Imagine you want to know if eating more apples makes you better at math. You collect data and place each result as a dot on a graph. In a no correlation scatter plot, the dots spread out randomly with no clear line or pattern. This tells you the two things are not related. When you spot no correlation, you avoid guessing connections that do not exist.
You see a scatterplot when you want to compare two sets of numbers. In a no correlation scatter plot, the dots appear scattered all over the graph. The points do not form a line or curve. You cannot draw a trend line through them. This random spread means that changes in one variable do not affect the other. For example, if you plot shoe size against intelligence, the dots will not show any pattern. The lack of a pattern tells you there is no connection between the two things.
When you look at a scatterplot with no correlation, you notice that the data points do not cluster around any line. The graph does not show an upward or downward trend. The dots look like they are placed randomly. This visual clue helps you understand that the variables are unrelated.
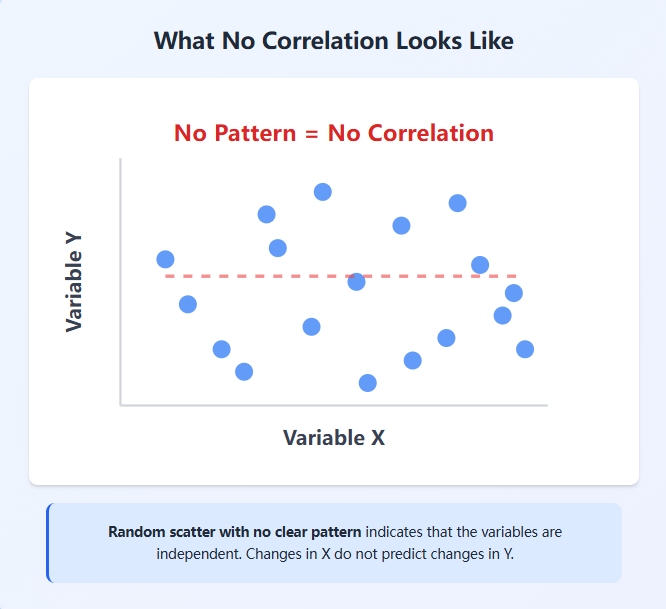
Tip: Always check for patterns in your scatterplot before making decisions. A random scatter means no correlation.
You can use statistical measures to confirm what you see. Pearson's correlation coefficient helps you check for a relationship. If the value is zero, it means there is no observable linear relationship. The table below shows how you can use these measures:
| Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Zero Correlation (r=0) | Indicates no observable linear relationship between the two variables. |
| No Linear Trend Line | If no linear trend line can be drawn through the data, it confirms the absence of linear correlation. |
You need to recognize no correlation in your scatterplot to avoid mistakes. If you think two things are related when they are not, you might make poor choices. In business intelligence, this can lead to wasted time and money. Here are some problems that happen when you misinterpret a scatterplot with no correlation:
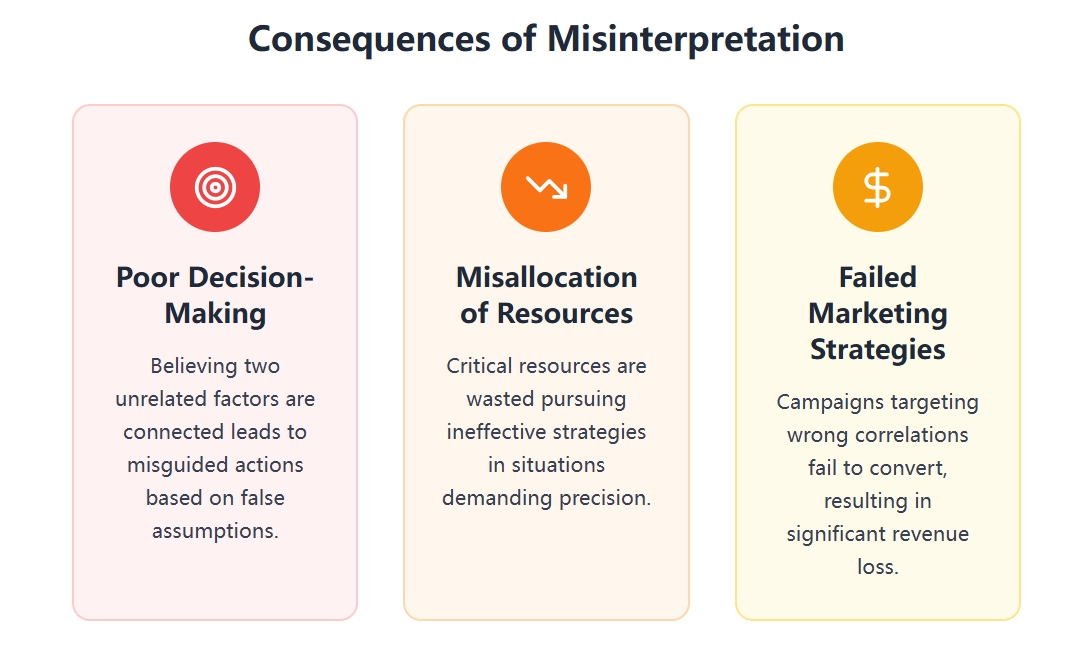
You should always inspect your scatter plots carefully. Many people believe that a steep slope means strong correlation, but that is not true. The strength of a correlation depends on how closely the points cluster around a line, not the slope itself. Sometimes, scatterplots can mislead you if you do not consider outliers or nonlinear relationships. Visual inspection helps you spot these issues.
Data analysts use several methods to check for no correlation in large datasets. The table below lists some common approaches:
| Method | Description | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| CUTIE | Detects false positives and negatives in correlation analysis. | Limited to identifying cases where significant correlations become non-significant. |
| Cook’s distance (Cook’s D) | Measures the effect of individual observations on the regression line. | Not symmetric with respect to 'x' and 'y' variables. |
| DFFITS | Identifies influential data points affecting regression results. | Similar limitations as Cook’s D; not symmetric. |
| Non-parametric methods | Spearman and Kendall rank-transform data to limit influential observation effects. | Less powerful than Pearson; should be used when data violates linear regression assumptions. |
| Log-transformations | Reduces skewness effects when using Pearson’s correlation. | Difficult to apply consistently across variables; selective transformation is challenging. |
You can use FineBI from FanRuan to make this process easier. FineBI lets you create scatterplots with a drag-and-drop interface. You can connect to many data sources and visualize your data in real time. The software helps you spot no correlation quickly. You can apply filters, check for outliers, and use built-in statistical tools. FineBI supports self-service analytics, so you do not need advanced technical skills. You can share your findings with your team and make better decisions.
Note: FineBI helps you avoid common mistakes by making it easy to inspect scatterplots and confirm no correlation.
FineBI and FanRuan give you the tools to analyze your data with confidence. You can focus on what matters and ignore unrelated variables. This leads to smarter business decisions and better results.
You might wonder if drinking more coffee makes you smarter. When you plot coffee consumption against intelligence scores on a scatterplot, you see the dots scattered randomly. There is no pattern or trend. Studies show no link between how much coffee people drink and their cognitive abilities or memory. The table below summarizes these findings:
| Aspect | Result |
|---|---|
| Global Cognition | No evidence of association |
| Memory | No evidence of association |
| Genetic Variation by Coffee | No variation |
| Non-coffee Drinkers | No association |
FineBI lets you create this scatterplot in seconds. You simply drag the coffee consumption data to one axis and intelligence scores to the other. The random spread of points makes it clear that there is no correlation.
Some people believe taller students perform better on exams. When you use a scatterplot to compare height and exam scores, you see no clear relationship. The points do not form a line or cluster. Research supports this observation:
Scatterplots help you and your students see that not all data pairs show a connection. FineBI’s data visualization tools make it easy to explore these relationships and teach the concept of no correlation scatter plot.
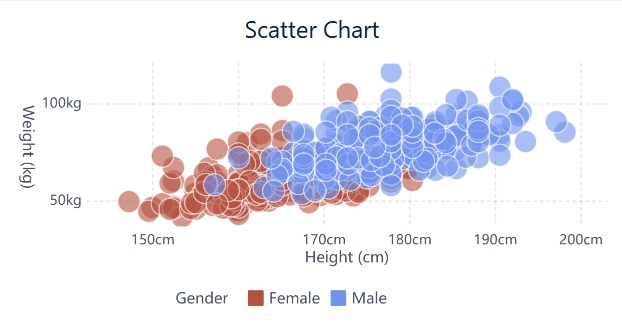
If you plot shoe size against the number of movies watched, you get a classic example of a no correlation scatter plot. The dots appear everywhere with no pattern. Shoe size has nothing to do with movie preferences. This example works well in classrooms or business meetings to show how unrelated variables look on a scatterplot. FineBI’s drag-and-drop dashboard lets you visualize this instantly, helping you spot unrelated data.
You may think owning more pets could affect your weight or fitness. However, when you plot weight against the number of pets owned, the scatterplot shows no pattern. Studies with thousands of participants found no significant link between pet ownership and obesity or fitness. The lack of association holds true for all age groups and types of pets.
FineBI allows you to visualize this data quickly. You can connect your survey results, drag the fields onto a scatterplot, and see the random distribution for yourself.

Tip: Use real-world examples like these in FineBI to help your team or students understand the power of data visualization and the importance of recognizing no correlation.
You can create a scatterplot in FineBI with just a few clicks. Start by connecting your data source. FineBI supports many types of data, including Excel files, databases, and cloud platforms. Once you connect your data, you can select the fields you want to compare. Drag one variable to the X-axis and another to the Y-axis. FineBI instantly generates a scatterplot for you.
The drag-and-drop interface makes the process simple. You do not need to write any code. You can adjust the chart style, add filters, or highlight specific data points. FineBI updates your scatterplot in real time as you make changes. This feature helps you explore different data relationships quickly. If you want to check for a no correlation scatter plot, you can easily swap variables and see how the dots appear.
FineBI also allows you to combine data from multiple sources. You can merge tables, clean your data, and build custom datasets. This flexibility gives you more control over your analysis. You can save your scatterplots and share them with your team for further discussion.
When you look at your scatterplot in FineBI, pay attention to the pattern of the dots. If the points spread out randomly, you see no correlation. This means changes in one variable do not predict changes in the other. Recognizing this helps you avoid misleading interpretations of data relationships.
FineBI’s data visualization tools make it easy to spot these patterns. You can use built-in statistical features to check for correlation values. If you see a lack of correlation, you know that focusing on these variables will not improve your business outcomes. This understanding leads to more informed decisions based on actual data patterns.
FineBI empowers you to explore, visualize, and interpret your data with confidence. You can rely on clear scatterplots to guide your next steps.
You see that not all variables connect. Recognizing no correlation helps you avoid misleading conclusions and encourages you to search for real insights. When you use FineBI, you gain self-service analytics, interactive dashboards, and real-time data analysis. These features let you explore your own data and make smarter decisions.
Understanding scatterplots with no correlation gives you the confidence to focus on what truly matters for your business or studies.
How to Create Good Data Visualization Examples for Beginners
Histogram vs Bar Graph: How They Enhance Data Visualization
Understanding Component Bar Chart in Data Visualization

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles

Top 8 Data Visualization softwares You Should Try in 2025
Compare the top 8 data visualization software for 2025, including FineReport, Tableau, Power BI, and more to find the best fit for your business needs.
Lewis
Dec 19, 2025
10 Must-Have Data Visualization Tools for Modern Businesses
Compare the top 10 data visualization tools for 2025 to boost business insights, streamline analytics, and empower smarter decision-making.
Lewis
Dec 17, 2025

7 Leading Big Data Visualization Tools for the Year Ahead
Compare the top big data visualization tools for 2025 to find advanced analytics, scalability, and interactive dashboards for your business.
Lewis
Dec 17, 2025