out when compared to other financial metrics:
| Metric | Importance in Business Performance Evaluation |
|---|---|
| EBITDA | Provides insights into operational performance, useful for valuation. |
| Other Metrics | Necessary for a comprehensive analysis, accounting for cash flow. |
EBITDA does not show cash flow or capital spending, so you should use it with other metrics for a complete view. Modern BI tools like FineBI from FanRuan make it easier for you to analyze EBITDA margin and visualize performance trends.
You use ebitda margin to see how much profit a company makes from its core operations before paying interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. This margin shows you the percentage of revenue that turns into earnings before these costs. Many investors and analysts rely on ebitda margin because it helps you compare companies without worrying about their capital structure or accounting choices.
You should remember that ebitda margin focuses only on operational performance. It does not show you the full picture of a company's financial health. Some people think ebitda margin is the same as cash flow, but this is not true. ebitda does not include changes in working capital or capital expenditures. You might see companies report high ebitda margin, but this can sometimes hide important costs or risks.
💡 Tip: Always look at ebitda margin along with other financial ratios. This helps you avoid common mistakes and gives you a better understanding of a company's real performance.
You will often see ebitda margin compared to other types of profit margin. Each margin tells you something different about a company's ability to make money. Here is a table that shows how ebitda margin compares to gross margin, operating margin, and net profit margin:
| Margin Type | Calculation Formula |
|---|---|
| Gross Margin | (Sales - Cost of Goods Sold) / Sales |
| Operating Margin | (Sales - Cost of Goods Sold - Other Operating Expenses) / Sales |
| EBITDA Margin | (Net Income + Taxes + Interest Expense + Depreciation + Amortization) / Sales |
| Net Profit Margin | Net Income / Sales |
Gross margin tells you how much money is left after paying for the goods sold. Operating margin goes further by subtracting operating expenses. ebitda margin adds back some non-cash and non-operating costs, so you see how well the core business performs. Net profit margin shows you the final profit after all expenses, including taxes and interest.
You should know that ebitda margin is not always the best measure for every company. Some industries have very different typical ebitda margin ranges. For example, manufacturing companies often have ebitda margin multiples between 7.0x and 11.1x, while real estate companies can have much higher multiples. Always compare ebitda margin to industry averages for a fair view.
Many people misunderstand ebitda margin. Here are some common misconceptions:
You can use ebitda margin to compare companies, but always check other profit margin ratios and financial data. This approach gives you a more complete and accurate picture of business performance.

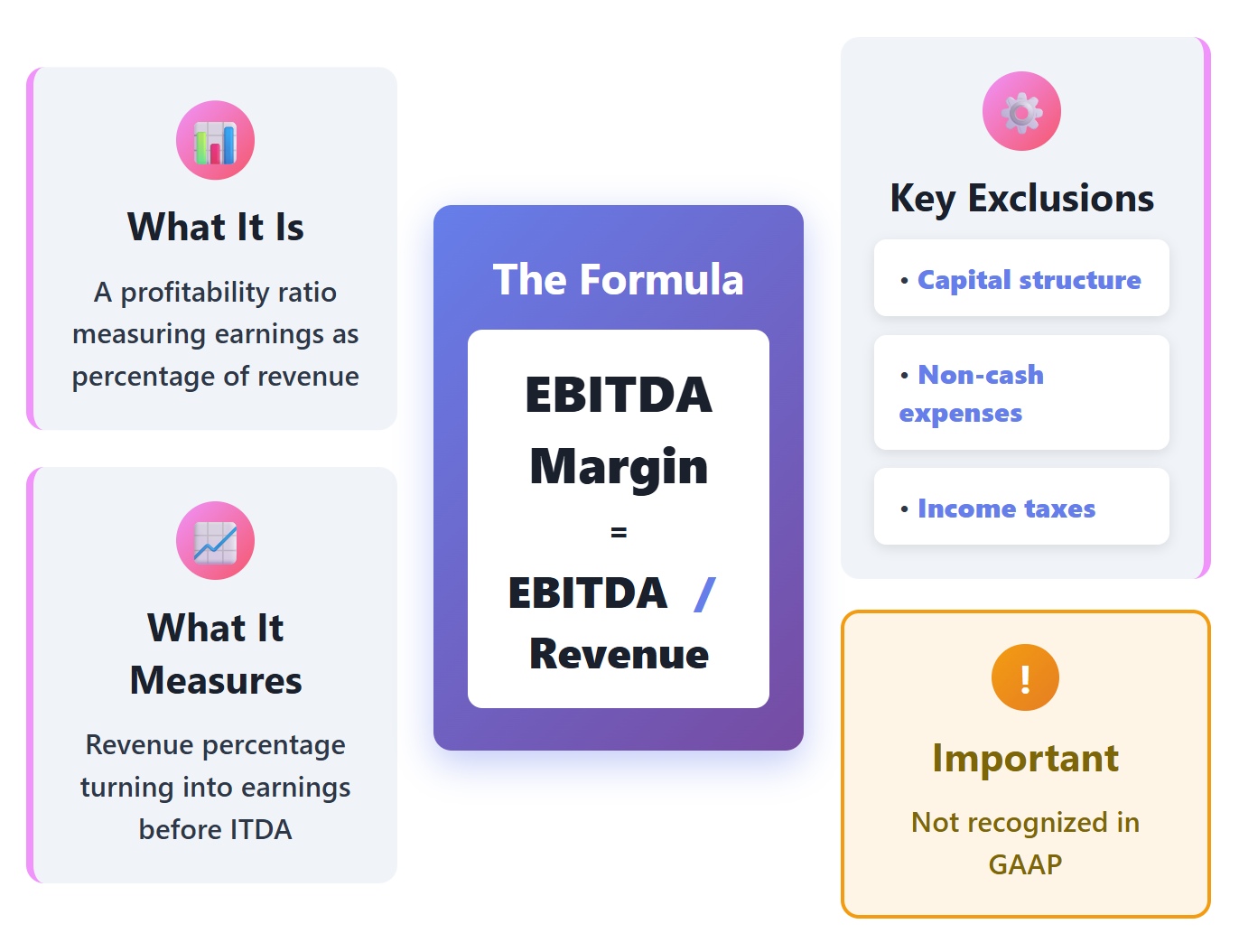
You can calculate ebitda margin using a simple formula. This formula helps you see how much of your revenue turns into earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. The ebitda margin formula is:
EBITDA Margin (%) = (EBITDA ÷ Net Revenue) × 100
You need to understand each part of this formula. The table below breaks down the main components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| EBITDA | Operating Income (EBIT) + Depreciation & Amortization |
| Net Revenue | Gross Revenue – Returns – Discounts – Sales Allowance |
| EBITDA Margin (%) | EBITDA ÷ Net Revenue (expressed as a percentage) |
You find ebitda by starting with operating profit and then adding back depreciation and amortization. These numbers usually come from your income statement and cash flow statement. Net revenue is your total sales after subtracting returns, discounts, and allowances. When you divide ebitda by net revenue and multiply by 100, you get the ebitda margin as a percentage.
To calculate ebitda margin, you need two main figures: ebitda and sales (or revenue). You can find sales in the income statement. Depreciation and amortization details often appear in the cash flow statement or in the notes to the financial statements. Make sure you use the correct numbers from your financial reports.
⚠️ Note: EBITDA margin is a non-GAAP measure. When you report it, you must also show comparable GAAP margins. The SEC requires companies to disclose non-GAAP measures with equal prominence and clear explanations.
Accounting standards can affect your calculation. For example, ASC 842 changes how you report operating leases. Lease payments are no longer directly expensed, so ebitda increases because lease expenses are removed from the calculation. Always check for recent changes in accounting rules before you calculate ebitda margin.
You can follow a clear process to calculate ebitda margin for any company. Here is a step-by-step example:
You can see that 25.8% of your revenue turns into ebitda. This means your core operations are efficient, and you keep a good portion of your sales as earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
💡 Tip: Many business intelligence tools, such as FineBI by FanRuan, make this calculation even easier. You can create formula columns in FineBI to calculate ebitda margin automatically. The platform lets you filter, group, and summarize your data. You do not need advanced technical skills. FineBI’s self-service datasets help you perform these calculations quickly and visualize the results in real time.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Users can create formula columns to calculate ebitda margin by inputting the relevant formula. |
| 2 | The formula used is EBITDA Margin = (EBITDA / Revenue) × 100. |
| 3 | The platform allows filtering, grouping, and summarizing data effectively. |
| 4 | Self-service datasets enable users to perform calculations without extensive technical knowledge. |
When you use FineBI, you can avoid many common errors. Some people use the wrong starting figures or miscalculate growth rates. Others overcomplicate the process or forget to adjust for working capital or capital expenditures. FineBI helps you keep your calculations accurate and your analysis clear, you can perform basic data cleaning in FineBI before analyzing your data.
You should always double-check your numbers and use the right data sources. FineBI’s dashboards and visualizations help you spot trends and outliers, making your ebitda margin analysis more reliable.
When you use EBITDA margin in your analysis, you gain several important benefits:
💡 Tip: If you want to improve EBITDA margin, you can conduct internal audits, automate manual processes, reduce overhead costs, and negotiate better terms with vendors. These steps help you control expenses and boost profit from your revenue.
While EBITDA margin is a powerful tool, you should know its main drawbacks:
EBITDA margin can sometimes give you the wrong impression about a company’s financial health. For example, a manufacturing company might show a strong EBITDA margin but face high costs for new equipment. This could make the business seem more stable than it really is. Also, when companies adjust EBITDA to remove one-time expenses, you might miss ongoing problems in their operations. Always look closely at these adjustments to avoid being misled.
You now understand that ebitda margin measures how much profit a company earns from its core operations before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. You can calculate this margin by dividing ebitda by revenue. FineBI by FanRuan helps you analyze these metrics with real-time analytics, self-service features, and easy customization, as shown below:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Real-time analytics | Analyze financial metrics, including ebitda margin, instantly. |
| Self-service capabilities | Explore data independently, reducing IT reliance. |
| Ease of use | User-friendly interface for quick adoption. |
| Customization | Design dashboards to fit your needs. |
| Scalability | Handle growing data demands easily. |
Remember to balance ebitda margin with other financial ratios like net profit margin and debt-to-equity ratio for a complete evaluation.
You use EBITDA margin to measure how well a company turns revenue into profit from its main operations. This ratio helps you focus on core business activities by removing the effects of interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. When you see a high EBITDA margin, you know the company manages its costs well and runs efficiently. A low EBITDA margin can signal problems with cost control or weak pricing power.
You should always check EBITDA margin against industry benchmarks. This helps you see if a company is leading or lagging behind its peers. Investors often use this ratio to spot growth opportunities and evaluate financial performance.
EBITDA margin makes it easy for you to compare companies in the same industry. Different sectors have different typical margins, so you need to look at industry averages. For example, real estate and leasing companies often have much higher EBITDA margins than retail or manufacturing firms.
| Industry | Median EBITDA Margin | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Real Estate & Leasing | 61.7% | 57.7-68.1% |
| Finance & Insurance | 40.8% | 37.4-56.4% |
| Utilities | 36.4% | 31.9-40.9% |
| Healthcare | 31.8% | 25.5-36.6% |
| Technology | 20.9% | 7.0-40.5% |
| Manufacturing | 20.2% | 13.4-24.1% |
| Retail Trade | 11.3% | 7.8-15.4% |
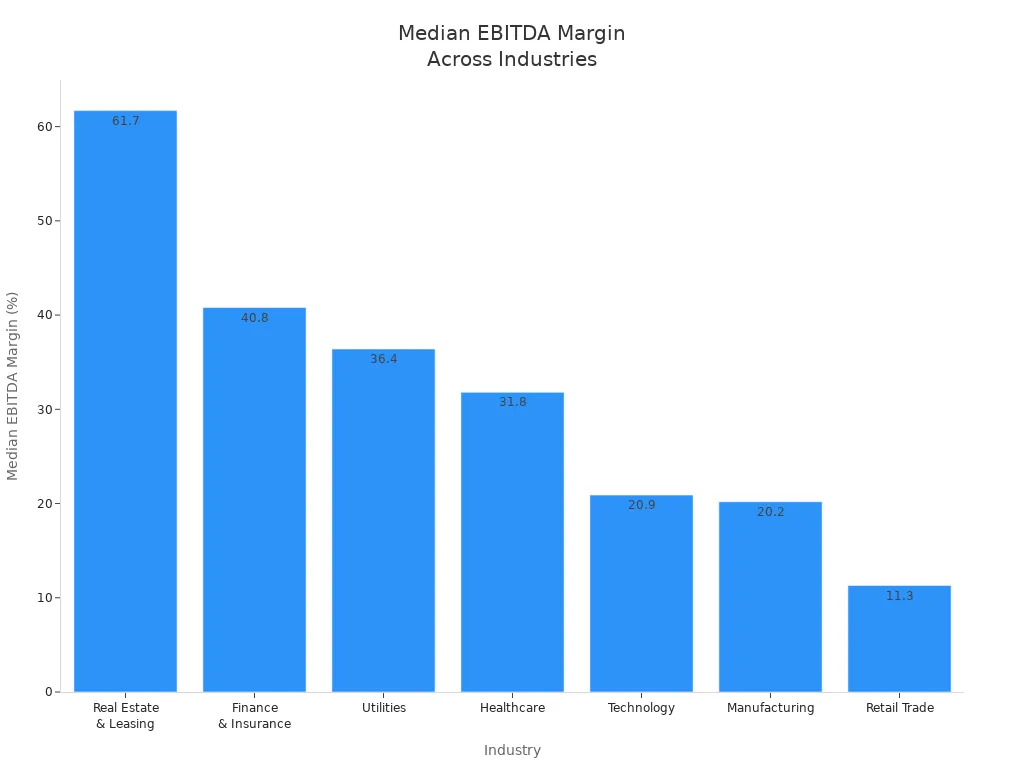
You can see that a higher EBITDA margin in technology or manufacturing often leads to better valuation multiples. In retail, even a small increase above the average margin can make a company stand out. Tracking EBITDA margin over time helps you measure progress and compare financial performance with industry peers.
You can use FineBI by FanRuan to analyze EBITDA margin quickly and accurately. FineBI gives you a drag-and-drop interface, so you do not need advanced technical skills. You can build dashboards that show EBITDA, revenue, and margin trends in real time. FineBI’s high-performance computing engine processes large datasets, so you always have up-to-date analytics.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Robust Analytics | Combines analytics with visualization for meaningful insights. |
| Drag-and-Drop Interface | Simplifies dashboard creation, making it accessible to users with minimal technical skills. |
| Real-Time Data Access | Enables instant response to changing conditions, crucial for timely EBITDA margin reporting. |
| High-Performance Computing Engine | Efficiently processes massive datasets, ensuring up-to-date analytics for accurate reporting. |
| Contextual Comments Integration | Enhances storytelling capabilities, aiding in effective communication of EBITDA insights. |
| Self-Service BI | Empowers users to analyze data independently, fostering a data-driven culture and faster decisions. |
With FineBI, you can track EBITDA margin, compare it to industry benchmarks, and share insights with your team. This helps you make better decisions and improve your company’s profitability metrics.
FanRuan
https://www.fanruan.com/en/blogFanRuan provides powerful BI solutions across industries with FineReport for flexible reporting, FineBI for self-service analysis, and FineDataLink for data integration. Our all-in-one platform empowers organizations to transform raw data into actionable insights that drive business growth.
A high EBITDA margin shows you run your core operations efficiently. You keep more profit from each dollar of sales. Investors often see this as a sign of strong management and good cost control.
1.Review and cut unnecessary expenses.
2.Automate manual tasks.
3.Negotiate better deals with suppliers.
4.Focus on higher-margin products or services.
Tip: Use tools like FineBI to track and analyze your progress.
No, EBITDA margin does not equal cash flow. EBITDA ignores capital spending, debt payments, and changes in working capital. Always check cash flow statements for a complete financial picture.
You should not compare EBITDA margins across unrelated industries. Each industry has its own typical margin range. Always compare your company’s margin to similar businesses in the same sector.

