A dashboard gives you a real-time visual summary of important information, helping you track and understand data quickly. The dashboard meaning can shift depending on your industry, but its main purpose always remains: to make complex data easy to see and act on. Many organizations rely on dashboards to monitor performance and support decision-making.
Dashboards differ from traditional reports in several ways:
| Feature | Dashboard | Report |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Interactive and visually engaging | Static and often text-heavy |
| Purpose | Quick analysis and real-time decision-making | In-depth analysis and historical data review |
| User Engagement | Higher due to interactivity and updates | Lower, often reviewed offline |
| Data Presentation | Real-time or near real-time data | Data as of a specific point in time |
| Accessibility | Easier for a wider range of users | May require more expertise to interpret |
You will find dashboards essential for making data-driven choices in any professional setting.
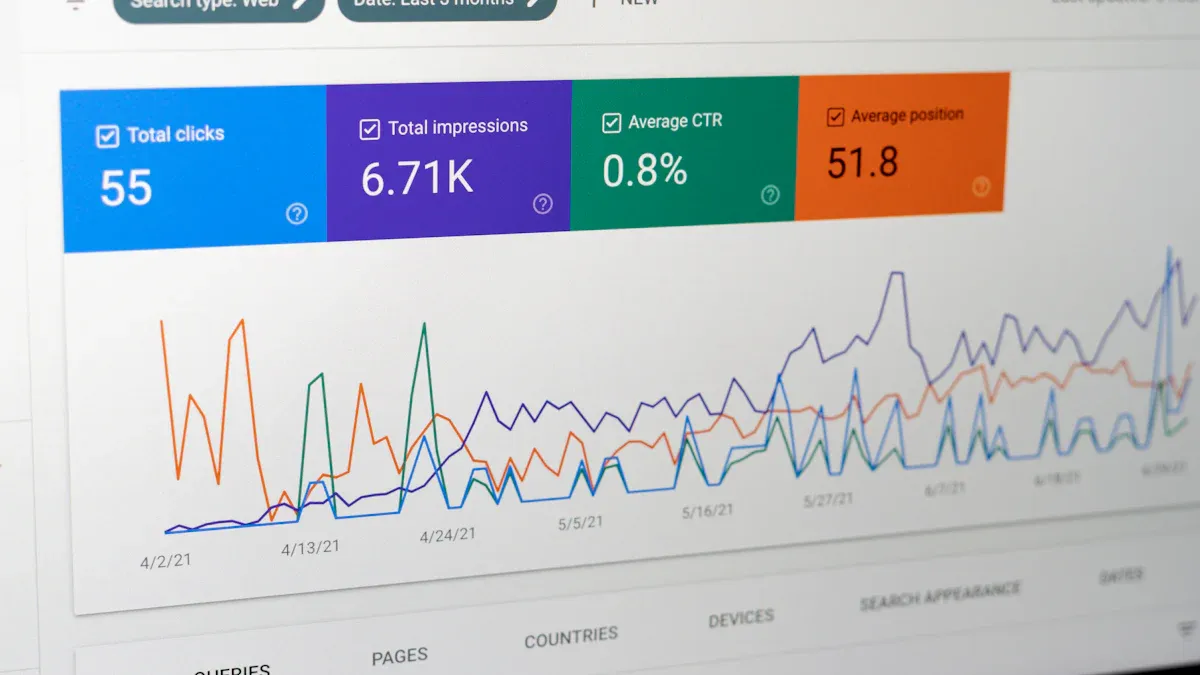
When you ask, "what is a dashboard," you are seeking a clear explanation of a tool that brings together important information in one place. A dashboard is a visual interface that displays key data points, metrics, and trends. You can use a dashboard to see performance at a glance, spot issues early, and make informed decisions. In business intelligence, a dashboard acts as a data visualization tool. It helps you manage information and supports decision-making by showing graphs, charts, and summaries of critical business data.
You will find that a dashboard simplifies complex data. It turns raw numbers into visuals that you can understand quickly. This makes it easier for you to track progress, compare results, and respond to changes. When you use a dashboard, you do not need to search through long reports or spreadsheets. Instead, you get a clear, real-time overview of what matters most.
A dashboard offers several features that make it a powerful tool for data analysis and monitoring. You can see these features in most modern dashboard platforms:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Integrations | Connects with various data sources for comprehensive data visualization. |
| UI Interactivity | Lets you interact with charts and tables for deeper insights, such as drilldown and drill-through. |
| Data Filter Capabilities | Allows you to filter data based on specific criteria for focused analysis. |
| User Roles | Provides different access levels, such as admin, editor, or viewer, to control who sees what data. |
| Advanced Graph Customization | Offers options to customize charts, including conditional formatting and secondary axes. |
| Predictive Analytics | Uses historical data to forecast future outcomes and trends. |
| Tabs | Enables you to organize and track multiple metrics across different tabs within the same dashboard. |
You will notice that dashboards are interactive and flexible. You can filter data, drill down into details, and customize how information appears. These features help you explore data from different angles and make better decisions.
You will encounter several types of dashboards, each designed for a specific purpose. Understanding the types of dashboards helps you choose the right one for your needs.
| Type of Dashboard | Definition and Purpose | Key Features | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operational Dashboard | Monitors and manages daily activities with real-time data. | Real-time monitoring, detailed metrics, alerts | Customer support, manufacturing, logistics |
| Analytical Dashboard | Supports deep data analysis and exploration. | Advanced visualizations, historical data analysis | Marketing, sales, finance |
| Strategic Dashboard | Gives a top-level view of performance against long-term goals. | High-level metrics, goal tracking, trend analysis | Executive management, board meetings |
| Financial Dashboard | Shows financial performance metrics like revenue, expenses, and cash flow. | Financial KPIs, budget tracking, cash flow analysis | Finance departments, accounting |
You can use an operational dashboard to track real-time events and respond quickly. An analytical dashboard helps you dig into data and find patterns or trends. A strategic dashboard lets you see how your organization is performing against its goals. A financial dashboard focuses on money-related data, helping you manage budgets and cash flow.
After you understand what is a dashboard and the types of dashboards available, you can look for platforms that make dashboard creation easy. FineBI is one example of a modern dashboard platform. It supports self-service analysis, seamless integration with many data sources, and a user-friendly drag-and-drop interface. With FineBI, you can build dashboards that fit your business needs without needing advanced technical skills.
A dashboard is different from a report. While a report often presents static, detailed information, a dashboard gives you a dynamic, interactive view of your data. You can use a dashboard for quick analysis and real-time decision-making, while reports are better for in-depth reviews and historical analysis.
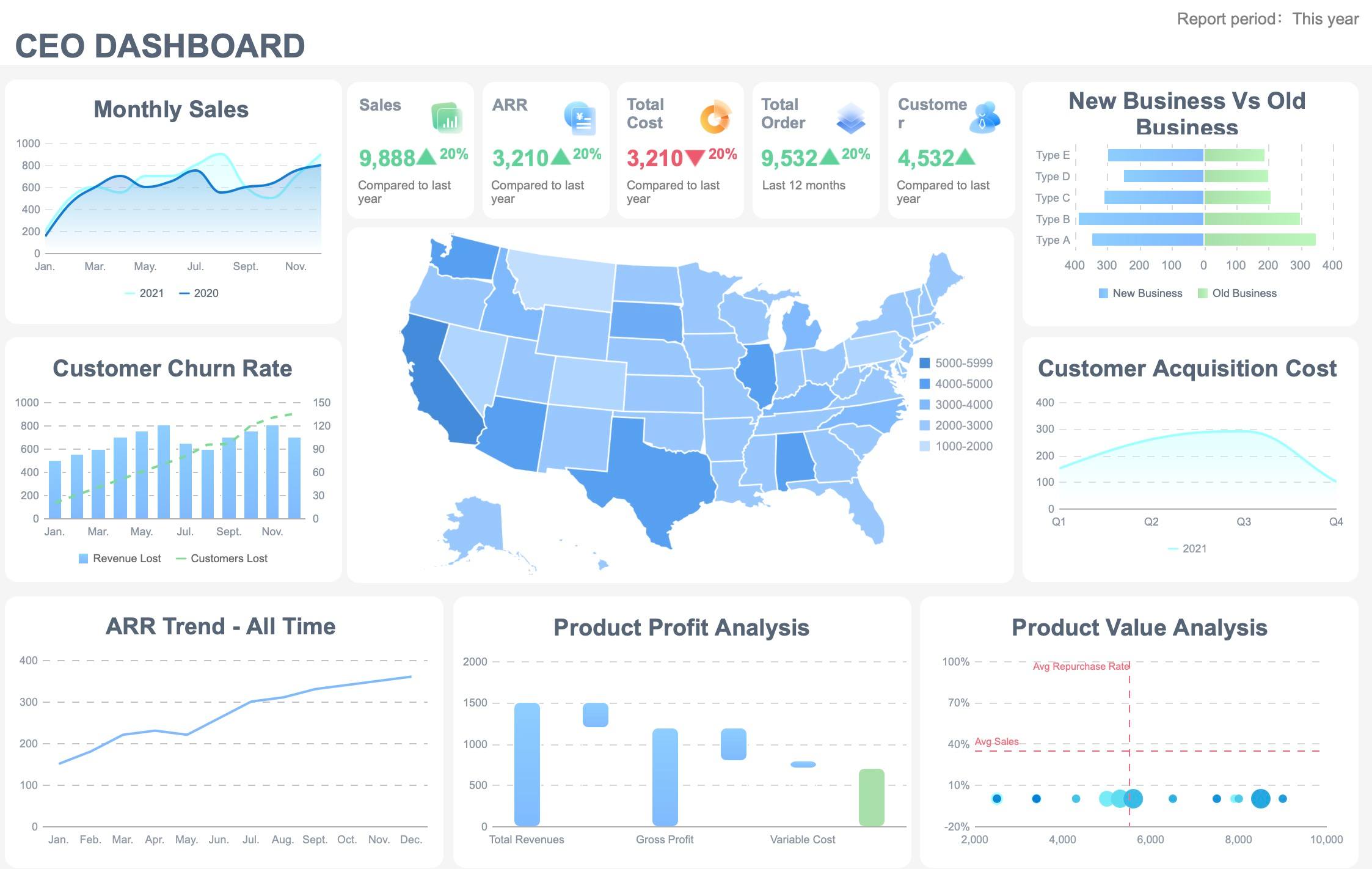

You will see that the dashboard meaning changes depending on your field. Each industry uses dashboards to solve unique problems and highlight specific data. A dashboard always brings together important information, but the type of data and the way you use it can look very different from one industry to another. Understanding how dashboards work in your industry helps you get the most value from your analytics.
In business and analytics, the dashboard meaning centers on giving you a clear, real-time view of your organization’s performance. You use dashboards to track key performance indicators (KPIs), monitor trends, and make fast decisions. A dashboard in this context often displays sales numbers, marketing campaign results, or customer satisfaction scores. You can spot problems early and act before they grow.
| Benefit of Dashboards | Description |
|---|---|
| Real-time insights | Dashboards provide immediate access to data, allowing for timely decision-making. |
| Automation of data analysis | They reduce the time spent on data preparation, enabling teams to focus on analysis instead. |
| Enhanced communication | Dashboards facilitate better sharing of information, improving collaboration in decision-making. |
| Focus on KPIs | They help organizations track important metrics that drive performance and strategy. |
| Identification of issues | Dashboards allow for early detection of problems and opportunities for growth. |
| Support for fact-based culture | They promote data-driven decision-making across the organization. |
| Reduction in debate time | Dashboards streamline discussions by providing clear data, allowing for quicker decisions. |
You will find that dashboards in analytics help you identify problems before they escalate and spot new opportunities. You can quickly test ideas with real data and foster a fact-based culture. Teams spend less time debating and more time acting.
FineBI plays a key role in this area. You can use FineBI to build self-service dashboards that give you real-time analytics and insights. FineBI lets you connect to many data sources, drag and drop charts, and share dashboards with your team. This makes it easier for everyone to see the same data and collaborate on decisions. With FineBI, you improve decision-making, monitor performance in real time, and increase visibility across your business.
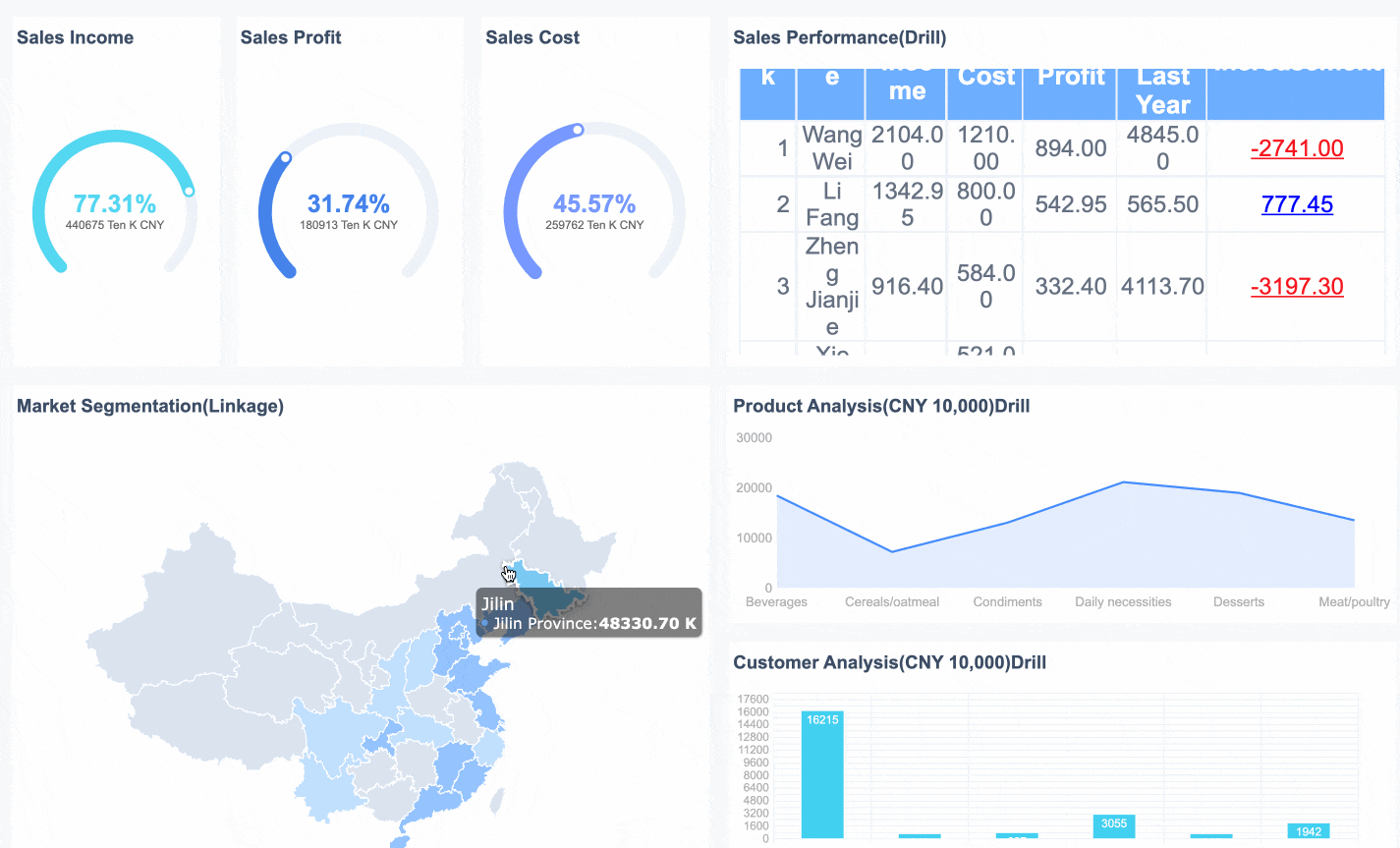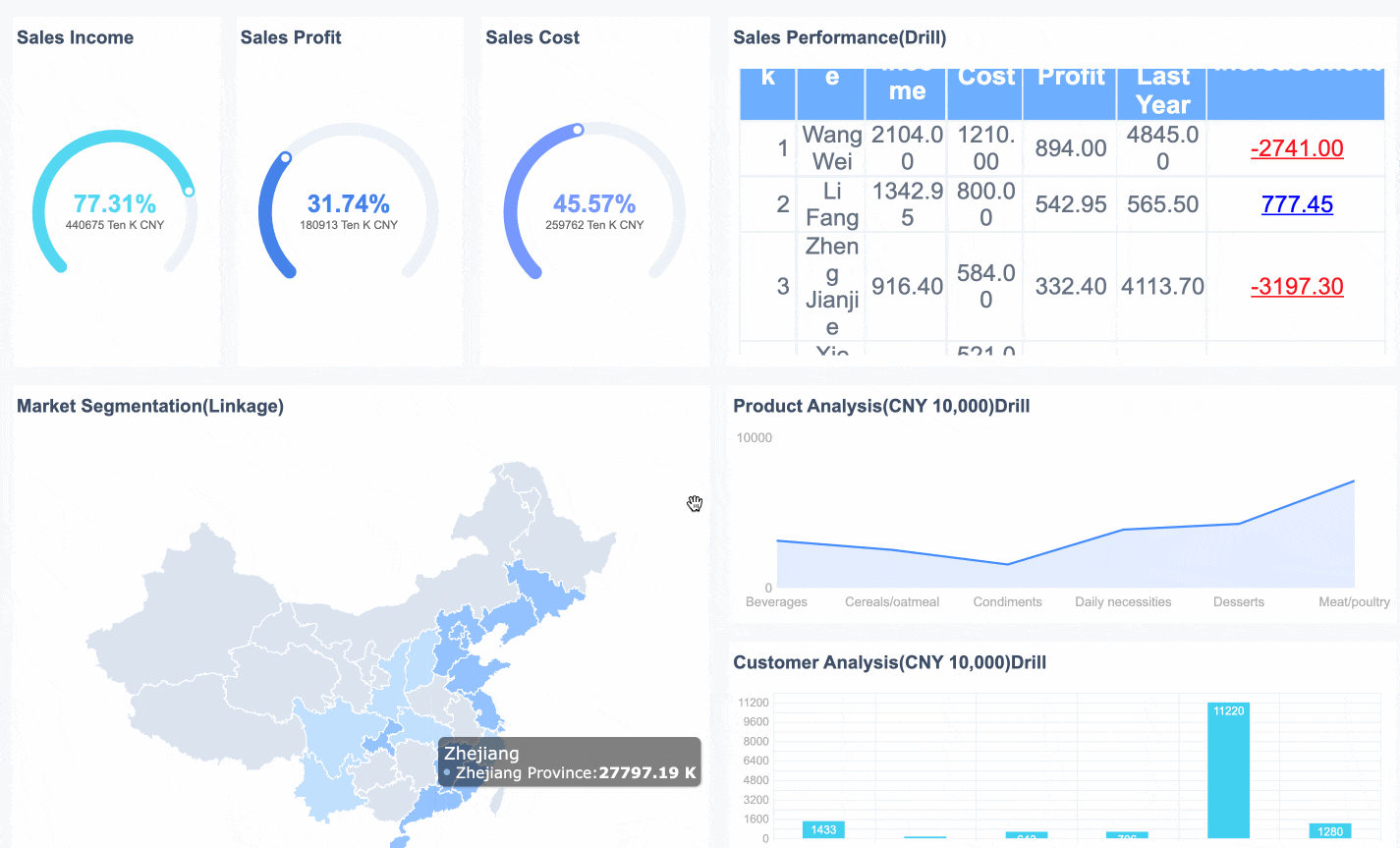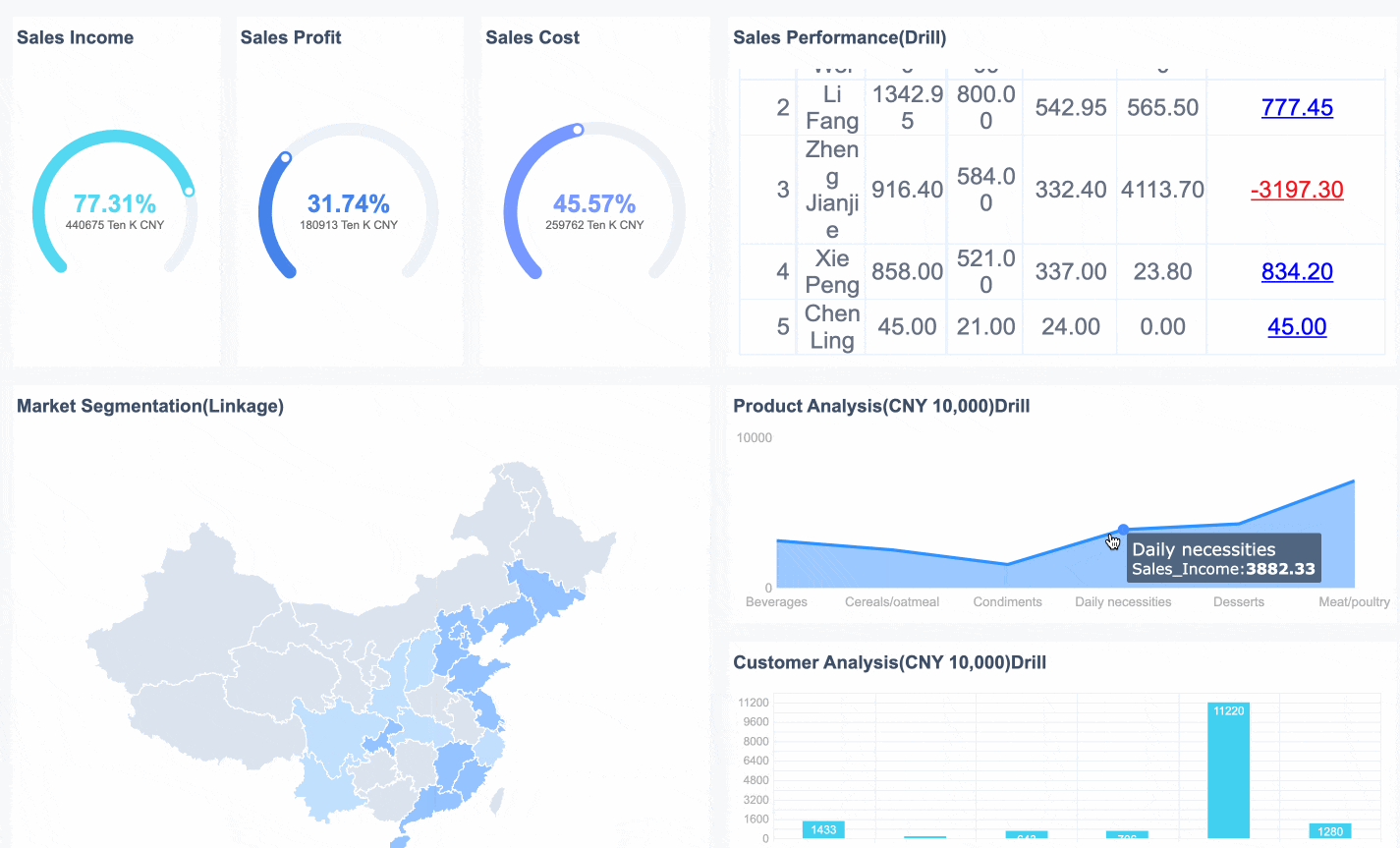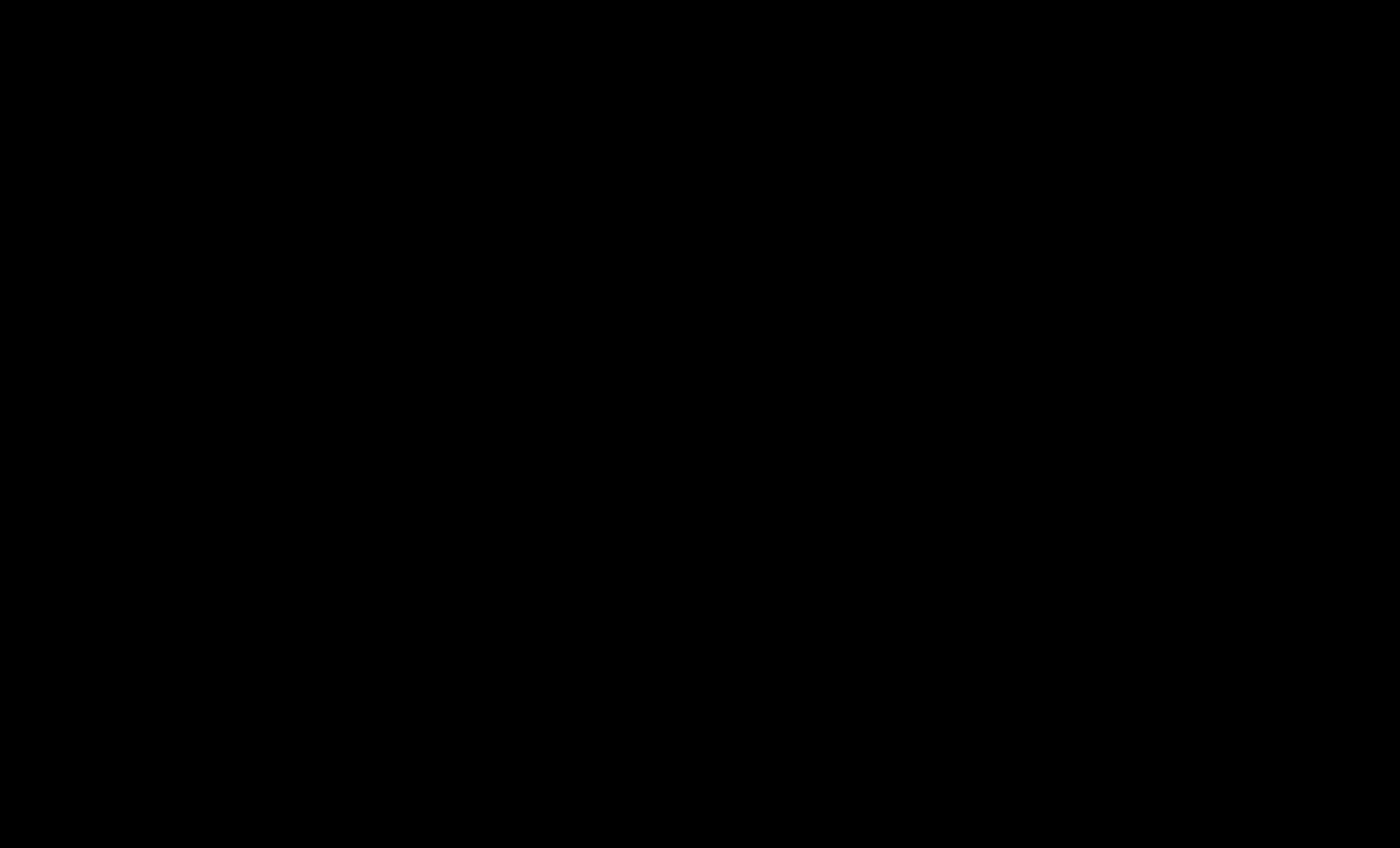
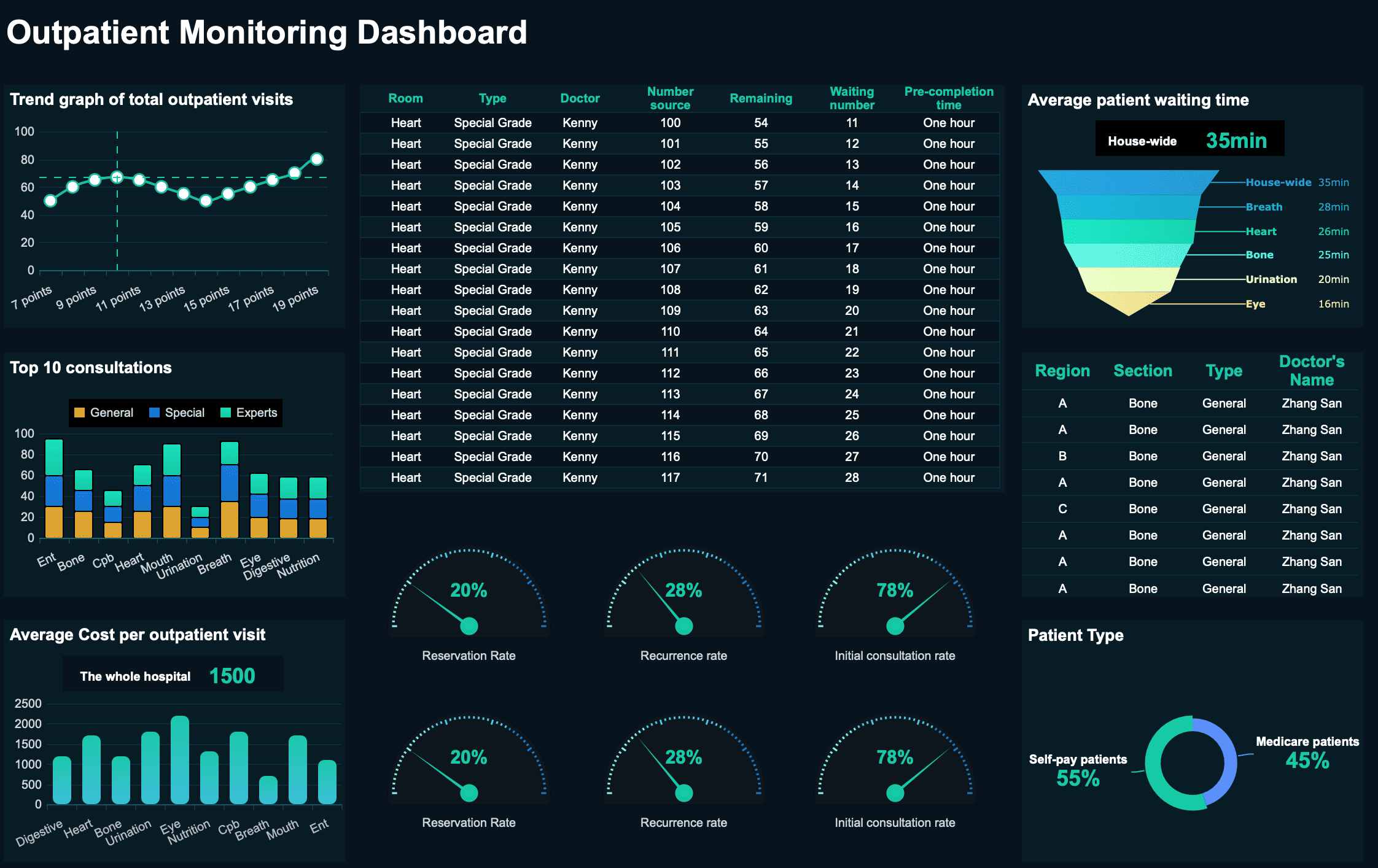
In healthcare, the dashboard meaning focuses on improving patient care and operational efficiency. You use dashboards to track clinical outcomes, monitor hospital resources, and manage finances. A dashboard can show you infection rates, patient wait times, or the status of medical equipment.
| Dashboard Type | Primary Uses |
|---|---|
| Clinical | Offers a comprehensive view of treatment outcomes, infection monitoring, and patient data. |
| Operational | Tracks hospital efficiency, resource utilization, and wait times. |
| Financial | Provides insights into the financial health of organizations, monitoring costs and revenue cycles. |
Dashboards help you see trends in patient care and spot areas that need attention. For example, after implementing dashboards, hospitals have seen improvements in key outcomes:
| Outcome | Before Implementation | After Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| NEWS2 recording | 64% | 83% |
| Referral completion (n) | 170 | 6800 |
| Assessment completion (n) | 23 | 540 |
You can use dashboards to make faster decisions, improve patient safety, and manage resources more effectively.
In education, the dashboard meaning is about tracking student performance and school operations. You use dashboards to see academic achievement, attendance, and engagement. A dashboard can help you identify students who need extra support or spot trends in test scores.
You can use dashboards to improve teaching strategies, allocate resources, and ensure students stay on track.
In IT and software, the dashboard meaning relates to project management and system monitoring. You use dashboards to track project progress, manage resources, and monitor system health. A dashboard can show you which tasks are on schedule, which systems need attention, and where risks might appear.
You benefit from improved visibility into project progress, better alignment across teams, and faster decision-making. Dashboards also help you track costs and schedules, making sure projects stay on target.
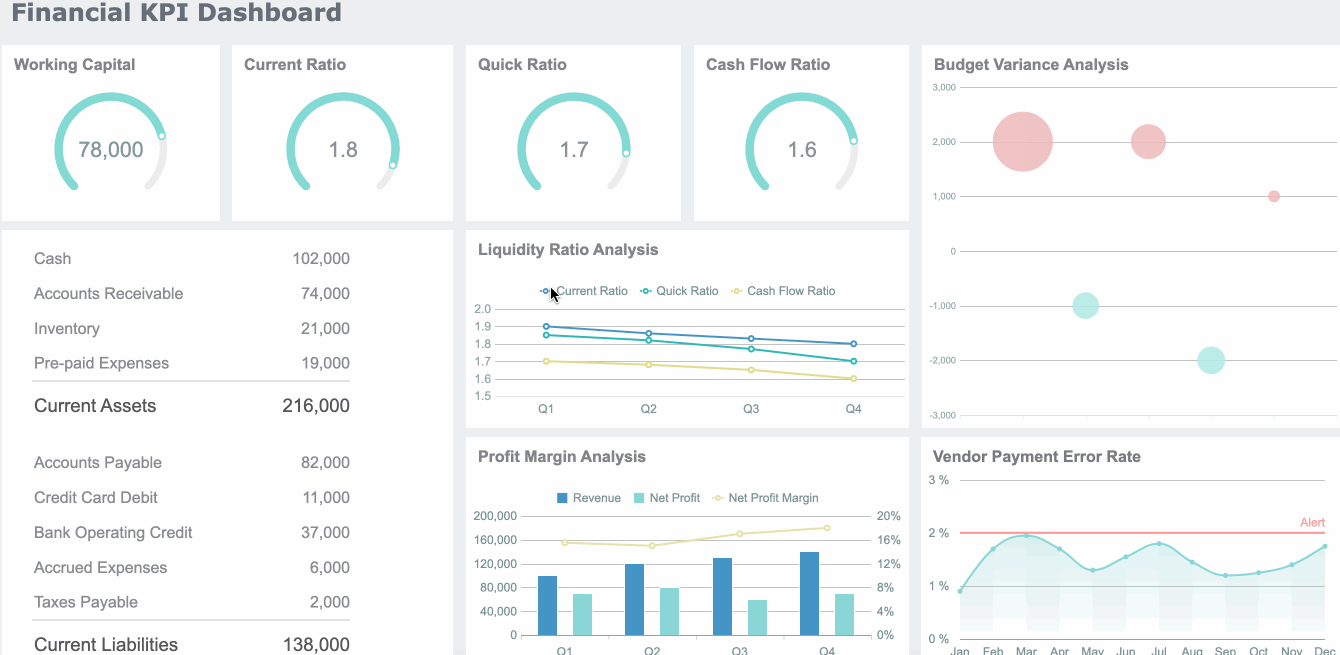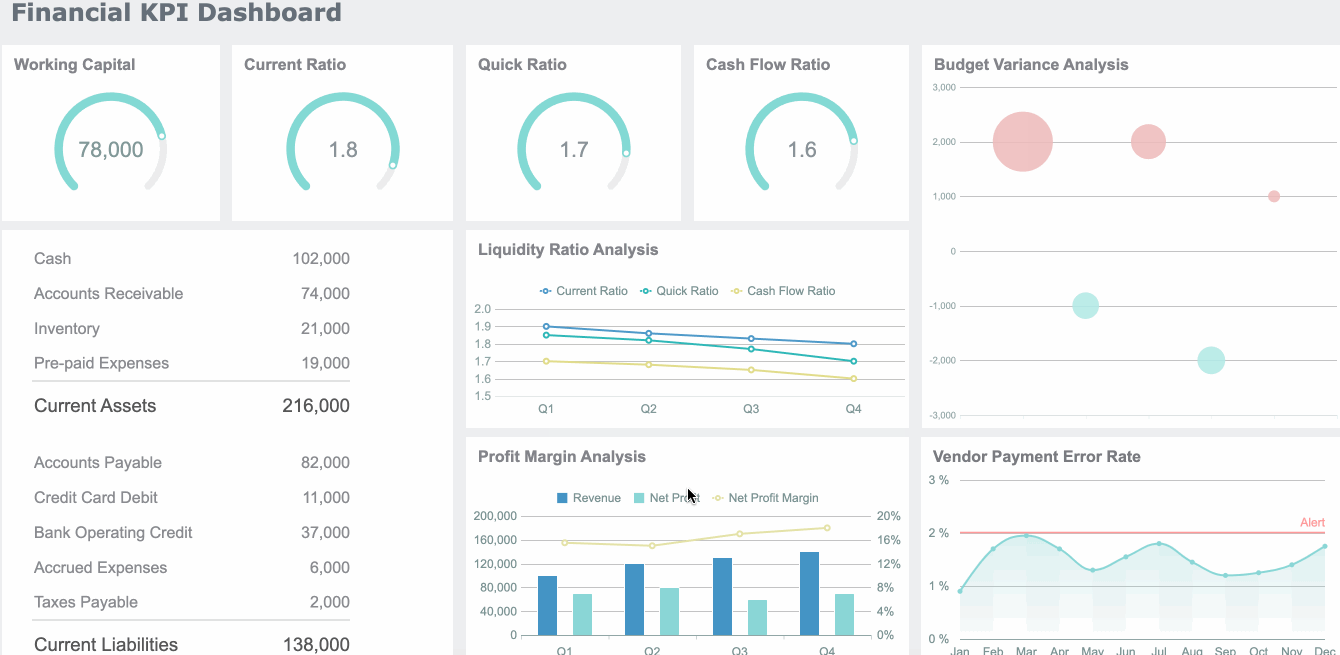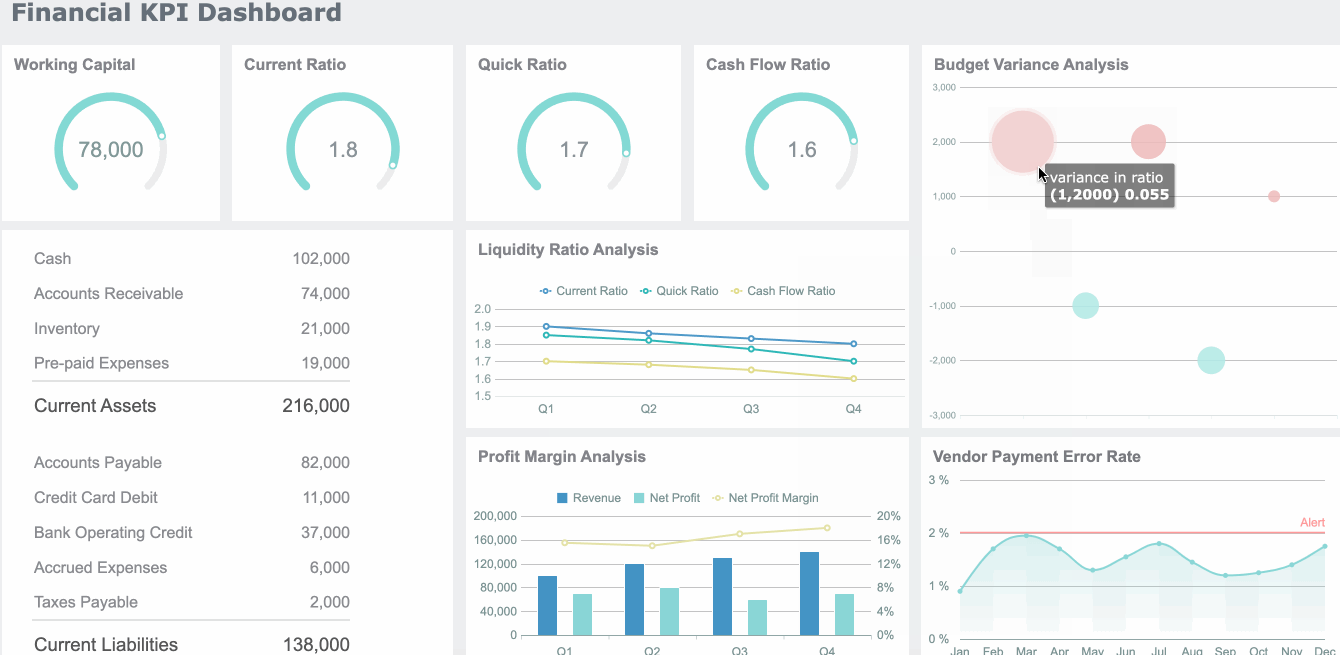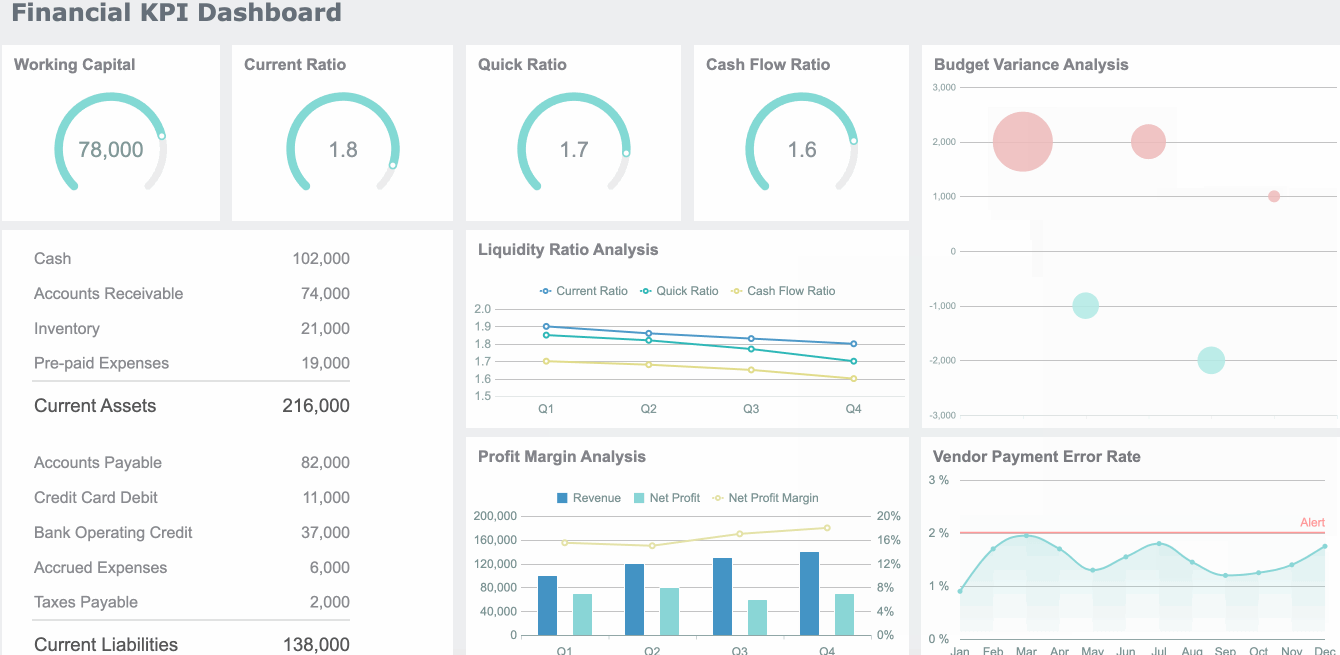
In finance, the dashboard meaning centers on risk management, compliance, and performance tracking. You use dashboards to monitor financial KPIs, detect anomalies, and ensure regulatory compliance. A dashboard can display revenue, expenses, cash flow, and risk alerts.
| Benefit Description | Quantitative Impact |
|---|---|
| Cost reductions through enhanced visibility | Up to 15% within the first year |
| Reduction in budget variance | 20% |
| Improvement in key performance indicators (KPIs) | Aim for 10% improvement within the first year |
You can use dashboards to identify profitable segments, allocate resources strategically, and make data-driven pricing decisions.
In supply chain and logistics, the dashboard meaning is about improving operational efficiency and visibility. You use dashboards to integrate data from shipping, inventory, and procurement. A real-time dashboard gives you a holistic view of your supply chain, helping you make better decisions.
For example, Kintetsu World Express used dashboards to integrate customer and logistics data. Their real-time dashboards improved information management and operational efficiency. Sales teams gained access to comprehensive customer data, which led to better decision-making and streamlined operations.
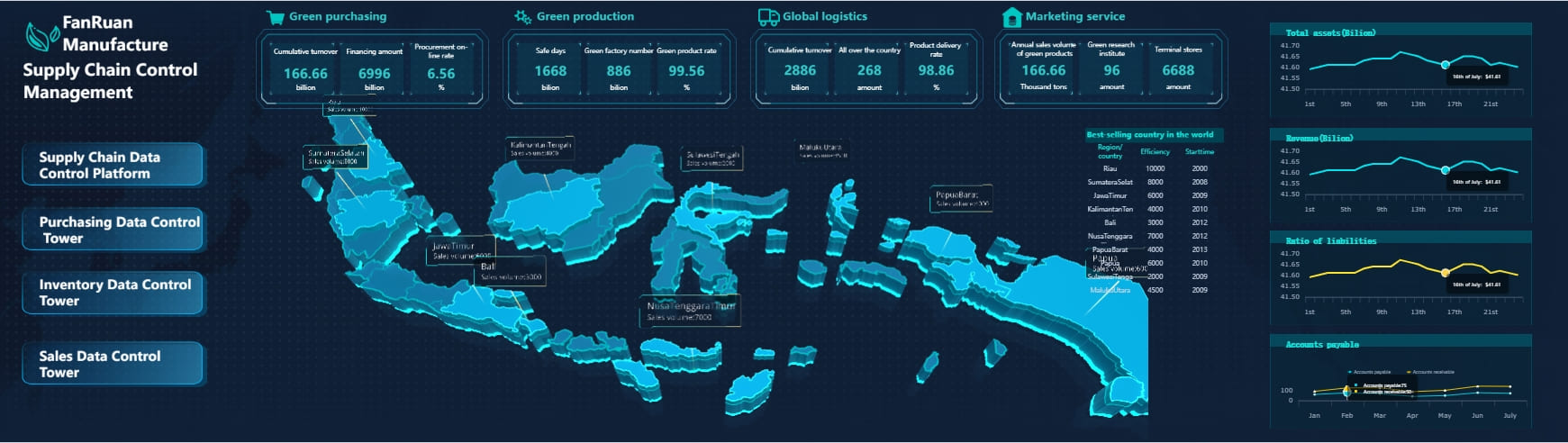
In manufacturing, the dashboard meaning focuses on quality control and process optimization. You use dashboards to monitor production efficiency, track defects, and manage equipment health. A dashboard can display metrics like overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), defect rates, and machine utilization.
| Metric/KPI | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) | Measures production efficiency by evaluating availability, performance, and quality. |
| Number of Units Produced per Hour | Indicates output levels and helps identify bottlenecks. |
| Downtime Metrics | Highlights disruptions and maintenance needs by tracking stoppages. |
| Defective Rate | Measures product quality by tracking the percentage of faulty units. |
| Machine Utilization | Assesses how effectively equipment is being used to optimize resources. |
| Defects per Million Opportunities (DPMO) | Measures overall defect rates and identifies trends in production quality. |
| Customer Complaint Rate | Provides insights into product issues reported by end users. |
| Quality Achievement Rate (%) | Tracks the percentage of products meeting quality standards, ensuring compliance. |
You can use dashboards to see total production, current defect rates, and cycle times. Visual tools help you analyze trends and costs, and identify defects by category. Predictive maintenance dashboards can cut downtime by up to 50% and reduce maintenance costs by up to 40%. AI-powered dashboards improve defect detection and help you coordinate repairs, leading to higher quality and efficiency.
FineReport offers a quality control solution for manufacturing. You can use dashboards to monitor qualification rates, defect rates, and scrap rates. These dashboards help you identify root causes of defects and optimize production processes. By using dashboards, you maintain high quality standards and reduce costs.
In every industry, the dashboard meaning adapts to your needs. You use dashboards to turn complex data into clear, actionable insights. This helps you make better decisions, improve performance, and achieve your goals.
A dashboard brings together the most important information you need to monitor and manage your business. When you look at the core components of a modern dashboard, you see how each part works together to turn raw data into clear, actionable insights. The dashboard gives you a single place to view key metrics, track progress, and make decisions based on real-time information.
Visual elements form the foundation of every dashboard. You use charts, tables, and graphs to turn complex data into visuals you can understand at a glance. The most effective dashboards position the most important metrics at the top or in larger fonts. You often see color and size contrast to highlight essential information. Logical arrangement puts primary metrics front and center. Common visual tools include:
Consistent color coding and layout templates help you quickly interpret the dashboard. FineBI's drag-and-drop interface lets you build these visual elements easily, making it simple to customize your dashboard for any need.
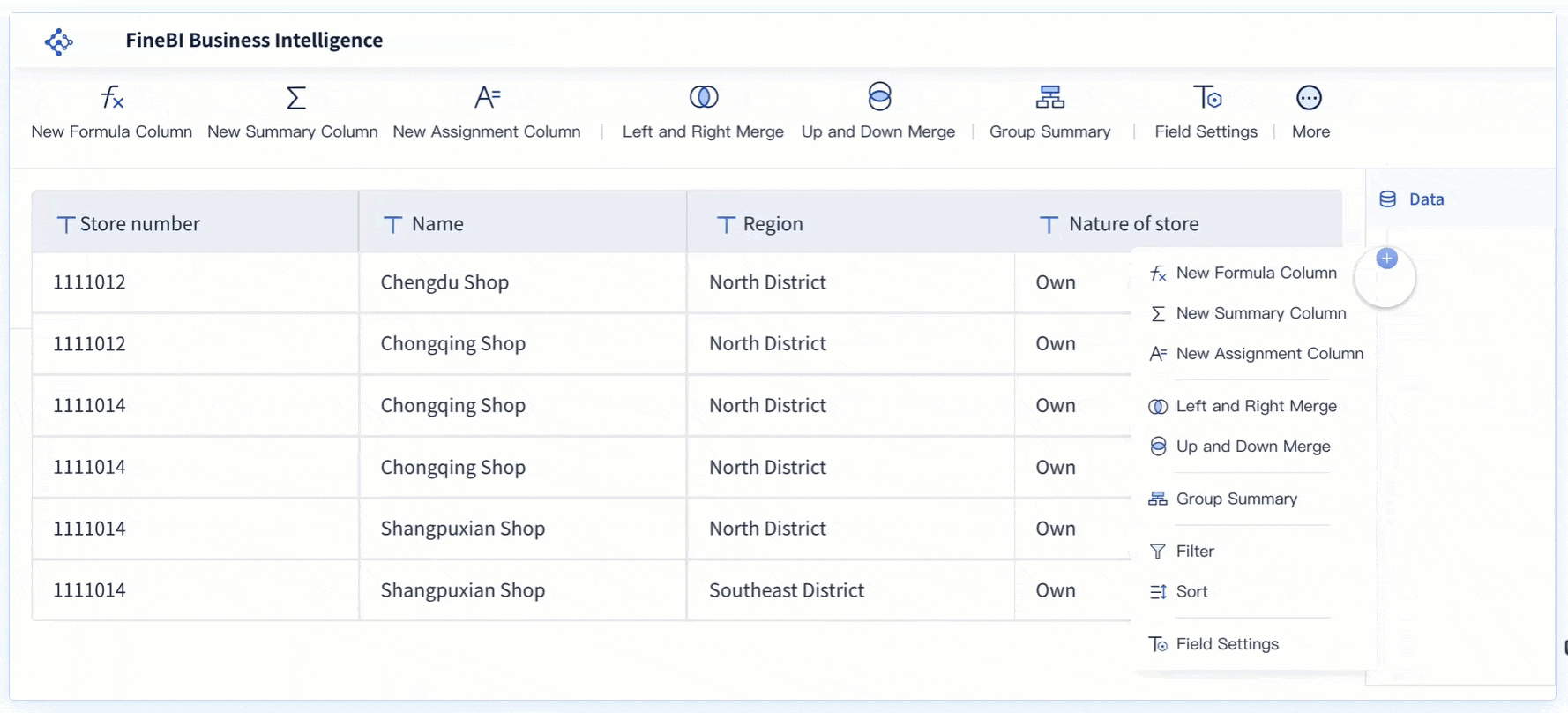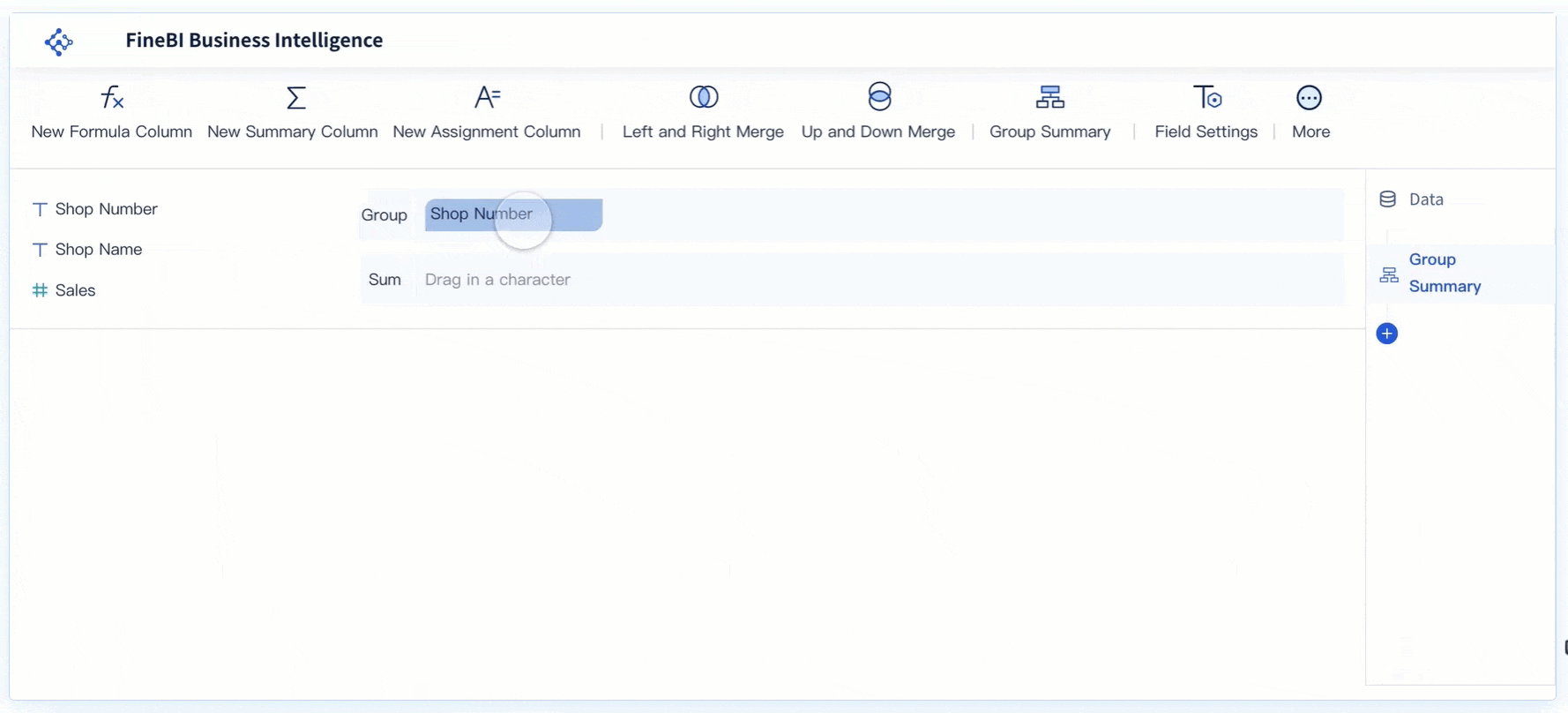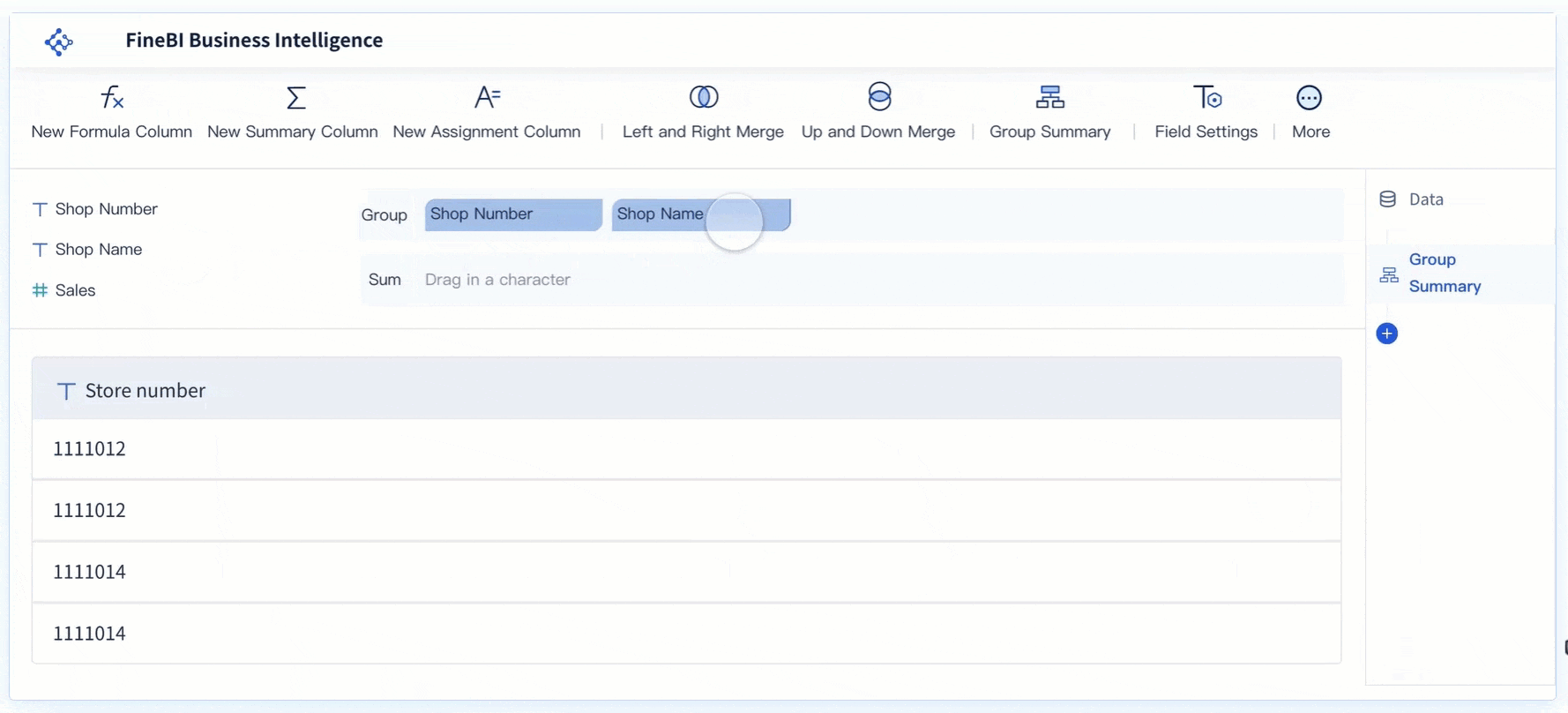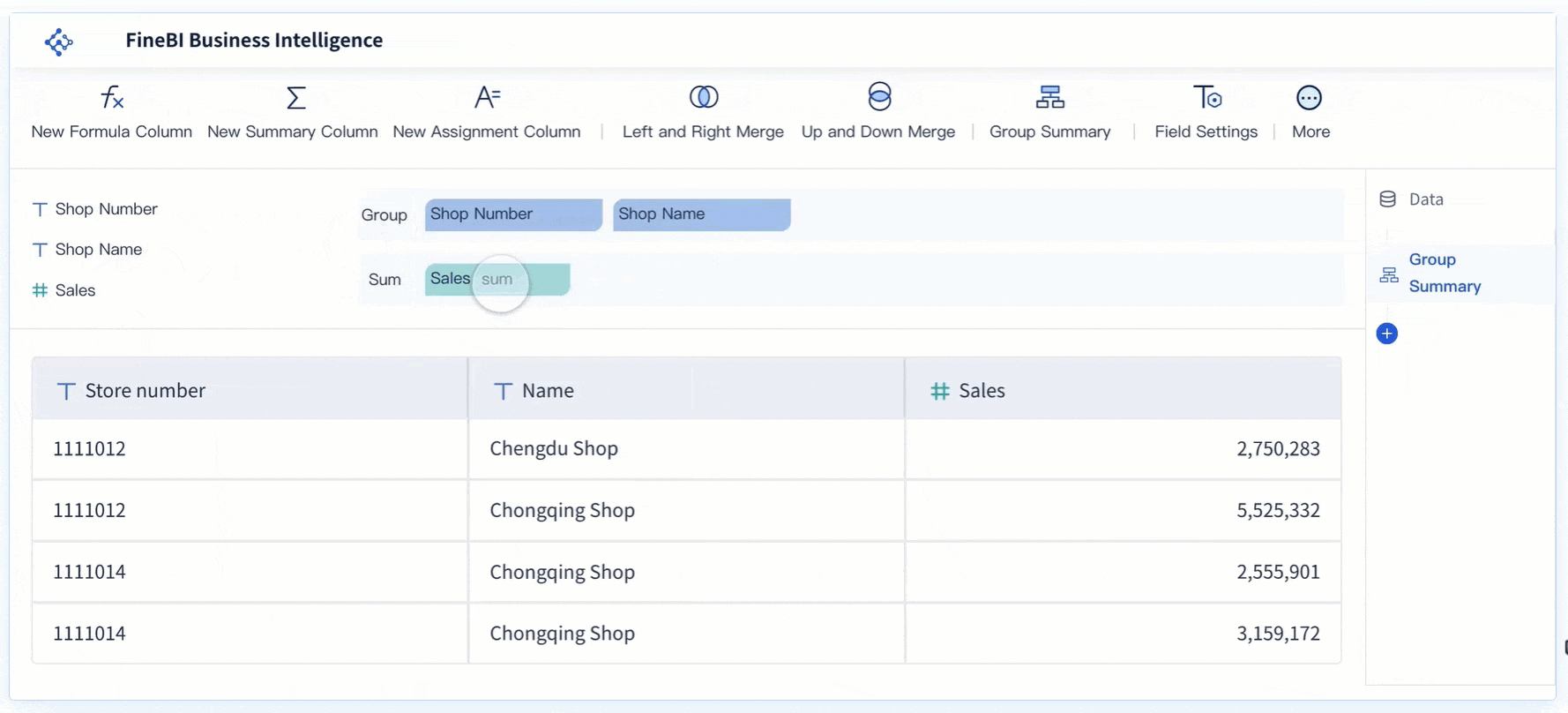
Metrics and KPIs are the heart of any dashboard. You track sales, production output, customer engagement, or financial performance depending on your goals. The core components of a modern dashboard always include a focused set of metrics that matter most to your business. For example, a sales dashboard might show total revenue, conversion rates, and average deal size. A manufacturing dashboard could display overall equipment effectiveness, defect rates, and machine downtime. Real-time dashboards update these metrics instantly, giving you live visibility into your operations. Tracking the right metrics helps you measure progress, uncover opportunities, and improve accountability.
| Dashboard Type | Key Metrics Tracked |
|---|---|
| Sales Dashboard | Total sales revenue, Conversion rates, Average deal size, Client engagement, Sales cycle length |
| Manufacturing Dashboard | Overall Equipment Effectiveness, Production output, Defect rates, Machine downtime |
| Financial Dashboard | Profit margins, Cash flow projections, Operational expenses, Budget variance, ROI |
Interactivity sets a modern dashboard apart from static reports. You can filter data, drill down into specific metrics, and explore trends in real-time. Filters let you narrow your view to a specific time period or business unit. Drill-down options allow you to click on a metric and see more detail. Tooltips provide extra context when you hover over a data point. Customization is a key feature—each user can select the data and visualizations that fit their needs. FineBI supports real-time filtering and dynamic exploration, making it easy for you to adapt the dashboard as your business changes. The core components of a modern dashboard must include these interactive features to help you make smarter, faster decisions.
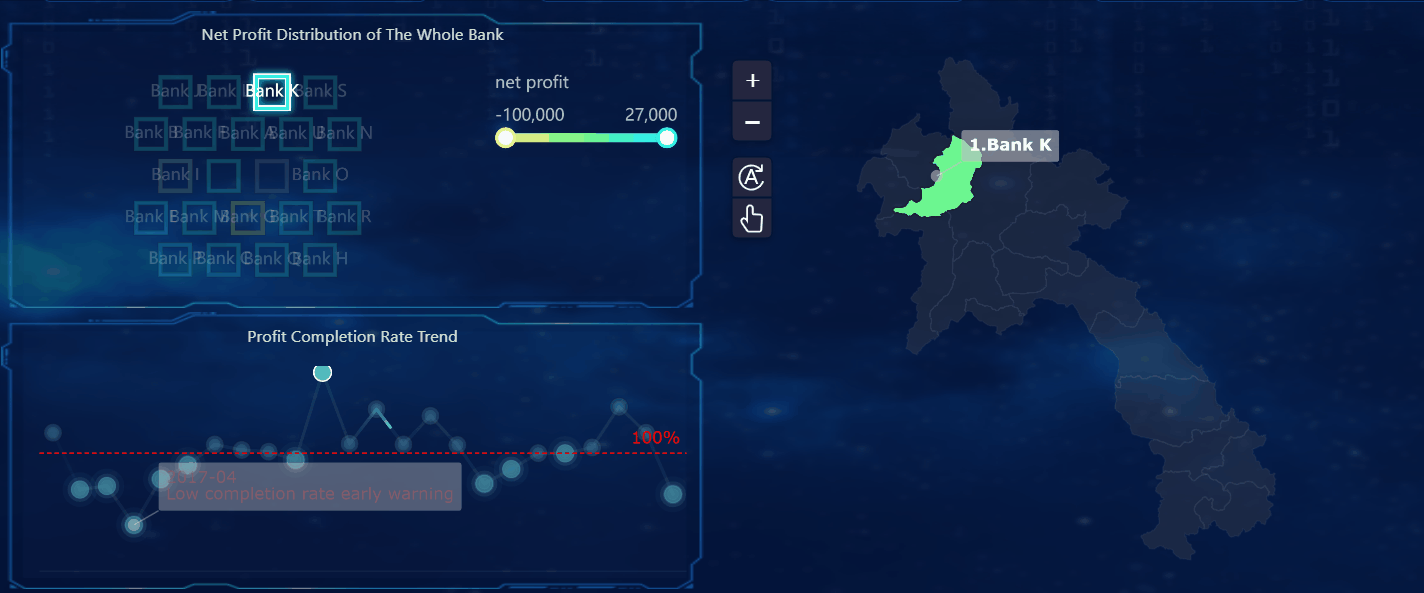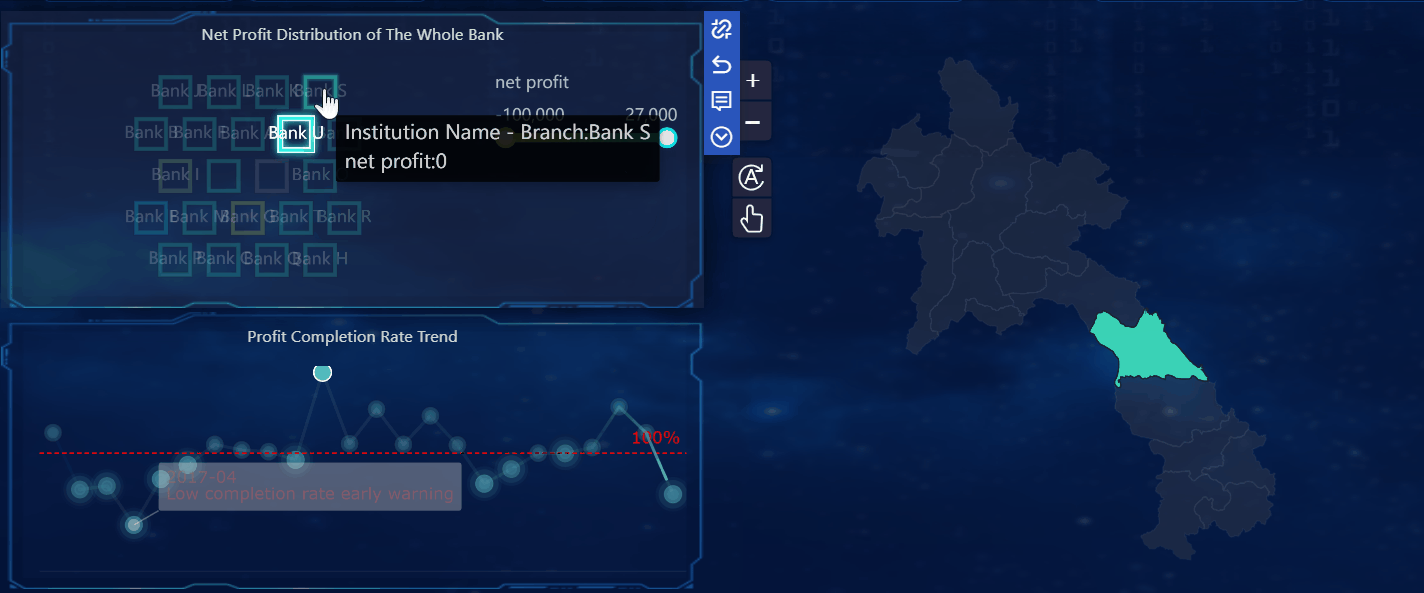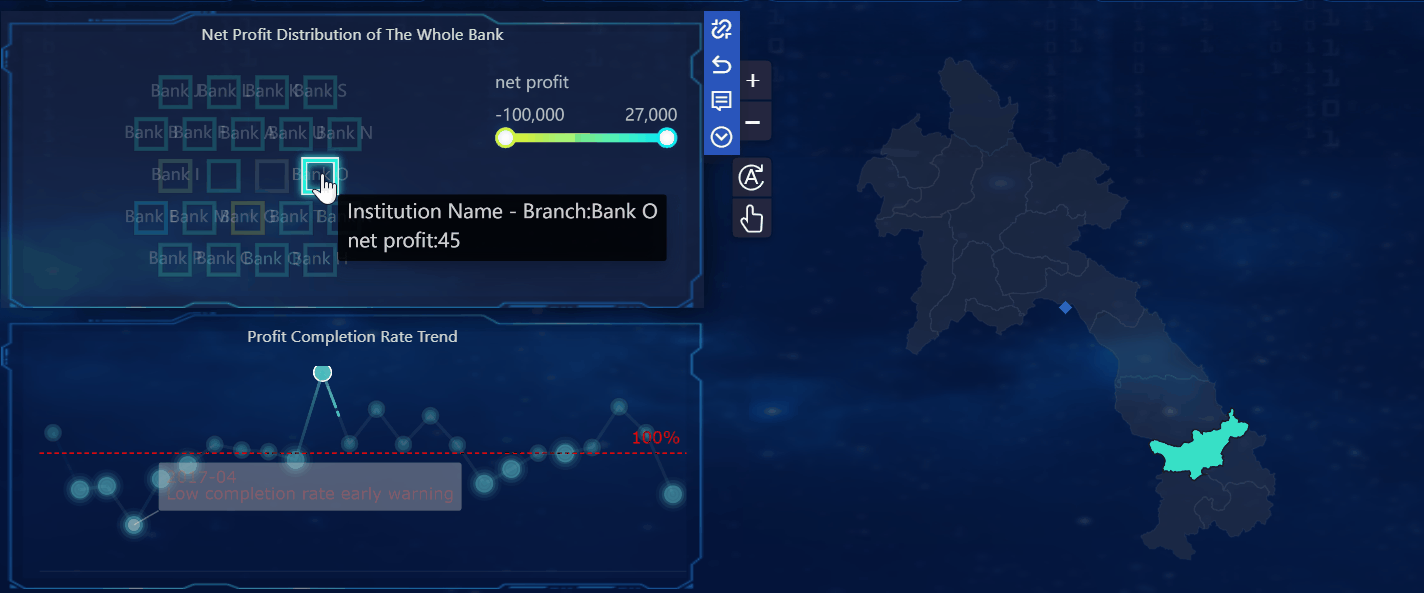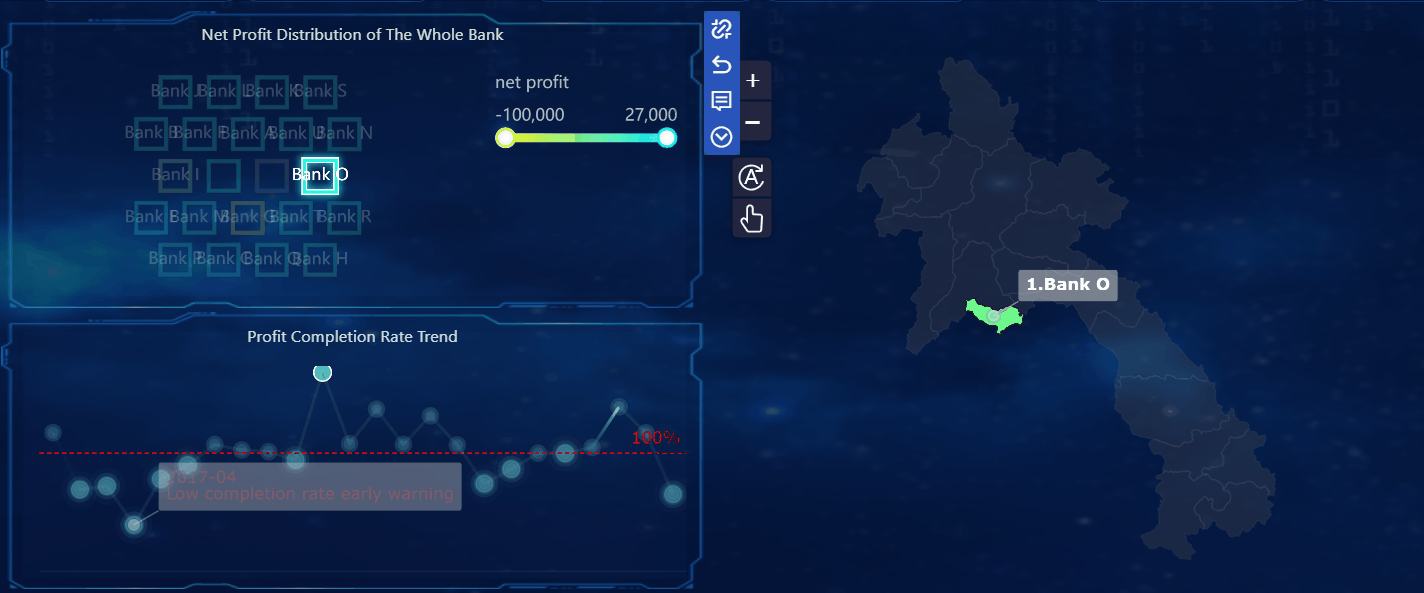
When you compare a dashboard to a report, you see that each serves a unique purpose in how you view and use data. A dashboard gives you a real-time, interactive overview of your most important data. You can filter, explore, and adjust the dashboard to see the latest information as it happens. This means you always have access to up-to-date data, which helps you respond quickly to changes.
A report, on the other hand, presents data as it was at a specific point in time. Reports are usually static and do not allow you to interact with the data or make real-time changes. You use reports to review historical data, analyze trends, and share detailed findings with others.
Here is a quick comparison:
| Feature | Dashboard | Report |
|---|---|---|
| Interactivity | Filter and modify data instantly | Static, no real-time modifications |
| Data Refresh | Real-time updates possible | Manual or scheduled refresh |
| Data Presentation | Up-to-the-minute data | Data as of a specific moment |
A dashboard allows you to apply filters and drill down into specific data points. Reports give you a fixed view of data, which is useful for audits or compliance.
You should use a dashboard when you need real-time insights and want to monitor data as it changes. Dashboards work best for continuous progress tracking, proactive issue detection, and real-time collaboration. For example, you can use a dashboard to watch sales numbers, track website traffic, or monitor production lines as events unfold.
Reports are better when you need to analyze historical data or share detailed findings. You might use a report for executive summaries, client updates, or interdepartmental communication. Reports help you review past performance and make long-term plans.
FineBI supports both dashboards and reports. You can create interactive dashboards for real-time data analysis and also generate detailed reports for deeper reviews. FineBI emphasizes self-service and agility, so you can build the dashboard or report you need without waiting for IT support. This flexibility helps you stay informed and make better decisions with your data.
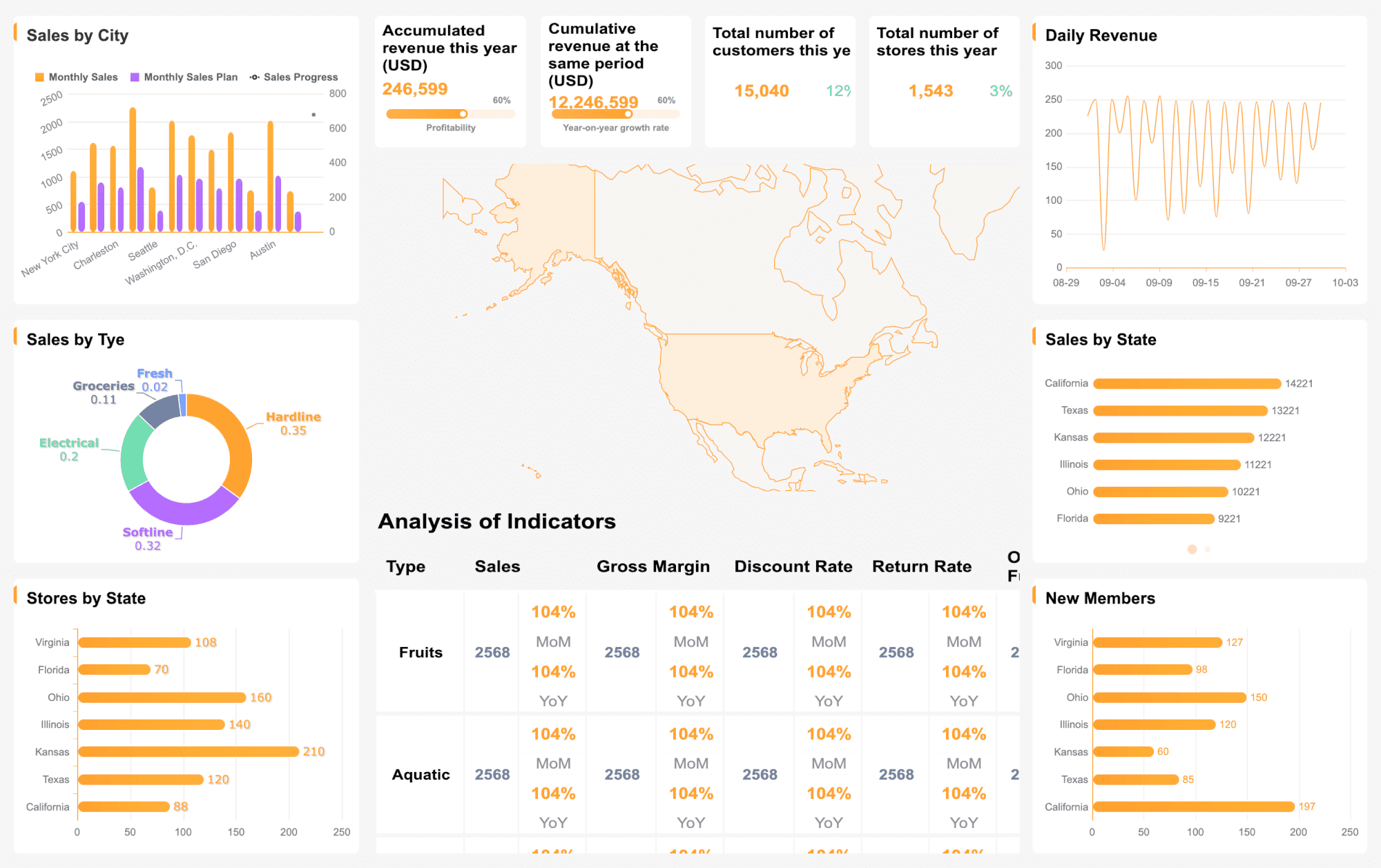
You have seen how the dashboard meaning shifts across industries, but its core value stays the same. Dashboards help you make data-driven decisions by consolidating data from different sources and providing real-time, actionable insights. You can use dashboards to improve efficiency, support strategic planning, and optimize resources.
How to Quickly Build a Core App Dashboard
Store Performance Dashboard: Your Retail Command Center
Dynamic Dashboard: A Game Changer for Data Analysis
Master the Square Dashboard in Easy Steps
How to Design a Client Dashboard That Delivers Results
Draft Dashboard Review - Is It the Ultimate DFS Tool?
Mastering the Twitch Dashboard for Streamer Success
Using the Blooket Dashboard to Boost Student Engagement
Mastering the Unity Cloud Dashboard for Effective Use
How to Access the Clover Dashboard Easily
How to Access the Chrysler Employee Portal Easily
Covers Dashboard: Find Your Perfect Match

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles
What Is a Lead Generation Dashboard and How Does It Work
A lead generation dashboard tracks, analyzes, and visualizes lead data, helping teams optimize marketing and sales efforts for better conversion rates.
Lewis
Feb 05, 2026
15 Top Modern Dashboard Design Templates for 2026
See 15 top modern dashboard design templates for 2026 with clean UI, advanced features, and flexible layouts to streamline your business data insights.
Lewis
Feb 05, 2026

Top 10 Client Dashboard Software for Agencies in 2026
Compare the top client dashboard software for agencies in 2026 to find the best tools for reporting, integration, customization, and client management.
Lewis
Feb 05, 2026