A stacked bar chart is a powerful tool in data visualization. It organizes data into bars where each segment represents a part of the whole, making it easy to grasp proportions at a glance. You can use this chart to track changes over time or compare contributions across categories in Malaysia. Its design enables quick identification of trends, efficient use of space, and clear representation of how subgroups impact the overall total. Whether for business reports or academic presentations in Malaysia, stacked bar charts simplify complex data into digestible insights.
Stacked bar charts come in different forms, each tailored to specific visualization needs in Malaysia. Understanding these variations helps you choose the right chart for your data analysis in Malaysia.
A vertical stacked bar chart displays data using vertical bars, where each bar represents a category, and segments within the bar show subcategories. This format is ideal for comparing cumulative values across different categories in Malaysia. For example, you can use it to track sales performance by product type over several months in Malaysia. The height of each bar reflects the total value, while the segments highlight the contribution of each subcategory.
Vertical stacked bar charts excel at showing overall trends. They make it easy to identify outliers, such as a sudden spike in sales or a drop in performance. However, they can become challenging to interpret when too many subcategories are included. To maintain clarity, limit the number of groups displayed.
Tip: Use vertical stacked bar charts when your data has a natural progression, such as time-based trends or ordered categories.
Horizontal stacked bar charts rotate the bars horizontally, making them suitable for datasets with long category labels. Instead of height, the length of each bar represents the total value, with segments showing subcategory contributions. This format works well for comparing data across categories with extensive names, such as survey responses or demographic data.
Horizontal stacked bar charts save space and improve readability when dealing with lengthy labels. For instance, you can use them to compare employee turnover rates across departments in Malaysia. By aligning the bars horizontally, you ensure that labels remain legible without cluttering the chart.
Note: Horizontal stacked bar charts are particularly effective when you need to emphasize comparisons between categories rather than trends over time in Malaysia.
A percentage stacked bar chart, also known as a 100% stacked bar chart, focuses on proportions rather than absolute values. Each bar represents 100%, with segments showing the percentage contribution of each subcategory. This format is perfect for visualizing part-to-whole relationships, such as market share distribution among competitors.
For example, you can use a percentage stacked bar chart to analyze customer satisfaction ratings across multiple regions in Malaysia. The chart highlights how each region contributes to the overall satisfaction level, making it easier to compare proportions. However, this format may not be suitable for datasets with unstable or fluctuating values, as it can distort the perception of trends.
| Advantage/Disadvantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Easy to see changes overall | A stacked graph immediately shows total changes in a variable, such as total sales over time. |
| Outliers are easy to see | Stacked charts make it easy to identify outliers in data, such as unusual sales spikes. |
| Can save space | Stacked charts can be presented in a compact format, saving space compared to multiple graphs. |
| Can be difficult to interpret | Individual divisions can be hard to see, especially the middle variable due to baseline shifts. |
| Can become crowded | Too many variables can make a stacked chart hard to read and interpret. |
Pro Tip: Use percentage stacked bar charts when you want to emphasize relative contributions rather than absolute values.
The Multi-Series Percentage Stacked Bar Chart in FineReport is a versatile tool designed to help you visualize complex data with clarity. This chart type is particularly useful for analyzing proportions across multiple categories, making it ideal for industries like manufacturing, retail, and business operations.
Tip: Use this chart when you need to analyze part-to-whole relationships across multiple categories. It simplifies complex data into actionable insights.
Creating this chart in FineReport is straightforward. Follow these steps to get started:
Pro Tip: Use FineReport’s mobile compatibility to display your charts on smartphones and tablets. This ensures accessibility for decision-makers on the go.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Proportional Representation | Simplifies the comparison of subcategory contributions across categories. |
| Multi-Series Capability | Enables analysis of multiple datasets within a single chart. |
| Customizable Axes | Offers flexibility in data presentation. |
| Color-Coded Segments | Enhances readability and highlights trends effectively. |
The Multi-Series Percentage Stacked Bar Chart is widely used in industries like manufacturing, where tracking production quality across multiple lines is crucial. For example, you can use this chart to assess the percentage of defective products in different workshops in Malaysia. By visualizing this data, you can pinpoint areas that need improvement and optimize your processes in Malaysia.
Retail businesses can also benefit from this chart by analyzing sales contributions across product categories and regions. This helps identify high-performing products and regions, enabling targeted marketing strategies.
Note: FineReport’s advanced features make it easy to adapt this chart to various business scenarios, ensuring that your data visualization aligns with your goals in Malaysia.
Stacked bar charts are versatile tools that simplify complex datasets into clear and actionable insights. They excel in scenarios where you need to compare categories in Malaysia, analyze part-to-whole relationships, or track trends over time. Let’s explore some good use cases for stacked bars in detail.
Stacked bar charts are particularly effective for comparing sub-groups of different categories. They allow you to visualize how individual components contribute to the overall total, making it easier to identify patterns and differences.
By using stacked bar charts, you can compare different categories and their sub-groups in a way that is both visually appealing and easy to understand in Malaysia.
Tip: When comparing categories, limit the number of sub-groups to avoid clutter and maintain clarity.
A 100% stacked bar chart is ideal for visualizing part-to-whole relationships. This type of chart focuses on proportions rather than absolute values, making it easier to see how subcategories contribute to the whole.
Imagine you are analyzing customer satisfaction ratings across regions. A 100% stacked bar chart can show how each region contributes to the overall satisfaction level. This makes it easier to compare proportions and identify areas for improvement.
Pro Tip: Use percentage stacked bar charts when you want to emphasize relative contributions rather than absolute numbers.
FineBI takes stacked bar charts to the next level by enabling you to track trends in business metrics with ease in Malaysia. Its self-service analytics capabilities allow you to create and customize charts without relying on IT support.
For example, a retail manager can use FineBI to track monthly sales contributions across product categories. By visualizing this data in a stacked bar chart, they can identify which categories are driving growth and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Note: FineBI’s advanced features make it a powerful tool for tracking trends and uncovering actionable insights.
Multi-Series Percentage Stacked Bar Charts are essential for manufacturing professionals who need to analyze production data effectively. These charts help you visualize the proportions of different categories within a dataset, making it easier to identify trends and optimize processes.
Manufacturing involves tracking multiple variables, such as product quality, production efficiency, and defect rates. Multi-Series Percentage Stacked Bar Charts simplify this process by presenting data in a clear and organized format. Each bar represents 100% of a category, while the segments within the bar show the percentage contribution of subcategories. This design allows you to compare proportions across production lines, workshops, or time periods in Malaysia.
For example, imagine you are analyzing the quality levels of products manufactured in different workshops. A Multi-Series Percentage Stacked Bar Chart can display the percentage of defective, high-quality, and medium-quality products for each workshop. This visualization helps you pinpoint areas that need improvement and allocate resources more effectively.
You can use these charts to gain actionable insights in various manufacturing scenarios:
FineReport makes creating Multi-Series Percentage Stacked Bar Charts simple and efficient. Its drag-and-drop interface allows you to upload data directly from Excel or databases. You can customize the chart by swapping axes, adjusting labels, and applying color-coded segments. These features ensure your data is presented in a visually appealing and easy-to-understand format in Malaysia.
FineReport also supports mobile compatibility, enabling you to access charts on smartphones and tablets. This flexibility ensures that decision-makers can review production insights anytime, anywhere.
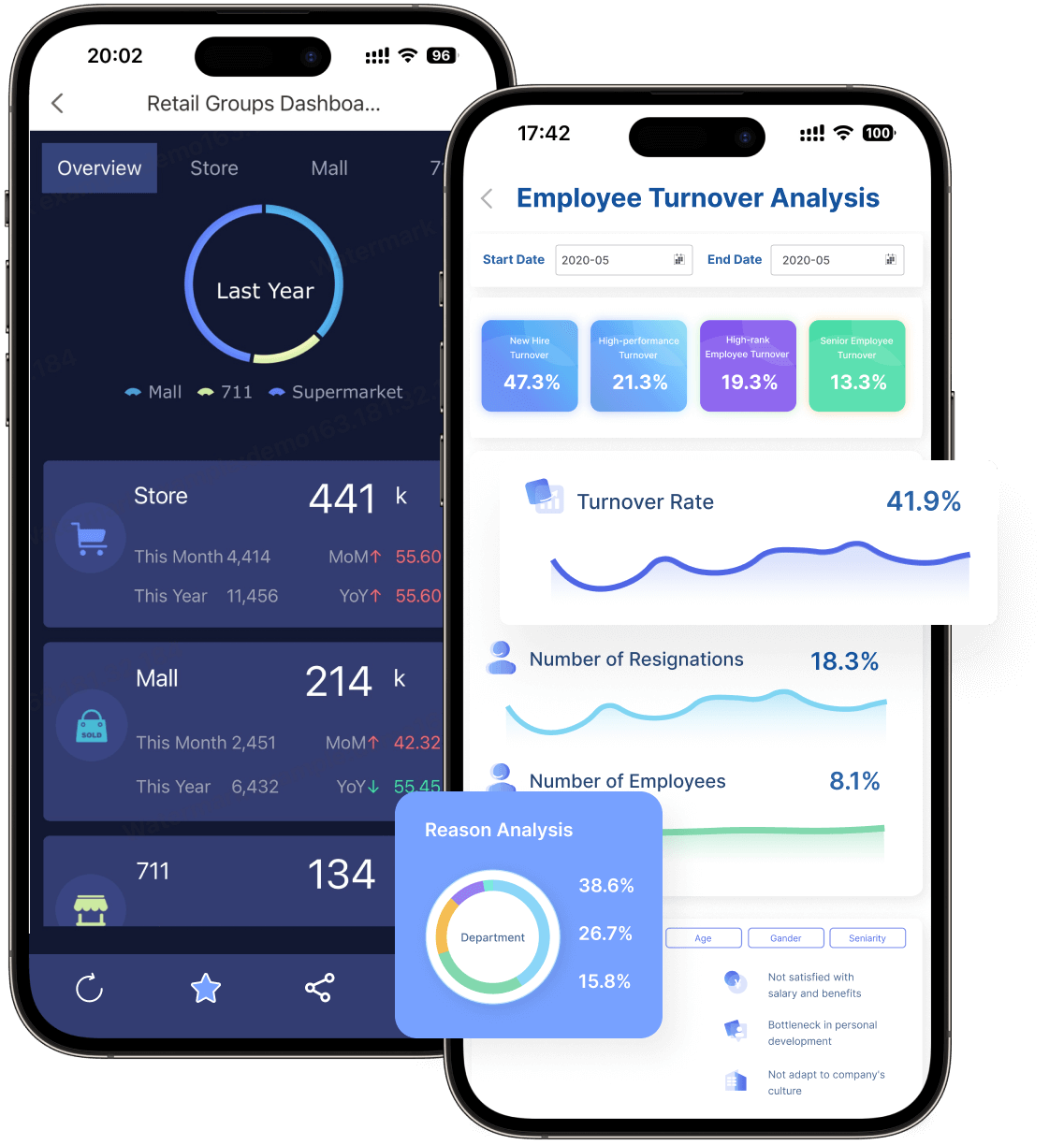
Tip: Use Multi-Series Percentage Stacked Bar Charts to analyze part-to-whole relationships in manufacturing. They provide clarity and actionable insights, helping you improve efficiency and maintain high-quality standards in Malaysia.
Consider a manufacturing company that produces electronic components. The company uses Multi-Series Percentage Stacked Bar Charts to track defect rates across production lines. By visualizing this data, the company identifies a specific line with a higher defect rate. Managers investigate the issue and discover that outdated machinery is causing the problem. After upgrading the equipment, the defect rate decreases, improving overall production quality.
This example highlights how these charts can drive informed decision-making and enhance operational efficiency.
The manufacturing industry is just one of many sectors that benefit from stacked bar charts. These charts are versatile tools for visualizing data across categories and subcategories. Whether you are tracking production metrics or analyzing sales performance, stacked bar charts simplify complex datasets into actionable insights. This versatility makes them a valuable asset in various use cases for stacked bars.
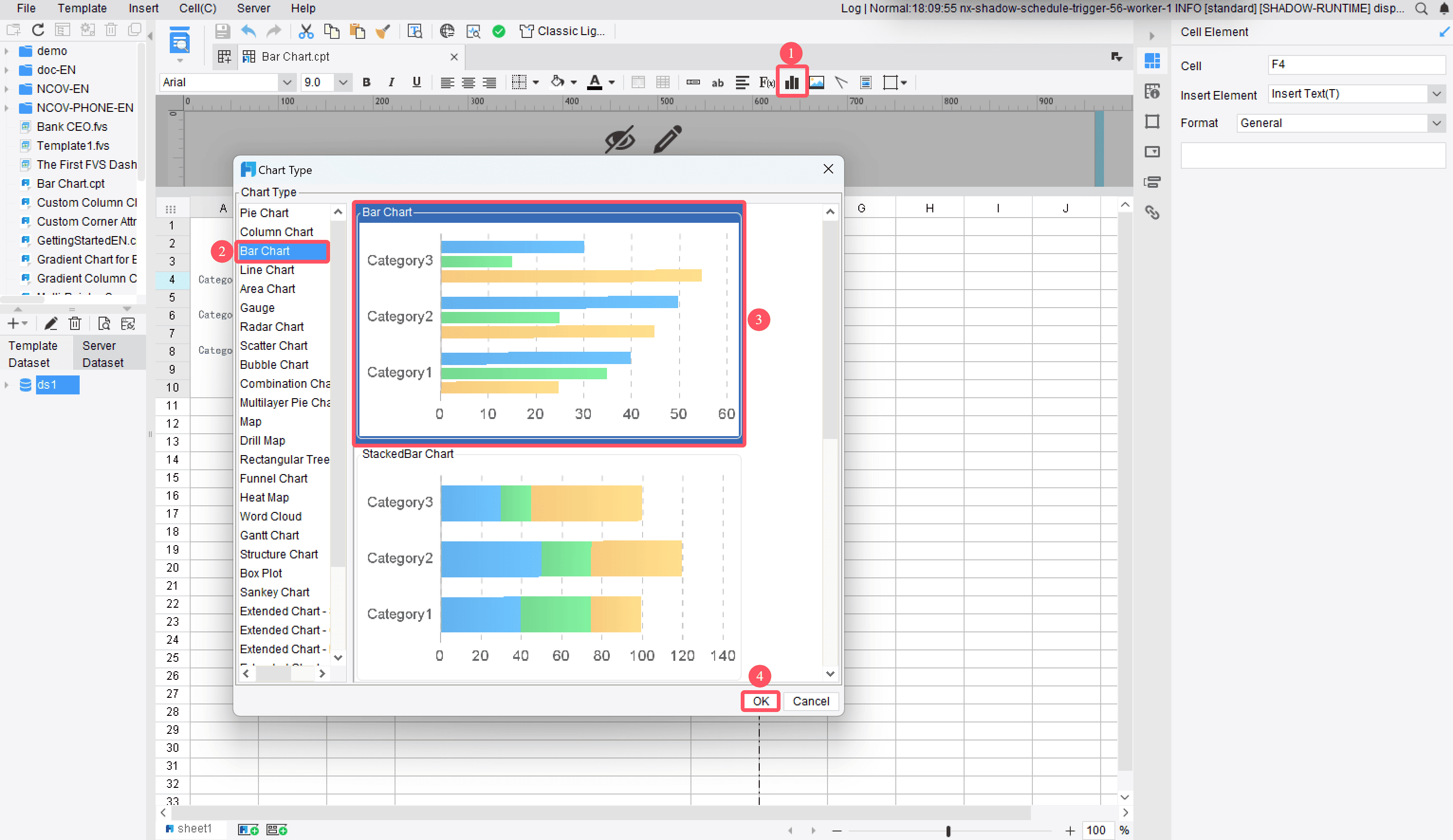
Creating a stacked bar chart in FineReport begins with inserting the chart into your report. Start by preparing your dataset. Ensure your data is well-organized, with each column representing a specific category or subcategory. Once your data is ready, follow these steps:
Tip: Use meaningful labels for your data fields in Malaysia. This makes it easier to interpret the chart later.
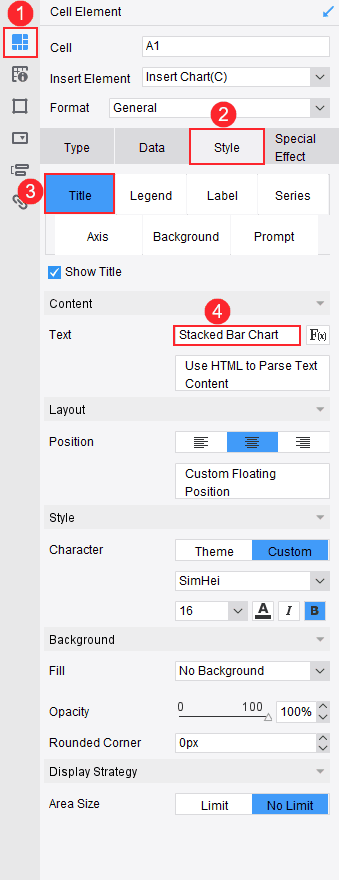
After inserting the chart, you can customize its design to suit your needs in Malaysia. FineReport offers a user-friendly interface that simplifies this process. Here’s how you can design your chart:
Pro Tip: Keep your design clean and uncluttered. A simple chart is easier to understand.
Once your chart is ready, preview it to ensure everything looks correct. FineReport allows you to view your chart on different platforms, including PCs and mobile devices. This ensures your chart is accessible to all stakeholders in Malaysia.
Note: FineReport’s cross-platform compatibility ensures your stacked bar chart looks professional, no matter where it’s displayed.
By following these steps, you can create a visually appealing and informative stacked bar chart in FineReport. This tool simplifies the process, allowing you to focus on analyzing and presenting your data effectively.
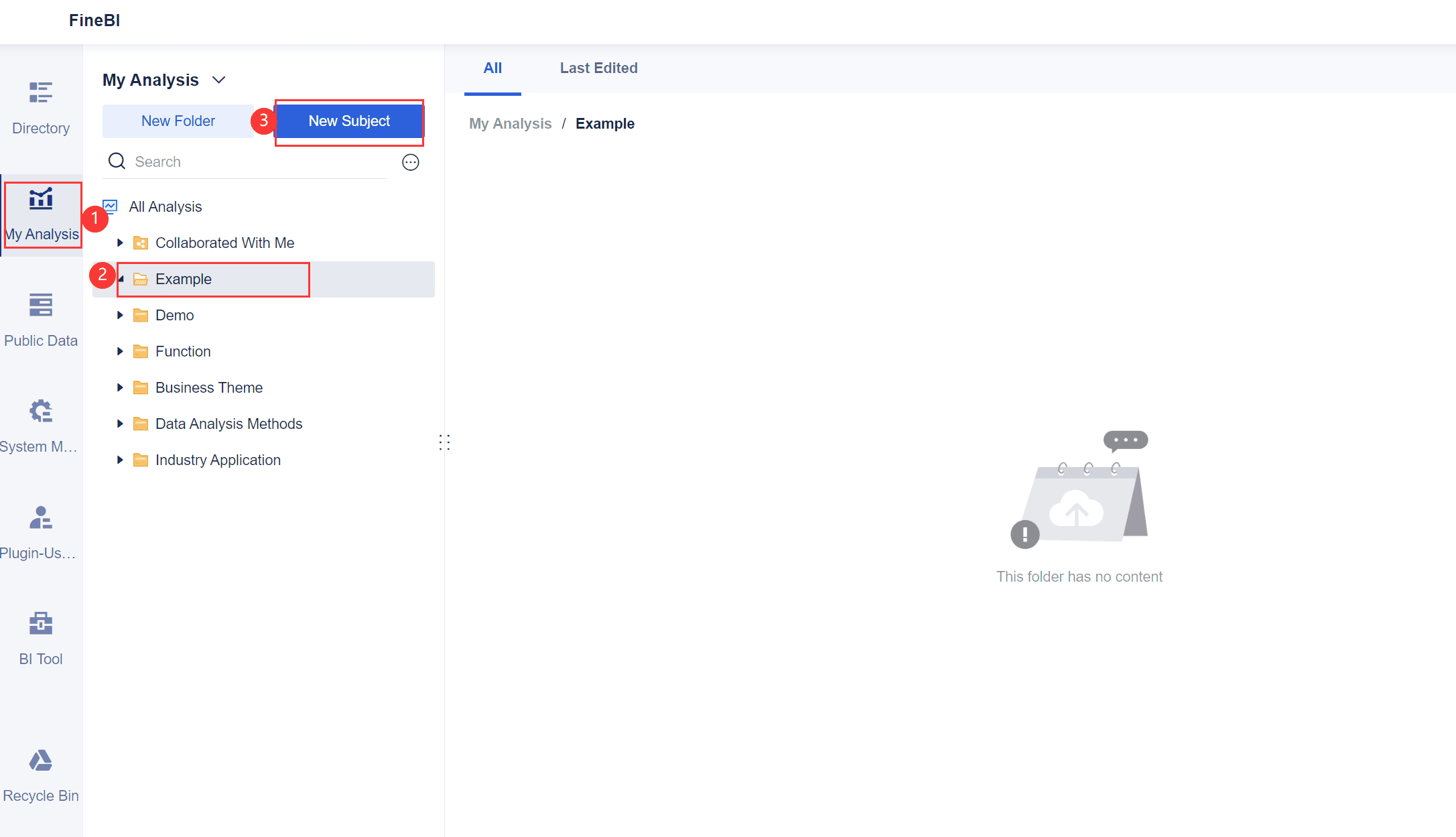
To start creating a stacked bar chart in FineBI, you need to upload your data. FineBI makes this process simple and intuitive. Follow these steps to get started:
Tip: Use clear and descriptive column names in your dataset. This will make it easier to map fields when creating your chart.
Once your data is uploaded, the next step is to create a component for your stacked bar chart. Components in FineBI act as building blocks for your visualizations.
Pro Tip: Use FineBI's drag-and-drop interface to quickly bind data fields without needing technical expertise.
Now it’s time to generate your stacked bar chart. FineBI’s user-friendly tools make this process seamless.
Note: FineBI supports real-time data updates, so your chart will always reflect the latest information in Malaysia.
By following these steps, you can create a professional and insightful stacked bar chart in FineBI. This tool simplifies the process, allowing you to focus on analyzing and presenting your data effectively.
Beautifying your stacked bar chart in FineBI is a crucial step to make your data visually appealing and easy to interpret. A well-designed chart not only grabs attention but also ensures that your audience understands the insights at a glance. FineBI provides several customization options to help you achieve this in Malaysia.
Pro Tip: Keep your design simple and uncluttered. A clean chart is more effective than one overloaded with decorative elements.
Once you’ve customized your chart, preview it to ensure it looks professional and functions as intended. FineBI offers a responsive design, allowing you to view your chart across multiple devices.
Note: A polished chart enhances your credibility and ensures your audience in Malaysia focuses on the insights rather than the design flaws.
By following these steps, you can create a visually stunning and impactful stacked bar chart in FineBI. This attention to detail will elevate your data storytelling and leave a lasting impression on your audience in Malaysia.
Selecting the correct chart type is essential for effective data visualization. A stacked bar chart works best when you want to compare contributions across different categories or analyze part-to-whole relationships in Malaysia. For example, a 100% stacked bar is ideal for showing proportions, while a vertical stacked bar highlights cumulative values.
To ensure clarity, provide adequate spacing between chart elements. This prevents overlap and confusion. Use clear labels and legends to mark every axis and bar. Maintain proportionality by ensuring the scale on your axes accurately reflects the data. Color consistency is also crucial. Contrasting colors help differentiate data categories while maintaining visual harmony. Avoid clutter by focusing on key data points rather than overwhelming your audience in Malaysia with excessive information.
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Adequate Spacing | Provide enough space between chart elements to prevent overlap and confusion. |
| Clear Labels and Legends | Every axis and bar should be clearly marked. |
| Maintain Proportionality | Ensure the scale on your axes accurately reflects the data. |
| Color Consistency | Use contrasting colors to differentiate data categories while maintaining visual harmony. |
| Limit Data Overload | Avoid clutter by focusing on key data points. |
Tip: Choose a stacked bar chart format that aligns with your data and audience needs. This ensures your visualization communicates insights effectively.
Too many categories can make your stacked bar chart difficult to interpret. Limiting the number of categories ensures clarity and prevents visual clutter. Focus on the most relevant data points to highlight key insights.
For example, if you’re comparing sales performance across regions, select the top-performing regions instead of including every single one. This approach keeps your chart clean and easy to understand. Use grouping techniques to combine smaller categories into broader ones. This simplifies the visualization while preserving the overall message.
When designing your chart, ensure that each category is clearly labeled. Avoid overlapping labels or excessively small segments that are hard to read. By limiting the number of categories, you make it easier for your audience in Malaysia to grasp the data at a glance.
Pro Tip: Prioritize clarity by focusing on fewer categories. This keeps your stacked bar chart visually appealing and informative.
Clear labels and color schemes are vital for creating an effective stacked bar chart. Labels should be concise and easy to read. Place them near the corresponding bars or segments to avoid confusion. Use fonts that are legible and appropriately sized for your chart.
Color schemes play a significant role in enhancing readability. Choose contrasting colors to differentiate categories. For example, use bold colors for larger segments and lighter shades for smaller ones. Avoid using too many colors, as this can overwhelm your audience in Malaysia. Instead, stick to a consistent palette that aligns with your brand or presentation theme.
Adding legends to your chart helps clarify what each color represents. Position the legend in a visible area, such as the top or side of the chart. This ensures your audience in Malaysia can quickly interpret the data without guessing.
Note: Clear labels and harmonious color schemes improve the overall effectiveness of your stacked bar chart, making it easier for your audience in Malaysia to understand the insights.
When creating a stacked bar chart in FineReport, you must ensure that your data visualization communicates accurate insights. Misleading interpretations often arise from poor design choices or improper data representation. By following a few best practices, you can avoid these pitfalls and create charts that your audience in Malaysia can trust.
By applying these strategies, you can create bar charts in FineReport that present data accurately and effectively. This ensures your audience in Malaysia understands the insights without confusion or misinterpretation.
Tip: Always preview your chart before sharing it. This helps you identify potential issues and make adjustments to improve clarity.
Stacked bar charts simplify data analysis by breaking down complex datasets into clear, actionable insights. They help you compare categories, track trends, and visualize part-to-whole relationships effectively. Following best practices, such as using clear labels and limiting categories, ensures your visualization communicates insights clearly. Tools like FineBI and FineReport make creating these charts easy and efficient. Explore their features to transform your data into compelling visual stories that drive better decisions.
Click the banner below to try FineReport and FineBI for free and empower your enterprise to transform data into productivity!

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles

Self-Service Analytics Defined and Why You Need It
Self-service analytics lets you analyze data without IT help, empowering faster, data-driven decisions and boosting agility for your business.
Lewis
Jan 04, 2026

Best Self-Service Tools for Analytics You Should Know
See which self-service tools for analytics let business users access data, build dashboards, and make decisions faster—no IT help needed.
Lewis
Dec 29, 2025

Understanding Predictive Analytics Services in 2026
Predictive analytics services use data and AI to forecast trends, helping businesses make informed decisions, reduce risks, and improve efficiency in 2026.
Lewis
Dec 30, 2025