Actual cost in accounting means the real amount you pay for an item, service, or activity. This cost includes everything spent, such as materials, labor, and overhead, as described in PwC’s Inventory Guide and supported by accounting standards like ASC 330. You need to know your actual cost to track business performance and make smart financial decisions. In today’s data-driven world, tools like FineBI from FanRuan help you capture and analyze actual cost quickly, giving you a clear view of your expenses.

When you look at actual cost in accounting, you see the real amount your business spends to make a product or deliver a service. This includes every dollar paid for materials, wages for workers, and overhead like utilities or rent. You do not rely on guesses or averages. Instead, you track the exact money that leaves your accounts.
Actual cost stands apart from other cost concepts in cost accounting. Standard cost uses a set amount based on past data or engineering estimates. Estimated cost projects what you might spend before you start production. With actual cost, you always use real numbers from your financial records. This approach gives you a clear picture of the true costs of production. You can see exactly what you paid, not just what you expected to pay.
You use actual costing to record the real expenses for each item or job. This method works well when you need to know the precise cost for contracts, custom orders, or when prices change often. In a work-order-driven environment, actual cost captures the real material and labor used, giving you immediate insight into your spending.
The main components of actual cost include:
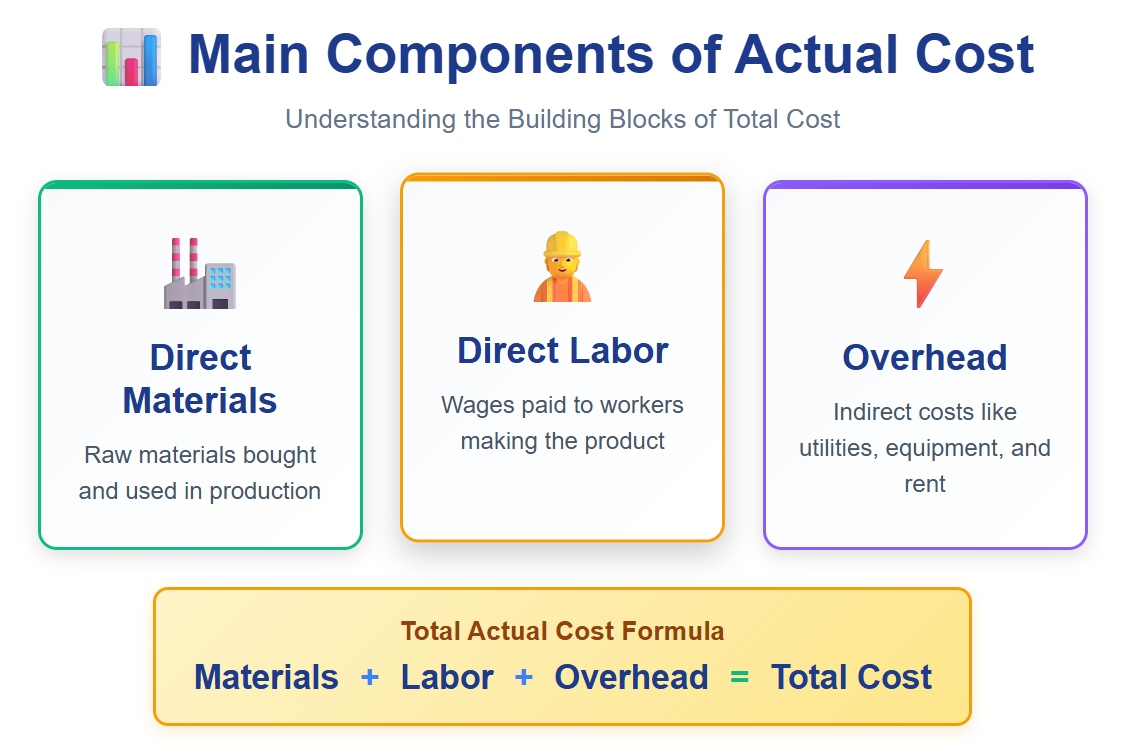
Actual cost covers both direct and indirect expenses. You add up all these amounts to find the total cost for each product or service.
Tip: Actual cost relies on historical, measurable transactions. You always base your numbers on what you actually spent, not on estimates.
Actual costing has several features that make it unique in cost accounting. You benefit from these features when you want accuracy and up-to-date information.
Here is a table that shows how actual costing compares to normal costing:
| Feature | Actual Costing | Normal Costing |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Costs determined after production is complete | Costs estimated and applied during production |
| Overhead Costs | Uses actual overhead costs | Uses estimated overhead rate |
| Precision | More accurate, based on actual expenditures | Less precise, based on estimates |
Actual costing gives you a detailed and accurate view of your business expenses. You can use this information to track performance, control costs, and improve your financial results. However, you need to collect and manage a lot of data, which can take more time and effort.
Note: Actual cost systems work best when you need to track costs closely and respond to changes quickly. They help you avoid surprises and keep your business on track.
You need to understand the difference between actual cost and budgeted cost to manage your finances well. Here is a clear breakdown:
Here is a table to help you compare:
| Aspect | Budgeted Cost | Actual Cost |
|---|---|---|
| When Calculated | Before operations | After operations |
| Based On | Estimates, forecasts, and past data | Real transactions and receipts |
| Purpose | Planning and resource allocation | Measuring real performance |
| Impact | Sets targets and expectations | Shows true spending and efficiency |
| Adjustments | Can change in future budgets | Cannot change; reflects what happened |
You gain many benefits when you track both actual costs and budgeted costs. Here are some reasons why this matters in accounting and cost accounting:
Tip: Using technology for real-time tracking and variance analysis makes it easier to manage costs and improve your financial results.
You need a clear process to calculate actual costing in your business. This helps you track every dollar you spend and understand your total actual cost. Here is a step-by-step outline you can follow:
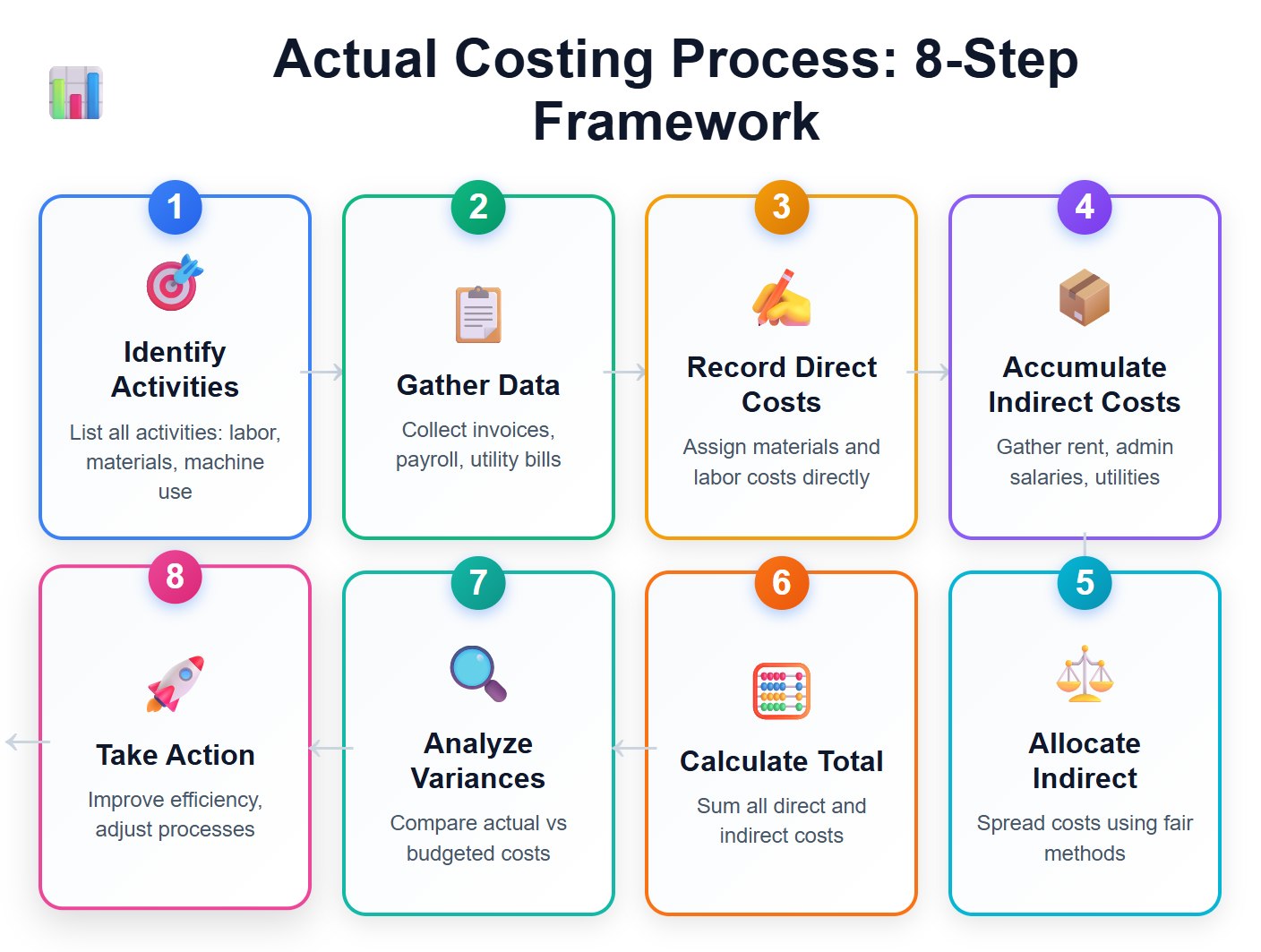
Tip: FineBI from FanRuan can help you automate these steps. You can connect your data sources, track actual expenditure in real time, and visualize cost trends. This makes it easier to calculate actual costing and spot issues quickly.
You need to understand the difference between direct and indirect costs when you calculate actual costing. Direct costs are expenses you can trace to a specific product or service. Indirect costs support your business as a whole.
Examples of direct costs:
Examples of indirect costs:
| Cost Type | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Costs | Costs directly tied to a product or service | Materials, labor, project equipment |
| Indirect Costs | Costs that support overall operations | Rent, utilities, admin salaries, insurance |
You must allocate indirect costs fairly to get an accurate picture of your actual costs. Document your methods and follow accounting standards. When you use FineBI, you can track both direct and indirect costs, ensuring your actual costing reports are complete and reliable.
You can transform your financial reporting process by using FineBI from FanRuan. FineBI gives you real-time tracking and visualization of actual cost data. You see up-to-date numbers on your dashboards, which helps you make decisions based on the latest information. FineBI’s high-performance data engine processes large amounts of data quickly. You can extract and analyze multi-dimensional data in seconds, not minutes. This speed means you always have access to the most current total actual cost and total expenses incurred.
FineBI lets you build custom dashboards with KPI cards, funnel charts, and flexible layouts. You can filter and link components to focus on the details that matter most. These features help you track actual costing across different departments or projects. You do not need to rely on IT for every report. FineBI supports self-service analysis, so you can create and modify reports on your own. Strict data permission controls keep your financial data secure and consistent across your organization.
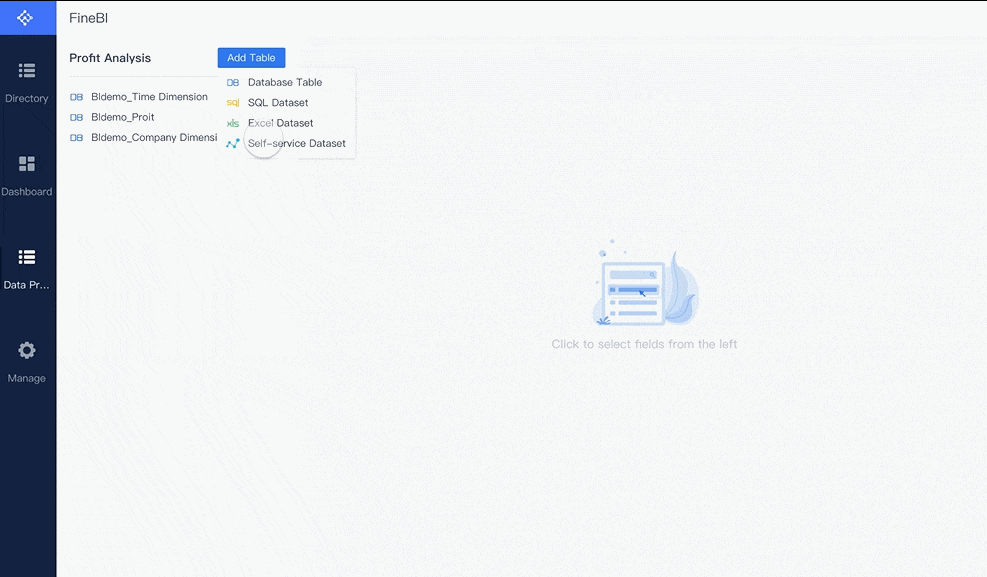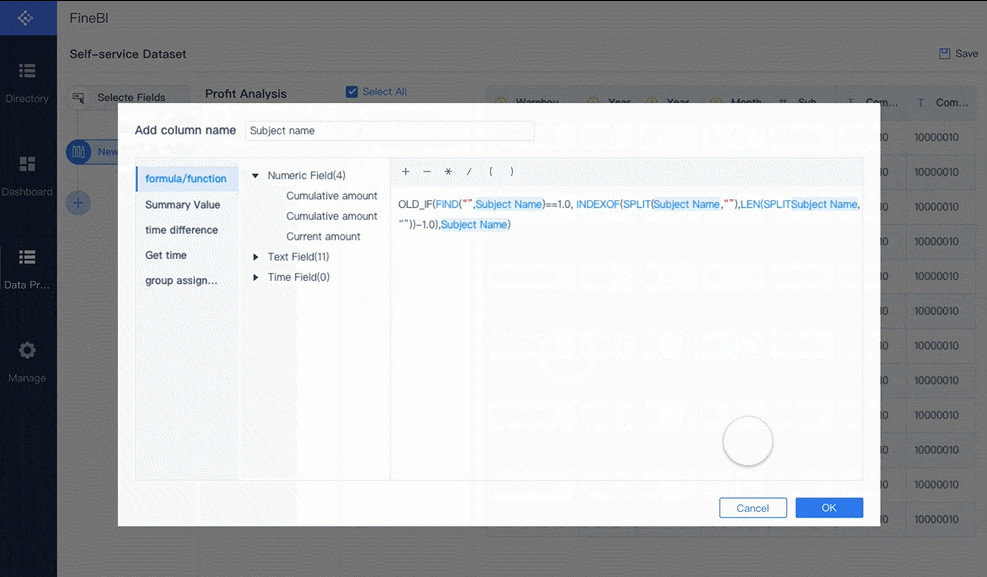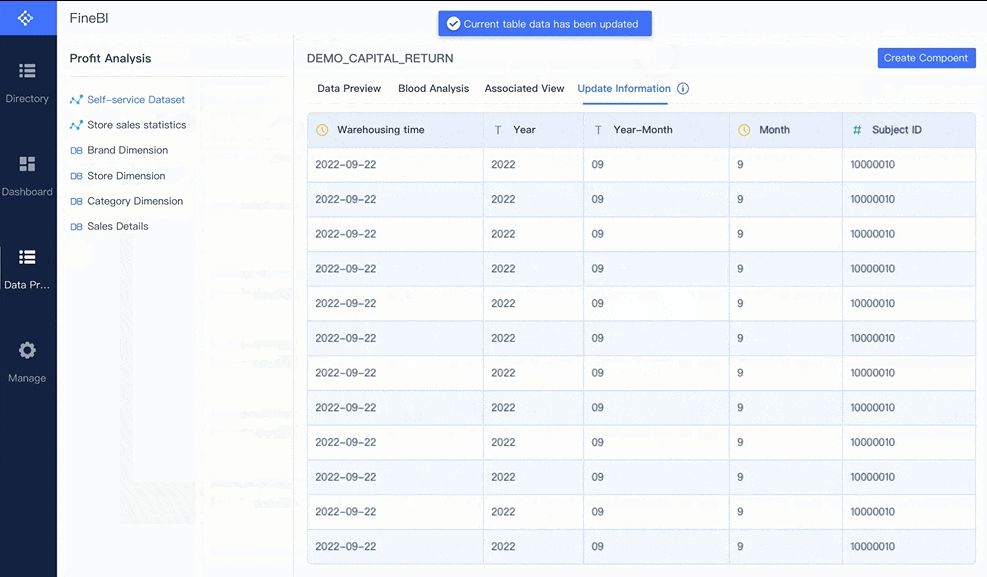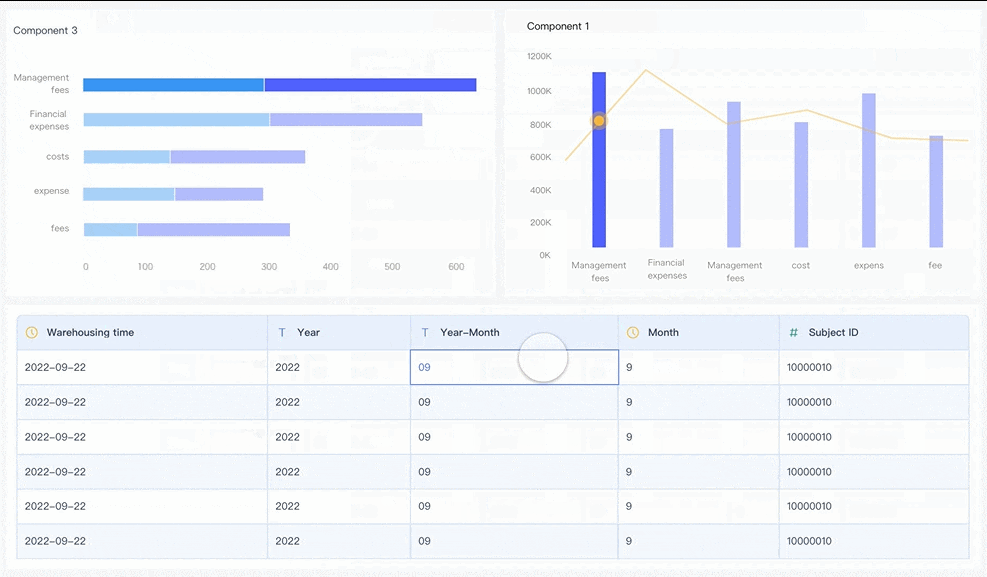
Tip: Real-time dashboards help you spot cost trends and issues as they happen, not after the fact.
You can use FanRuan solutions to improve cost control and analysis in your business. FineBI supports data-driven analysis that helps you monitor key financial indicators. The Data Alert plugin sends real-time notifications if costs go above set limits. You do not need to check reports manually every day. The system pushes alerts to the right people, so you can act fast to control costs.
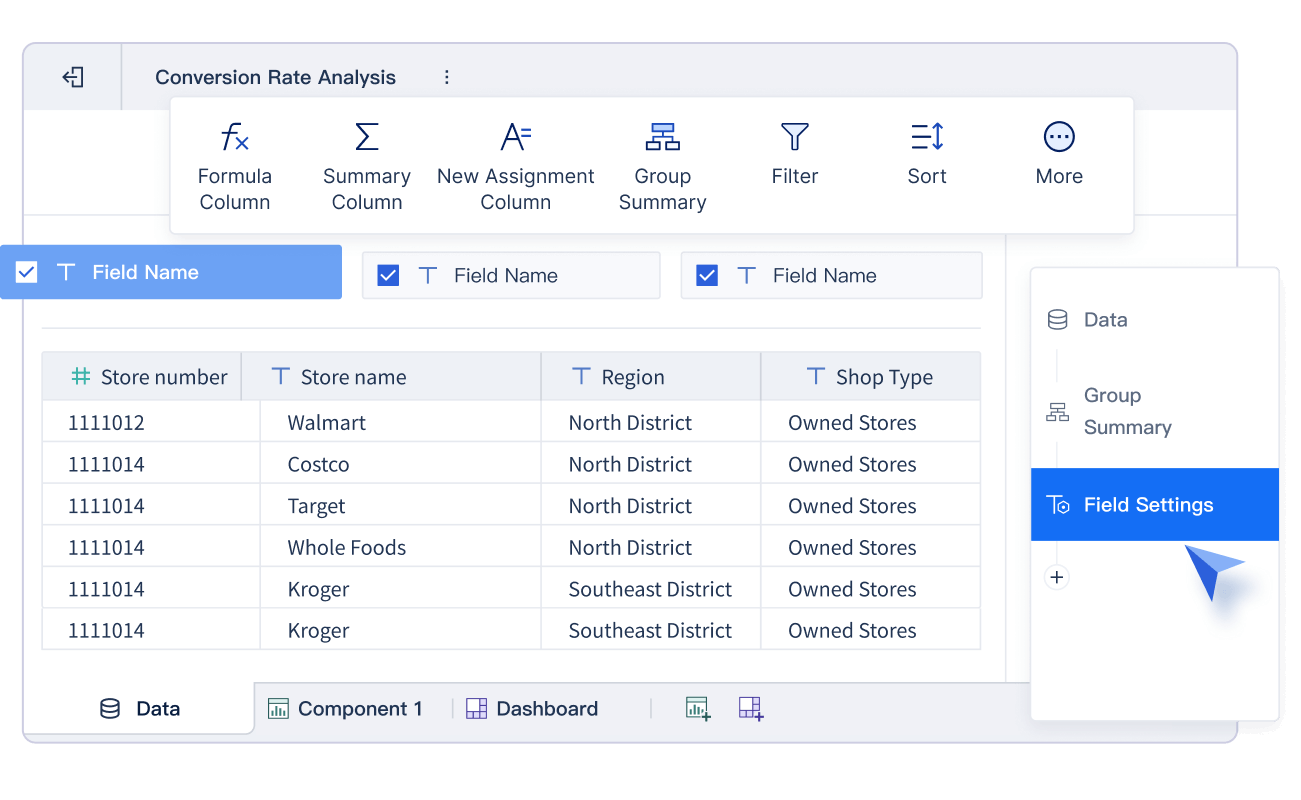
Here is a table showing how FanRuan solutions help your business grow:
| Feature/Benefit | How It Helps Your Business Grow |
|---|---|
| Customization | Tailors dashboards for precise cost control |
| Scalability | Handles large data and users without slowing down |
| Security-first Culture | Protects sensitive data and reduces risk |
| Integration | Unifies data sources for better analysis |
| Ease of Use | Lets non-technical users generate insights quickly |
| Support Services | Provides expert help and training for smooth operations |
You can also manage permissions by user role, which keeps your financial data safe and supports compliance. FineBI’s integration features bring all your cost data together, so you get a complete and accurate view. This unified approach helps you find ways to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
Also, You can join our upcoming FanRuan webinar series on Data Storytelling, where we’ll go beyond metrics and dashboards to explore how to:
Conduct meaningful cost analysis with context
Interpret gross profit and cost metrics correctly
Visualize and present your findings using real-world BI tools
Use data storytelling to justify strategic decisions
Prepare your data for AI-driven insights
Whether you're an analyst looking to improve your cost reporting or a business leader driving budget decisions, this session will give you the tools and mindset to turn cost data into a clear, actionable narrative.
When you track costs in your business, you may face several challenges. These problems can make it hard to get reliable numbers and can affect your financial results. Here are some of the most common issues:
If you do not address these issues, you risk making decisions based on bad data. This can lead to financial losses, billing errors, and even damage your reputation. For example, companies have lost millions due to payroll mismatches or billing mistakes. Inaccurate data can also cause you to miss business goals and lose trust with customers and partners.
You can improve the accuracy of your cost tracking by following some best practices. These steps help you avoid errors and make better decisions:

Tip: Investing in technology to automate and integrate your cost data is often cheaper than fixing mistakes later. Automation also frees up your team to focus on more valuable work.
By following these tips, you can improve transparency, reduce errors, and make smarter decisions for your business.
You gain a clear advantage when you track costs accurately and respond quickly to changes. Regular analysis helps you spot variances, reduce risks, and improve forecasting.
Stay ahead by using best practices and modern BI solutions. This approach supports smarter decisions and stronger financial results.
Click the banner below to try FineBI for free and empower your enterprise to transform data into productivity!
Unlocking Business Success with the AARRR Metrics Framework
What is Pareto Chart and How Does it Work
Essential Tips for Successful Customer Behavior Analysis
Making Metric Conversion Chart Easy for Everyday Life
What is Cost Analysis and Why Does It Matter in Business
What Is Sales Revenue and Why Is It Important for Businesses

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles

Self-Service Analytics Defined and Why You Need It
Self-service analytics lets you analyze data without IT help, empowering faster, data-driven decisions and boosting agility for your business.
Lewis
Jan 04, 2026

Best Self-Service Tools for Analytics You Should Know
See which self-service tools for analytics let business users access data, build dashboards, and make decisions faster—no IT help needed.
Lewis
Dec 29, 2025

Understanding Predictive Analytics Services in 2026
Predictive analytics services use data and AI to forecast trends, helping businesses make informed decisions, reduce risks, and improve efficiency in 2026.
Lewis
Dec 30, 2025